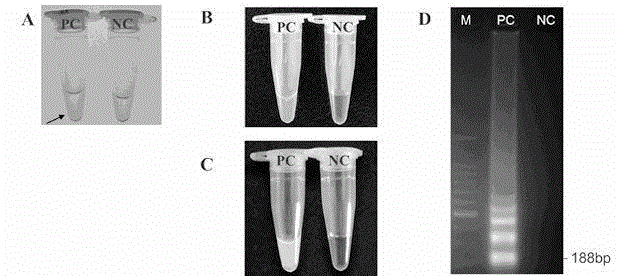
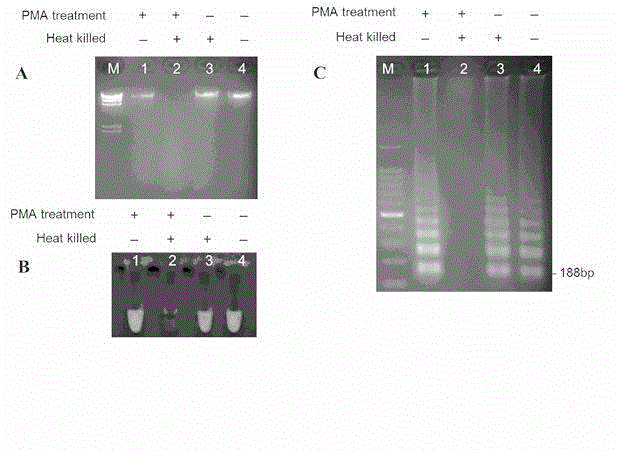
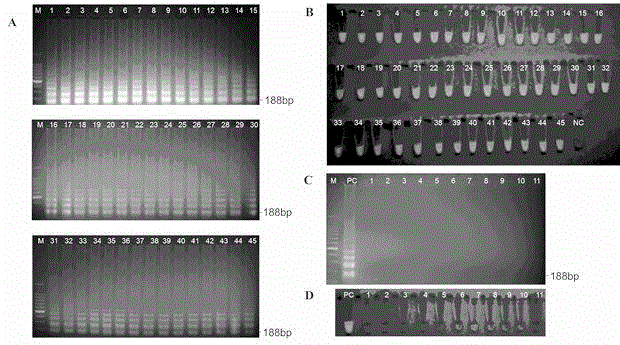
Method for rapidly detecting listeria monocytogenes in food
A Listeria mononuclear technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of low specificity, high labor intensity, low detection sensitivity, etc., and achieve the effect of simple result judgment, easy operation, and low detection cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0030] 1. Food sample pretreatment
[0031] Weigh 1 g of food sample, add 9 ml of phosphate buffered saline (PBS), grind to make a homogenate, centrifuge at 900 g for 5 min, remove large food residues, and take the supernatant (this process must be performed aseptically).
[0032] 2. PMA treatment
[0033] PMA was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), prepared into a 0.5 mg / mL PMA solution, and stored at -20°C in the dark. Take 500 μL of the prepared bacterial suspension and place it in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube, add 3 μL of 0.5 mg / mL PMA solution to make the final mass concentration of PMA 3 μg / mL; Incubate in the dark at room temperature for 5 min, and expose to a 500 W halogen lamp for 5 min. When cross-linking with light, place the sample on ice (to avoid overheating), and place the cross-linked suspension at 10,000 g at a distance of 20 cm from the light source. After centrifugation for 5 min, the resulting pellet was used for DNA extraction.
[0034] 3. Extracti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com