Flexible display substrate and preparation method thereof
A flexible display and flexible substrate technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, electrical solid-state devices, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing costs, improving quality, and fast response speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
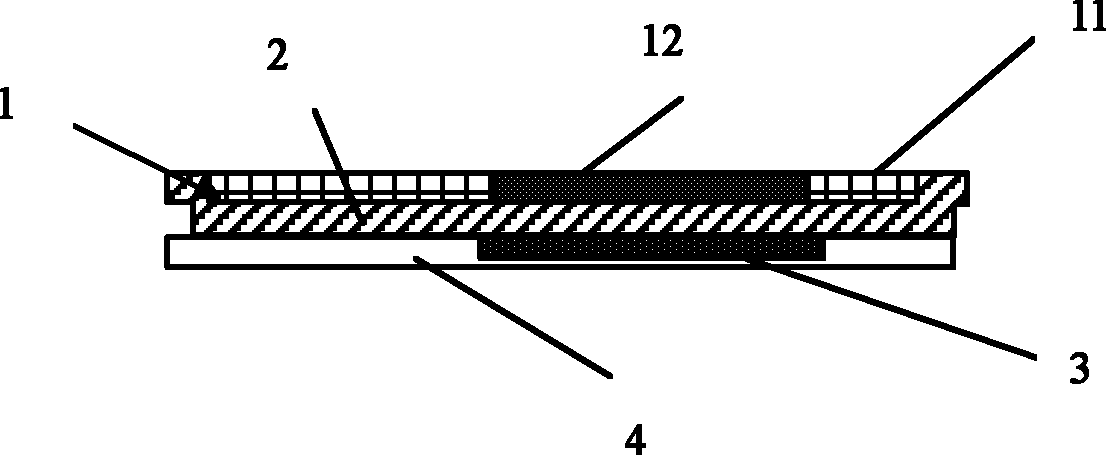
[0054] like figure 1 As shown, the flexible display substrate of the present invention includes a graphene layer 1 , an insulating layer 2 , and a gate electrode 3 in sequence. The graphene layer 1 and the gate electrode 3 are separated by an insulating layer 2, and the gate electrode 3 is covered with a PET film 4. The channel region of the graphene layer 1 is hydrogenated graphene 12, and the rest is intrinsic graphene 11. Intrinsic graphene 11 serves as source, drain and pixel electrodes, and hydrogenated graphene 12 serves as a semiconductor layer.
[0055] The graphene layer 1 is composed of a single-layer graphene layer formed by high temperature chemical vapor deposition.
[0056] The thickness of the PET film 4 is between 30-3000nm, specifically 30nm, 100nm, 500nm, 1000nm and 3000nm.
[0057] The insulating layer 2 is made of PMMA (polymethyl methacrylate), and its thickness is 200 nm.
[0058] The material of the gate electrode 3 is copper, and its thickness is 80 ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] like figure 2 As shown, the flexible display substrate of this embodiment is prepared according to the following method:
[0067] 1) Form a graphene layer on the surface of the copper foil by high-temperature chemical vapor deposition: place the copper foil in the middle of the quartz tube, put it into an electric furnace, and feed 500 sccm hydrogen into the quartz tube as a carrier gas. After 30 minutes, start heating. When the temperature in the central area of the electric furnace reaches 800°C, methane is introduced into the hydrogen gas as a carbon source for reaction. After the reaction has been carried out for 60 minutes, stop feeding methane, stop heating, cool to room temperature, and deposit a layer of graphene on the surface of the copper foil. , repeated twice to form 3 layers of graphene layer 1 .
[0068] 2) Spin-coat photoresist (Photoresist PR) on the graphene layer 1, etch after exposure and development to expose the graphene layer in the channel re...
Embodiment 3
[0074] like figure 2 As shown, the flexible display substrate of this embodiment is prepared according to the following method:
[0075] 1) Form a graphene layer on the surface of the copper foil by high-temperature chemical vapor deposition: place the copper foil in the middle of the quartz tube, put it into an electric furnace, and feed 100 sccm hydrogen and 200 sccm argon into the quartz tube as the carrier gas. After 10 minutes, , start heating, when the temperature in the central area of the electric furnace reaches 1500°C, feed methane into hydrogen and argon as a carbon source for reaction, after 60 minutes of reaction, stop feeding methane, stop heating, cool to room temperature, A layer of graphene is deposited on the surface of the foil, and repeated several times to form 10 graphene layers 1 .
[0076] 2) Spin-coat the photoresist (Photoresist PR) on the graphene layer 1, etch after the mask to expose the graphene channel region, and use the electron cyclotron r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com