Leadless free-cutting copper alloy and preparation method
A copper alloy, free-cutting technology, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve the problem of lead-containing copper alloy polluting the environment, etc., and achieve the effects of excellent cutting performance, safe and reliable environment, and simple production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
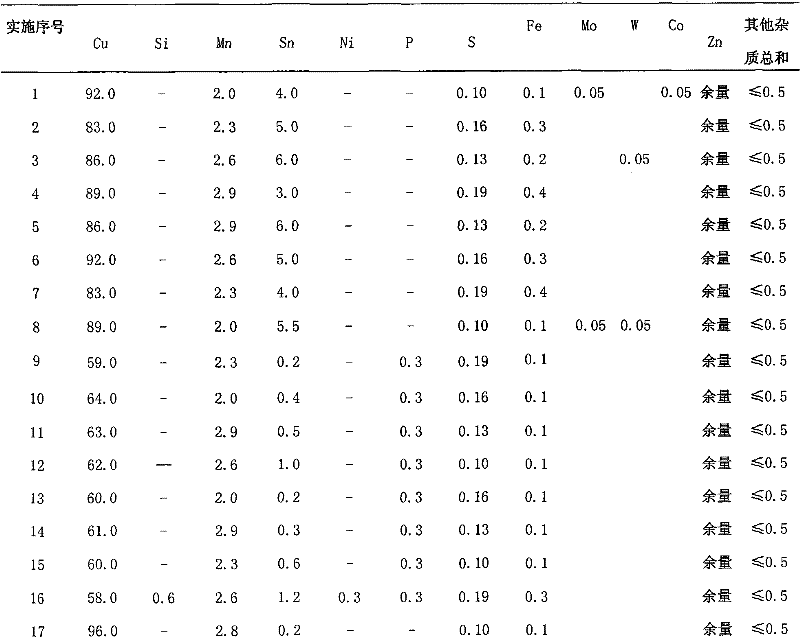
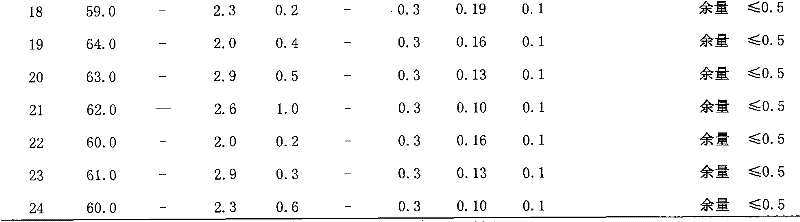
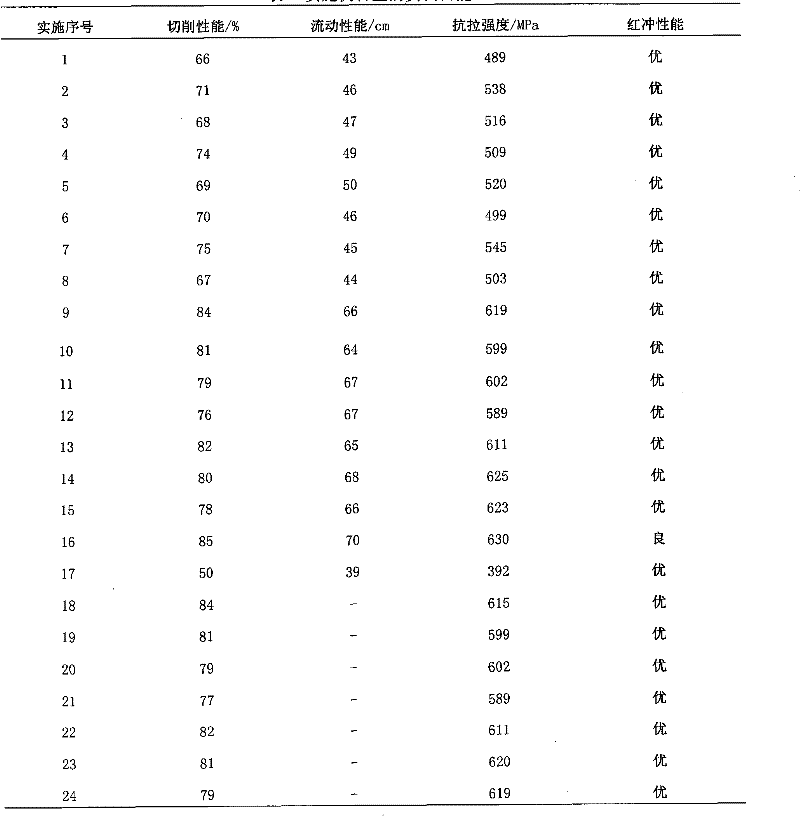
[0021]The mass fraction of metal elements in lead-free free-cutting copper alloy is: copper 92.0%, manganese 2.0%, tin 4.0%, sulfur 0.1%, iron 0.1%, molybdenum 0.05%, cobalt 0.05%, the balance is zinc (Zn), other The elements are all impurities, and the mass fraction of any impurity is ≤0.03%, and the sum of the mass fractions of all impurities is not more than 0.5%. After preparing the raw materials, first melt the red copper plate, then add manganese, iron, tin in the form of copper-tin intermediate alloy, add sulfur after refining, add sulfur in the form of a mixture of copper sulfide, molybdenum sulfide and cobalt sulfide, and finally add zinc . After all the alloy elements are melted evenly, it is poured into the iron mold and sand mold. The cutting samples and spiral samples were obtained, and the cutting performance, tensile performance and flow performance of the alloy were tested respectively. The brass fluidity of this composition is 43cm, the machinability is equi...
Embodiment 2
[0023] See implementation number 2 in Table 1 for the mass fraction of metal elements in lead-free free-cutting copper alloys. After preparing the raw materials, first melt the red copper plate, then add manganese, iron, tin in the form of copper-tin intermediate alloy, add sulfur after refining, add sulfur in the form of copper sulfide, and finally add zinc. After all the alloy elements are melted evenly, it is poured into the iron mold and sand mold. The cutting samples and spiral samples were obtained, and the cutting performance, tensile performance and flow performance of the alloy were tested respectively. The performance of this composition sees the implementation number 2 in table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0025] See implementation number 3 in Table 1 for the mass fraction of metal elements in lead-free free-cutting copper alloys. After preparing the raw materials, first melt the red copper plate, then add manganese, iron, tin in the form of copper-tin intermediate alloy, add sulfur after refining, add sulfur in the form of copper sulfide and tungsten sulfide mixture, and finally add zinc. After all the alloy elements are melted evenly, it is poured into the iron mold and sand mold. The cutting samples and spiral samples were obtained, and the cutting performance, tensile performance and flow performance of the alloy were tested respectively. The performance of this composition sees the implementation sequence number 3 in table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com