High-corrosion-resistance sintered neodymium-iron-boron-based permanent magnet material prepared by doping zinc nano-particles and preparation method thereof
A technology of nano-particles and permanent magnetic materials, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as micro-cracks, poor uniformity of coating methods, and low bonding force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
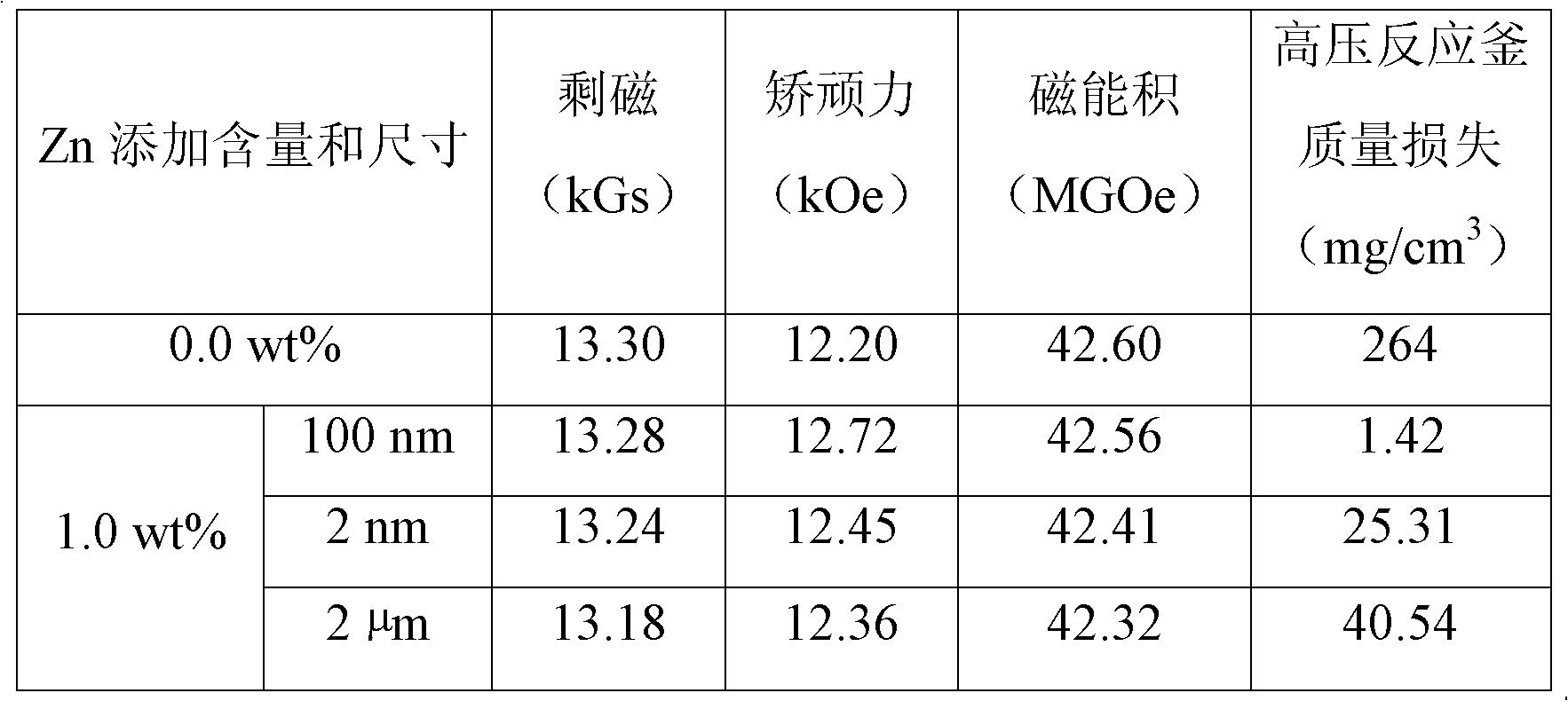
[0012] Use quick-setting technology to change the composition to Nd 13.7 Fe bal Al 0.3 B 6 (atomic percent content) of the alloy is prepared as flakes, and then the powder is made into a powder with an average particle size of 3 microns by using a hydrogen crushing-jet milling process. Then, 1.0% by weight Zn nano powder with an average particle size of 100 nm was added to the above initial powder, and the two powders were uniformly mixed by a mixer. The uniformly mixed powder was oriented in a magnetic field of 2.5T and pressed into shape. Then put the compact into a high-vacuum sintering furnace, and heat up to 1120°C for sintering for 3 hours. Afterwards, heat treatment is carried out in two stages, wherein the temperature of the primary heat treatment is 930°C for 2 hours, and the temperature of the secondary heat treatment is 580°C for 1 hour. That is, a sintered NdFeB-based magnet with high corrosion resistance is obtained.
Embodiment 2
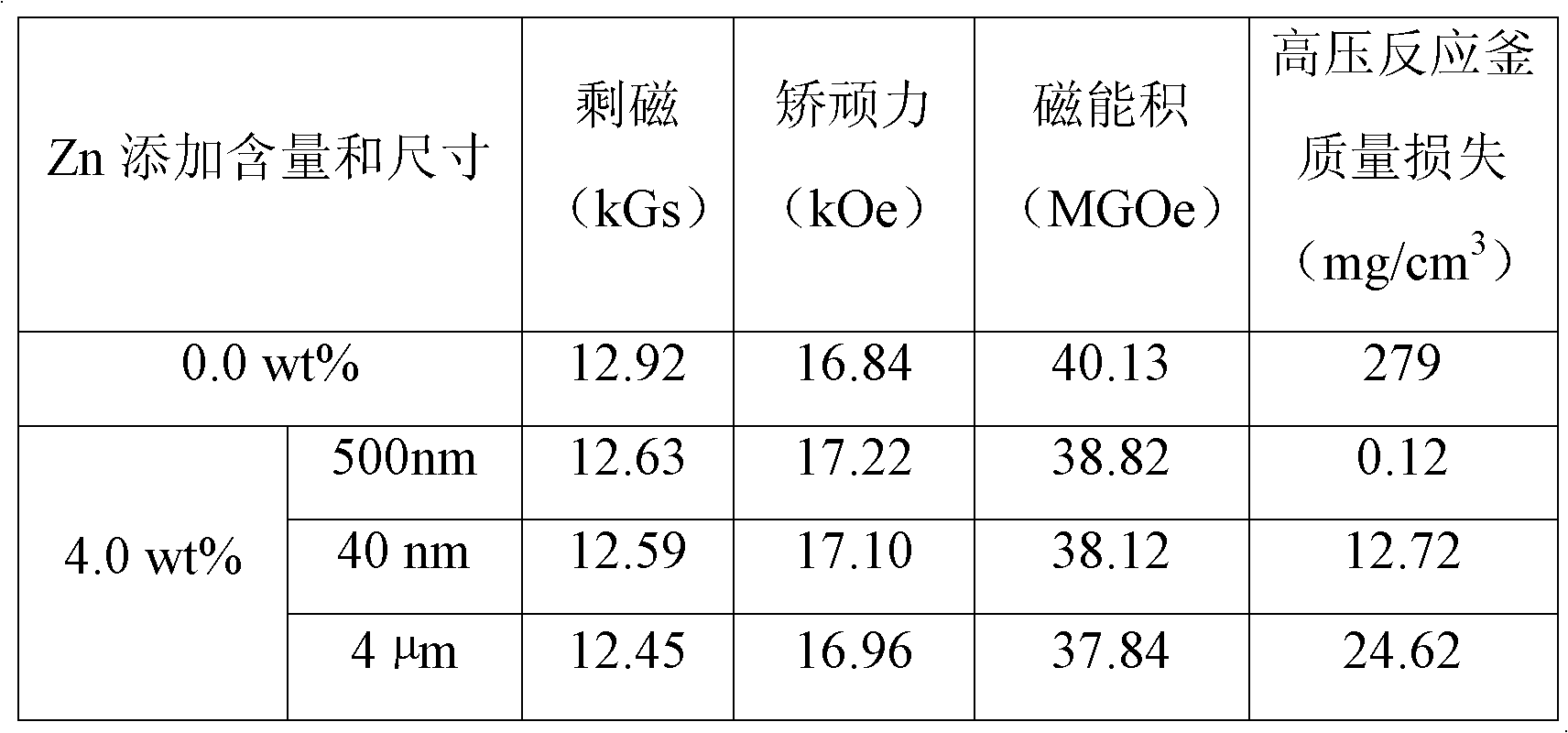
[0020] Use quick-setting technology to change the composition to Nd 12.8 Dy 0.5 Fe bal Al 1.0 Nb 0.3 B 6 (atomic percent content) of the alloy is prepared as flakes, and then the powder is made into a powder with an average particle size of 5 microns by using a hydrogen crushing-jet milling process. After that, 4.0% by weight Zn nano powder with an average particle size of 500 nm was added to the above initial powder, and the two powders were uniformly mixed by a mixer. The uniformly mixed powder was oriented in a magnetic field of 2.5T and pressed into shape. Then put the compact into a high-vacuum sintering furnace and heat up to 1020°C for sintering for 4 hours. Afterwards, heat treatment is carried out in two stages, wherein the temperature of the primary heat treatment is 830°C for 3 hours, and the temperature of the secondary heat treatment is 480°C for 3 hours. That is, sintered NdFeB magnets with high corrosion resistance are obtained.
[0021] comparative exam...
Embodiment 3
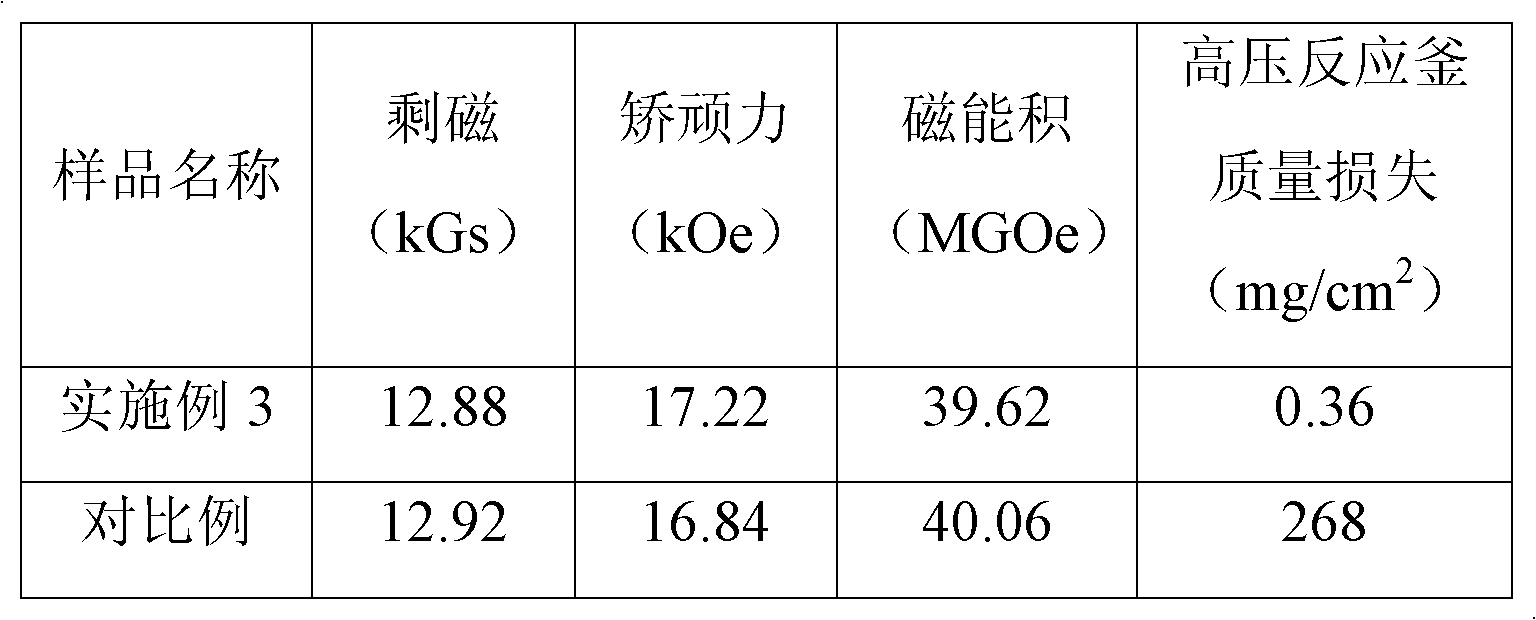
[0028] Use quick-setting technology to change the composition to Nd 12.3 Dy 1.0 Fe bal Nb 0.2 co 0.5 Al 0.1 B 6 (atomic percent content) of the alloy is prepared as flakes, and then the powder is made into a powder with an average particle size of 4 microns by using a hydrogen crushing-jet milling process. Then, 3.0% by weight of Zn nano-powder with an average particle size of 300 nanometers was added to the above-mentioned initial powder, and the two powders were uniformly mixed by a mixer. The uniformly mixed powder was oriented in a magnetic field of 2.5T and pressed into shape. Then put the compact into a high-vacuum sintering furnace and heat up to 1080°C for 2 hours for sintering. Then carry out secondary heat treatment, wherein the temperature of primary heat treatment is 900°C for 1 hour; the temperature of secondary heat treatment is 630°C for 2 hours. That is, sintered NdFeB magnets with high corrosion resistance are obtained.
[0029] comparative example
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com