Method for preparing surface-closed medicine-carrying porous polymer microsphere based on supercritical fluid technology
A technology of porous polymer and supercritical fluid, which is used in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of low solvent residue, mild operating conditions, and low drug loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0018] The method for preparing the surface-sealed drug-loaded porous polymer microspheres based on supercritical fluid technology comprises the following steps:
[0019] 1) Dissolve the mixture of polymer and poloxamer with a mass ratio of 7:3 in 30ml of dichloromethane to prepare a solution with a mass volume concentration of the mixture of 3-5%. Dissolve 2mg of the drug in this solution, and polymerize the obtained Add the mixed solution of drug and drug to 450ml of polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution with a mass volume concentration of 1%, stir for 3min at 3000rpm using a homogenizer, and place the obtained emulsion in a water bath at 30°C for 5h, then centrifuge at 8000rpm, wash and dry Obtain drug-loaded interconnected porous polymer microspheres;
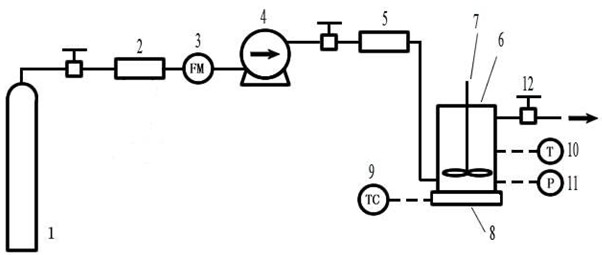
[0020] 2) Place 50 mg of the prepared drug-loaded interconnected porous polymer microspheres in the autoclave of the supercritical fluid porous polymer microsphere sealing system;
[0021] 3) Carbon dioxide is introduced into...
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: Preparation of Polylactic Acid Loaded Dexamethasone Closed Porous Microspheres
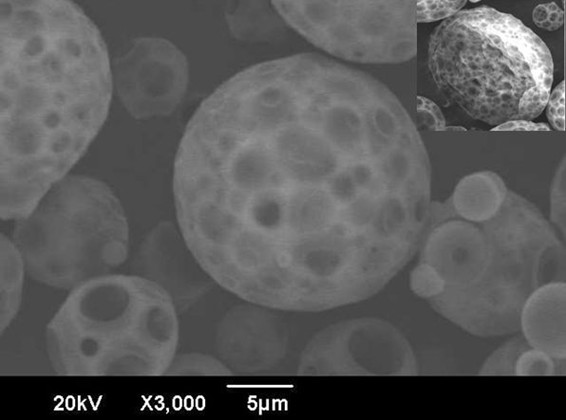
[0026] First, dissolve the mixture of polylactic acid (molecular weight 22000) and poloxamer f-127 with a mass ratio of 7:3 in 30ml of dichloromethane to prepare a solution with a concentration of 3%, and dissolve 2mg of dexamethasone in this solution , Pour the obtained polymer and drug mixed solution into 450ml of 1% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution, use a homogenizer to stir at 3000rpm for 3min, and the obtained emulsion is placed in a water bath at 30°C for 5h, and then at 8000rpm After centrifugation, washing and drying, the drug-loaded connected porous polylactic acid microspheres are obtained, and the particle diameter of the obtained microspheres is 14.69±4.48 μm. Put 50 mg of drug-loaded interconnected porous polylactic acid microspheres into filter paper and place them in an autoclave, and use a cooling tank to cool the carbon dioxide gas flowing out of the carb...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Preparation of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer loaded roxithromycin closed porous microspheres
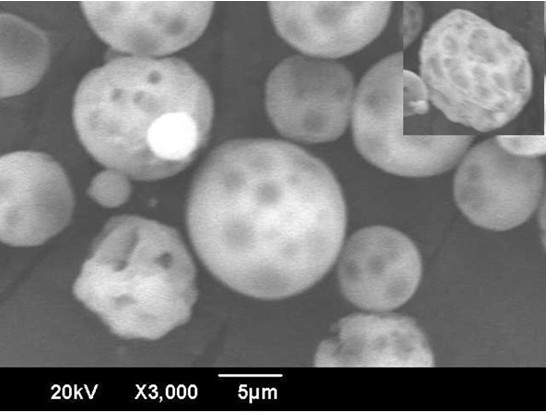
[0028] First, a mixture of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (LA:GA, 85:15; molecular weight 50,000,) with a mass ratio of 7:3 and poloxamer f-127 was dissolved in 30ml of dichloromethane to prepare a concentration of 3 % solution, take 2mg roxithromycin and dissolve in this solution, pour the resulting polymer and drug mixed solution into 450ml concentration of 1% (w / v) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution, use a homogenizer to stir at 3000rpm After 3 minutes, the obtained emulsion was placed in a water bath at 30°C for 5 hours, then centrifuged at 8000rpm, washed and dried to obtain drug-loaded interconnected porous polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres with a particle size of 15.32±5.48 μm. Put 50 mg of drug-loaded connected porous polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres into filter paper and place them in an autoclave, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com