Method for preparing indium and bismuth from coarse bismuth-containing indium
A technology of crude indium and bismuth indium, which is applied in the field of purifying rare and precious metals from rare and precious metal alloys by wet smelting, achieving the effects of low cost, small investment and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Raw material: 10 kg of crude indium containing bismuth: indium 95.7% bismuth 2% tin 0.2%
[0028] Auxiliary material: 10mol hydrochloric acid
[0029] Analysis of pure nitric acid
[0031] Iron powder 88%
[0032] Zinc flake 1#
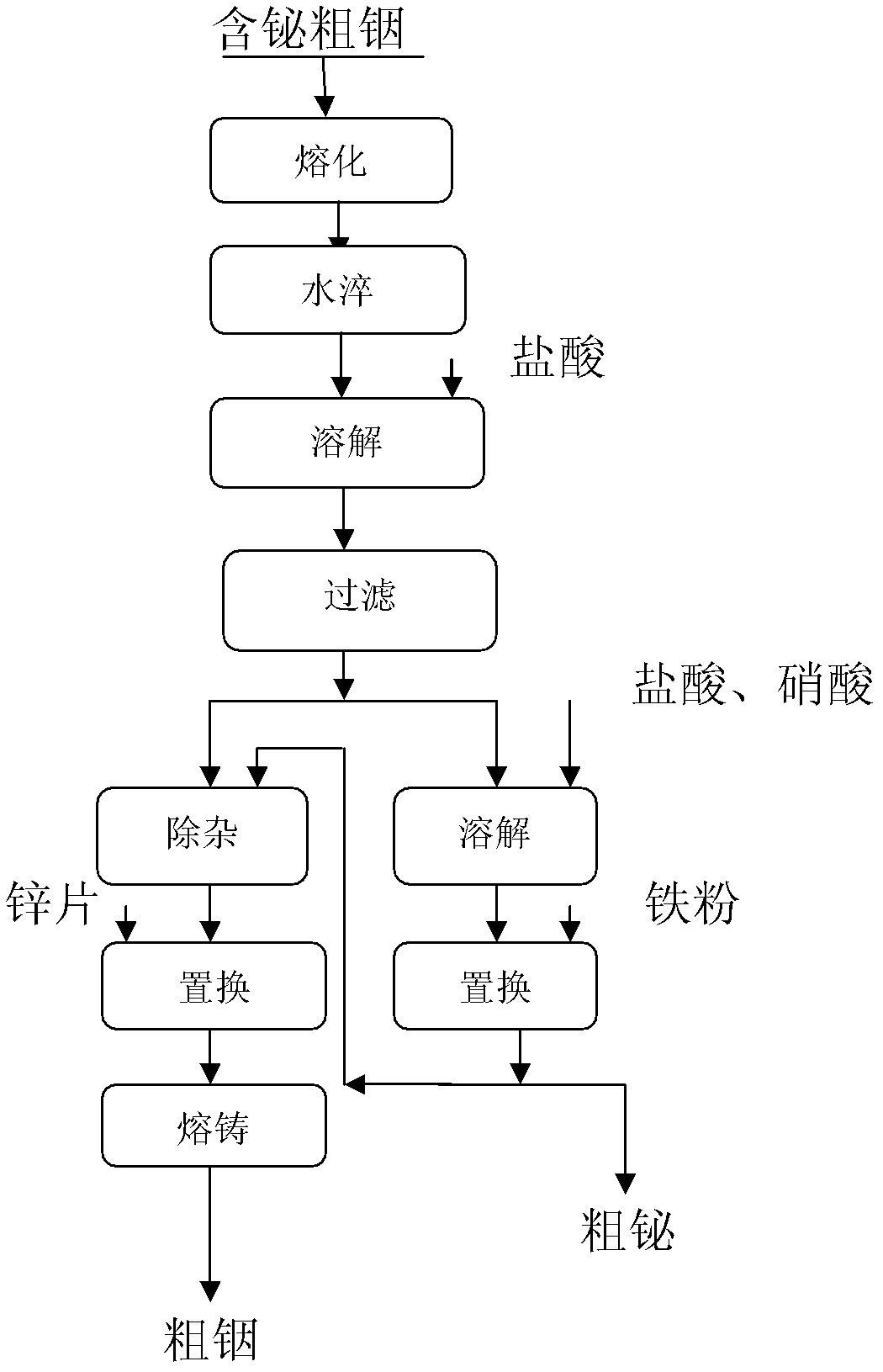
[0033] Melting: first put the crude indium in an iron pan and cover it with sodium hydroxide to melt it into a liquid metal at a temperature of 350-450°C.
[0034] Water quenching: quenching the metal liquid with water into alloy indium flower.
[0035] Dissolution: Put the alloy indium flower into a plastic bucket and dissolve it in 27 kg, 10 mol hydrochloric acid at room temperature to obtain an indium-rich solution.
[0036] Filtration: Vacuum filter the dissolved substance to obtain 26 liters of 280g / L indium solution and 3.5 kg of bismuth and indium slag.
[0037] Hydrolysis of impurities: Adjust the pH of the indium solution to 2-2.5 with sodium hydroxide to remove impurities such as ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Raw material: 100 kg of crude indium containing bismuth: indium 92.6% bismuth 6% tin 0.25%
[0047] Auxiliary material: 10mol hydrochloric acid
[0048] Analysis of pure nitric acid
[0049] Sodium hydroxide 98%
[0050] Iron powder 88%
[0051] Zinc flake 1#
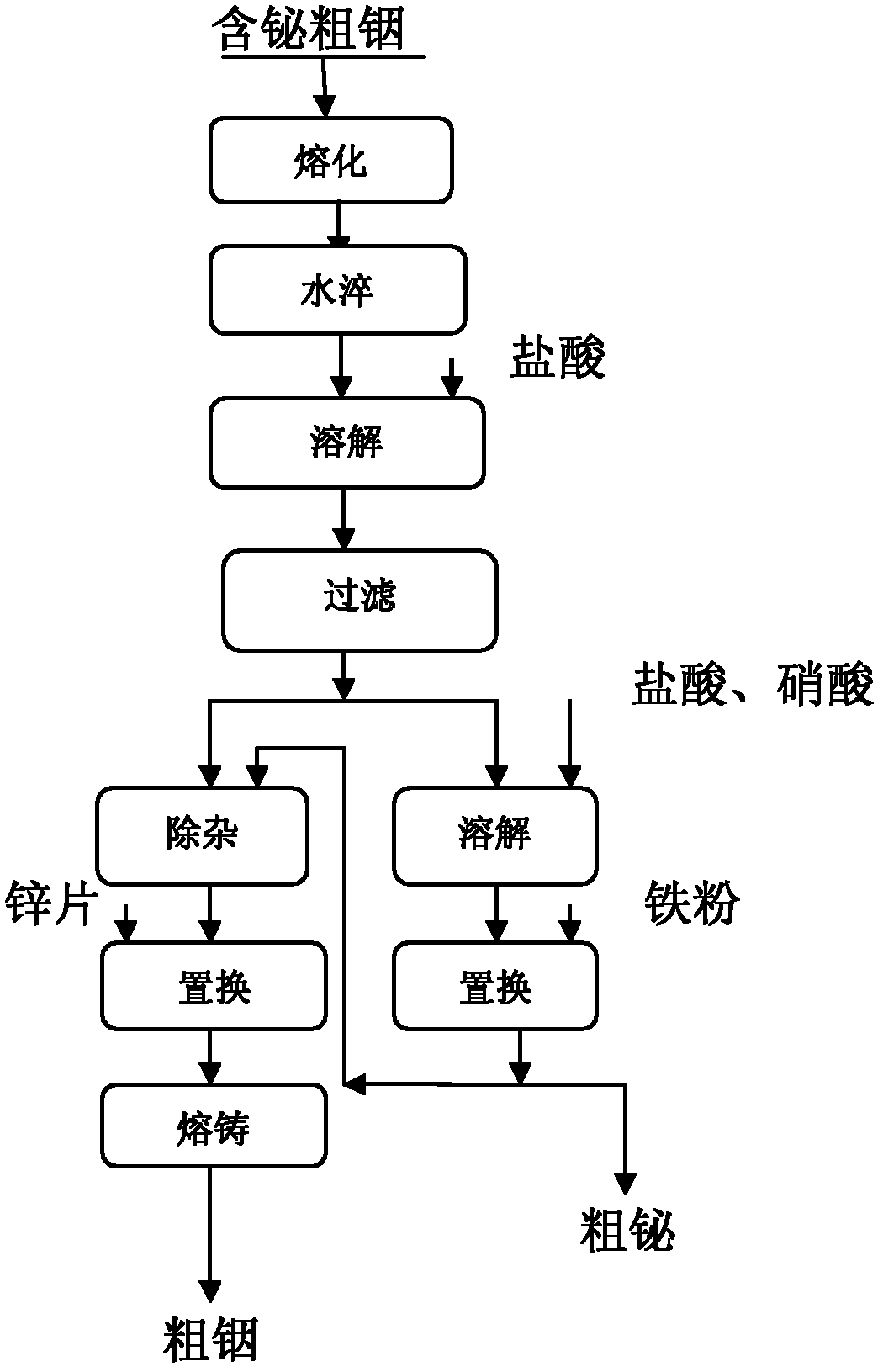
[0052] Melting: first put the crude indium in an iron pan and cover it with sodium hydroxide to melt it into a liquid metal at a temperature of 350-450°C.
[0053] Water quenching: quenching the metal liquid with water into alloy indium flower.
[0054] Dissolution: Put the alloy indium flower into a plastic reaction tank, and dissolve it in 300 kg, 10 mol hydrochloric acid at room temperature to obtain an indium-rich solution.
[0055] Filtration: Vacuum filter the dissolved substance to obtain 298 liters of 265g / L indium solution and 20kg of bismuth and indium slag.
[0056] Hydrolysis of impurities: Adjust the pH of the indium solution to 2-2.5 with sodium hydroxide to remove impuritie...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com