Film solar battery based on crystalline silicon and formation method thereof
A solar cell and thin-film technology, applied in circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of polluting the I-type amorphous silicon layer 13, reducing the bandgap width of thin-film solar cells, and reducing the photoelectric conversion efficiency of thin-film solar cells, etc. Achieve the effects of improving photoelectric conversion efficiency, reducing pollution, and increasing bandgap width
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] refer to figure 2 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for forming a thin-film solar cell based on crystalline silicon, including:
[0065] Step S1, providing a substrate made of monocrystalline silicon or polycrystalline silicon;
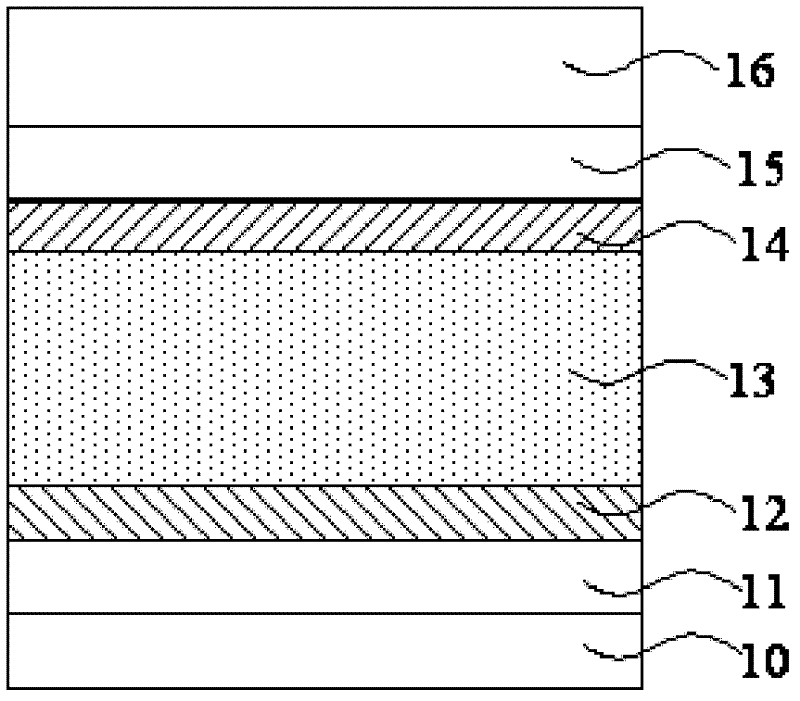
[0066] Step S2, forming a photoelectric conversion unit on the upper surface of the substrate, including: sequentially forming a P-type semiconductor layer, an I-type semiconductor layer, and an N-type semiconductor layer; forming the P-type semiconductor layer includes: forming a plurality of dopant ion concentration Different P-type semiconductor sub-layers, the P-type semiconductor sub-layers are sequentially stacked according to the doping ion concentration, and the P-type semiconductor sub-layer located on the surface of the I-type semiconductor layer has the smallest doping ion concentration; forming the N The N-type semiconductor layer includes: forming a plurality of N-type semiconductor sub-layers with different doping ion ...
Embodiment 2
[0118] This embodiment provides a method for forming a thin-film solar cell based on crystalline silicon, including:
[0119] The materials provided are monocrystalline silicon or polycrystalline silicon substrates;
[0120] An I-type semiconductor layer and a P-type semiconductor layer are sequentially formed on the substrate. The P-type semiconductor layer includes a plurality of P-type semiconductor sublayers with different dopant ion concentrations. The sizes are stacked in sequence, and the dopant ion concentration of the P-type semiconductor sub-layer located on the surface of the I-type semiconductor layer is the smallest.
[0121] Wherein, the substrate may be an N-type substrate.
[0122] Wherein, the steps of forming the I-type semiconductor layer and the P-type semiconductor layer are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. In this embodiment, the P-type semiconductor layer includes four P-type semiconductor sub-layers as an example.
[...
Embodiment 3
[0132] This embodiment provides a method for forming a thin-film solar cell based on crystalline silicon. The difference from Embodiment 2 is that in this embodiment, after forming the P-type semiconductor layer, an N-type semiconductor layer is also formed on the P-type semiconductor layer. .
[0133] Wherein, the dopant ion concentration in the N-type semiconductor layer may be evenly distributed, or may include multiple N-type semiconductor sub-layers with different dopant ion concentrations, which does not limit the protection scope of the present invention.
[0134] Specifically, refer to Figure 10 As shown, the thin-film solar cells based on crystalline silicon formed by the method of this embodiment include:
[0135] Substrate 30;
[0136] The I-type semiconductor layer 31, the P-type semiconductor layer 32, the N-type semiconductor layer 33, the anti-reflection layer 34 and the front electrode 35 which are located above the substrate 30 in turn; the P-type semicondu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com