Preparation method for oil soluble drag reducer
A drag reducing agent and oil-soluble technology, applied in the field of polymer drag reducing agent preparation, can solve the problems of high cost of low temperature pulverization, low embrittlement temperature, etc., and achieve the effects of fast dissolution rate, low production cost and difficult adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 10.0 g of polymer grade TiCl 3 Add 100ml of freshly distilled hexane solvent to make 100ml of main catalyst suspension; add 50ml of diethylaluminum chloride to 150ml of freshly distilled hexane solvent to make 200ml of cocatalyst solution. The experiments were carried out by using 250ml, 500, 3000ml glass polymerization bottles and filling them. After mixing the catalyst of titanium trichloride and diethylaluminum chloride, activate it for 30 seconds, then add it into the polymerization bottle containing olefin, and shake well.
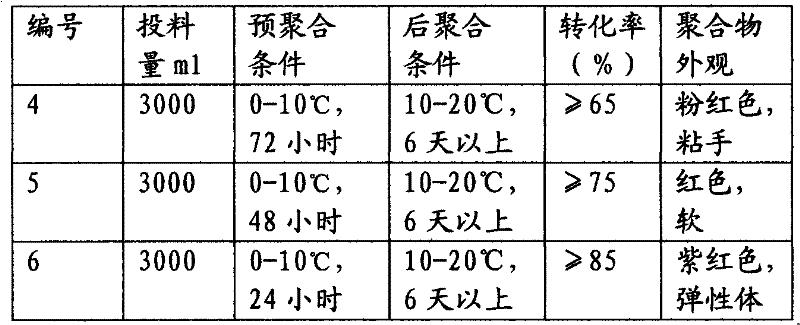
[0042] Table 1 The impact of the feeding amount on the reaction
[0043]
[0044] The amount of catalyst added in the reaction is too small, the polymerization reaction cannot be initiated or the reaction is difficult to continue to a certain extent, the monomer conversion rate is low, and the polymer can still flow after 24 hours, and it is necessary to add a catalyst to make the polymer achieve sufficient hardness. The amount of catalyst ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The polymerization reaction converts more than 50% within 24 hours, and the pre-polymerization temperature has a great influence on the reaction, and rapid cooling will be one of the technical difficulties. Corresponding forced cooling measures were taken. In addition to freezing the raw materials to below -5°C before adding the catalyst for polymerization, after the reaction started, the polymerization bottle was soaked in ice water to enhance heat dissipation, so that the heat generation of the polymerization bottle was slowed down, and the reaction temperature was always lower than 15°C. ℃, the reaction weakened after 6 hours and then transferred to another freezer to keep warm for one day. The experimental results are shown in Table 2.
[0047] Table 2 Prepolymerization temperature influence on reaction
[0048]
[0049] The low-temperature polymerization with slow reaction is beneficial to the synthesis of high-molecular-weight polymers, but after 24 hours, the...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The polymerization reaction conditions are very harsh, and impurities such as moisture and air have a great influence on the polymerization reaction. The influence of impurities existing under the experimental conditions was studied, and the experimental results are shown in Table 3.
[0052] The influence of table 3 impurities on the polymerization reaction
[0053]
[0054] If the raw material is not distilled after being dehydrated by molecular sieve, a small amount of molecular sieve will be brought in. Because the molecular sieve absorbs moisture, the raw materials around the molecular sieve are difficult to aggregate. If the polymerization bottle is not well sealed, the surface layer of the polymer is difficult to polymerize and turn white, and water may seep into it to prevent polymerization when it is soaked in ice water for forced cooling. If a plastic polymerization bottle is used, the raw materials close to the surface of the plastic are difficult to pol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com