Strain for producing 3-hydroxyl propionic acid at high yield and application thereof
A technology for high-yield and bacterial strains of hydroxypropionic acid, applied in fungi, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of insecurity, high production cost, and difficult separation and purification of products, and achieve the effects of stable genetic traits and high yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0011] The acquisition of embodiment 1 new bacterial strain CGMCC No.5344
[0012] (a) domesticate the wild fungus Candida sp.CCTCC NO: M 93018 with a medium containing propionic acid, and select the starting strain a;
[0013] (b) subjecting the starting strain a to ultraviolet-nitrosoguanidine-cobalt 60 compound mutagenesis to obtain mixed seed solution b;
[0014] (c) B is coated and cultivated completely to obtain a single bacterial colony screening medium;
[0015] (d) Cultivate and screen a single colony, and verify by fermentation detection, to obtain the mutagenized high-yielding strain CGMCC No.5344.
[0016] The acclimation concentration of propionic acid in step (a) is 0.5%-3%.
[0017] In step (b), irradiate with a 15W ultraviolet lamp for 70s, add nitrosoguanidine solution to make the final concentration 25mg / mL, and cobalt 60 dose is 1000Gy for the best mutagenesis effect.
[0018] In step (c), the complete medium formula is (g / L): glucose 20, peptone 20, yeas...
Embodiment 2
[0020] Example 2 Fermentation of mutant strain CGMCC No.5344 to produce 3-HP
[0021] (1) Seed liquid culture: inoculate the seed medium with the activated colonies, and cultivate at 220 r / min at 30° C. for 20 h. Seed medium (g / L): glucose / glycerol 20, yeast extract 10, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 15, KH 2 PO 4 9,K 2 HPO 4 3. MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.5, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.03, pH 6.8±0.2.
[0022] (2) Fermentation culture
[0023] Fermentation medium (g / L): yeast extract 10, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 15, KH 2 PO 4 9,K 2 HPO 4 3. MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.5, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.03, CaCl 2 0.04, propionic acid 15, TES 5mL, with KOH / H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH to 6.0±0.2, sterilize at 115°C for 15 minutes, and mix with 50g / L glucose / glycerol.
[0024] Inoculate with 4% inoculum, culture at 220r / min, 30°C, ferment for 96h, centrifuge the fermentation broth, dilute, and filter through a microporous membrane, then measure the 3-hydroxypropionic acid production of wild bacteria and mutant strain CGMCC No.5344...
Embodiment 3
[0025] The influence of embodiment 3 quiescent cells on the production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid
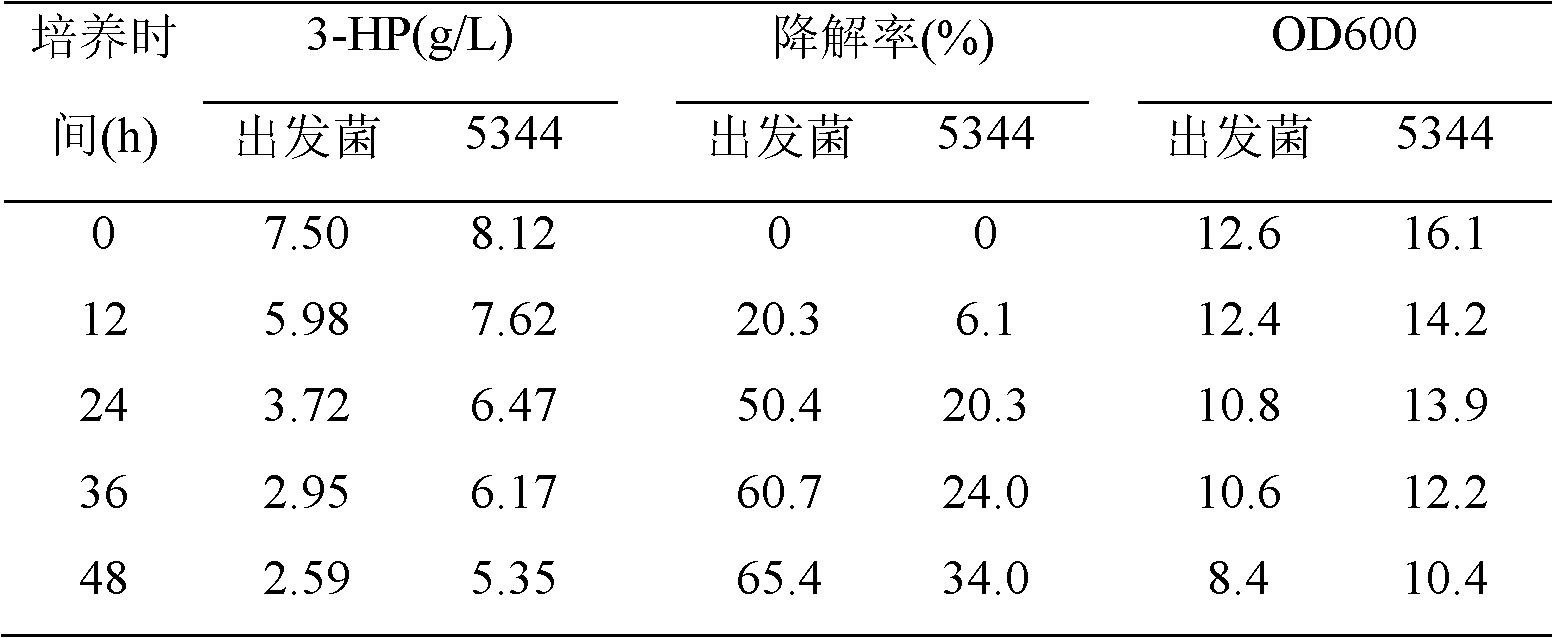
[0026] In the absence of exogenous carbon sources, 3-HP will be consumed by the bacteria to supply energy to maintain the normal metabolism of the bacteria. In comparison, the degradation rate of 3-hydroxypropionic acid in wild bacteria Candida sp. is higher than that of CGMCC No.5344 (as shown in Table 1).
[0027] Preparation and cultivation of resting cells: After culturing in the fermentation medium for 72 hours, the cells were collected by centrifugation, and the cells were washed twice with 0.2M phosphate buffer. Transfer to phosphate buffer solution containing 1% 3-hydroxypropionic acid, and culture on a rotary shaker at 220r / min at 30°C for 48h. Samples were taken every 12 hours to detect the bacterial concentration and the content of 3-HP.
[0028] Table 1 Degradation of 3-HP by resting cells of Candida sp. and CGMCC No.5344
[0029]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com