Protein nanometer particle for wrapping slightly soluble medicines and preparation method thereof
A technology of insoluble drugs and nanoparticles is applied in the field of protein nanoparticles encapsulating insoluble drugs and their preparation, which can solve the problems of loss of curative effect, unfavorable tumor targeting, easy failure of drugs, etc., so as to improve the convenience and safety of medication. , good in vitro and in vivo stability, good pharmacodynamic properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0134] Example 1 Preparation of Paclitaxel Albumin Nanoparticles by Melting Method
[0135] Dissolve 500 mg of paclitaxel in 9.0 mL of ethanol. After 1200 mg of polyethylene glycol was heated and completely melted in an oil bath at 60°C, the paclitaxel solution was added thereto, and stirred by magnetic force until it was completely mixed evenly. After the ethanol was removed by rotary evaporation, it was rapidly cooled under vigorous stirring conditions. After vacuum drying overnight, the solid dispersion was added to 85 ml of human serum albumin aqueous solution (4.5% w / v, g / ml, the same below). The mixture was premixed by a high-speed disperser (XHF-1, Shanghai Jinda Biochemical Instrument Factory) for 1 minute to form a coarse milk, and then transferred to a high-pressure homogenizer (EmulsiFlex-05, Avestin, Canada). High pressure homogenization at 5000-30,000 psi 2 Under certain conditions, the emulsion is repeatedly circulated at least 5 times to obtain a suspension of...
Embodiment 2
[0137] Example 2 Preparation of paclitaxel albumin nanoparticles by melt-solvent evaporation method
[0138] Dissolve 300 mg of paclitaxel in 6.0 mL of ethanol. Dissolve 900 mg of polyethylene glycol in 1.5 ml of absolute ethanol, heat and completely melt in an oil bath at 45°C, add the paclitaxel solution into it, stir magnetically until it is completely mixed, and remove the ethanol by rotary evaporation, quickly under vigorous stirring conditions cool down. After drying under vacuum overnight, the solid dispersion was added to 65 ml of aqueous human serum albumin (4.5% w / v). The mixture was premixed by a high-speed disperser (XHF-1, Shanghai Jinda Biochemical Instrument Factory) for 1 minute to form a coarse milk, and then transferred to a high-pressure homogenizer (EmulsiFlex-05, Avestin, Canada). Emulsified at 5000-30,000 lbs / in 2 Carried out under the conditions of the above conditions, the emulsion was repeatedly circulated at least 6 times to obtain a protein nanopa...
Embodiment 3
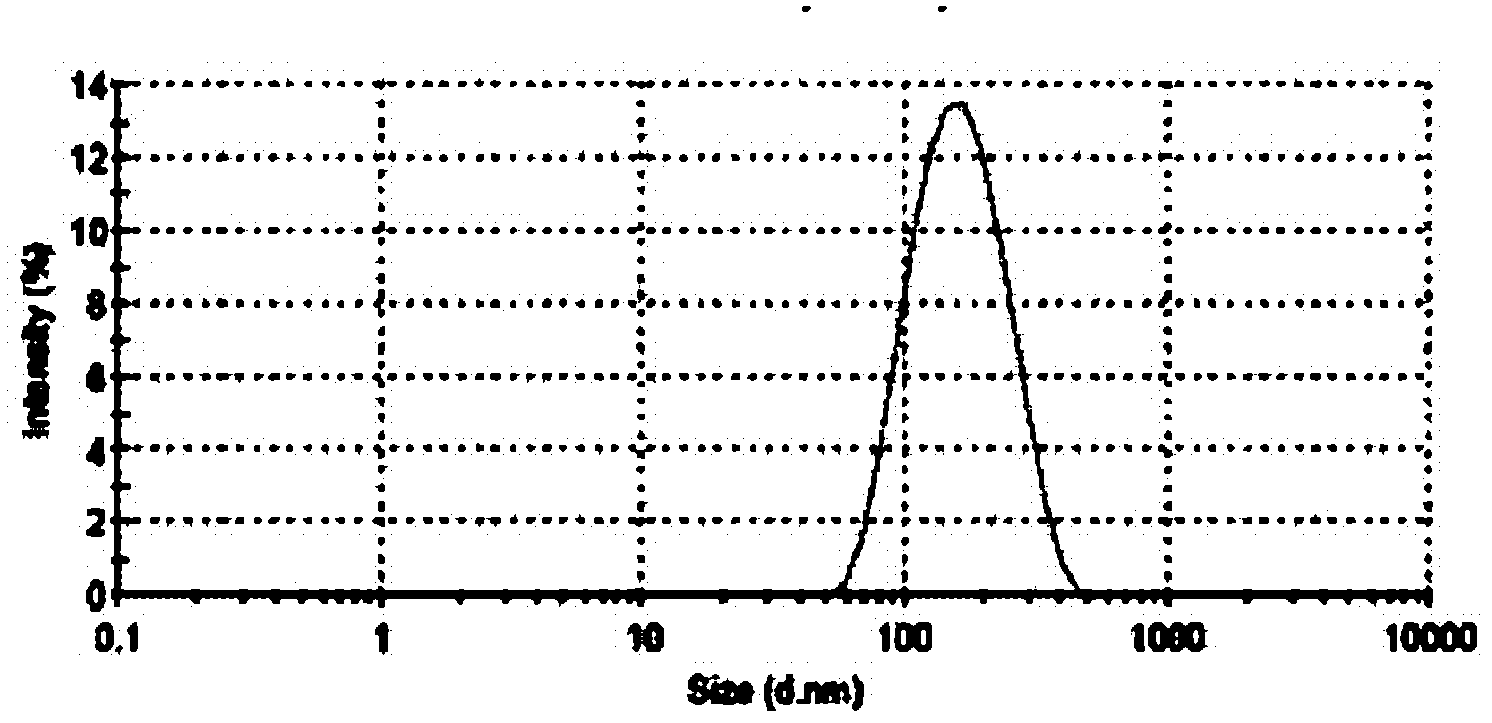
[0140] Example 3 Preparation of Sterile Filterable Paclitaxel Albumin Nanoparticles Less Than 200 Nanometers
[0141] Dissolve 500 mg of paclitaxel in 9.0 mL of ethanol. Dissolve 800 mg of polyethylene glycol in 1.5 ml of absolute ethanol, heat and completely melt in an oil bath at 45°C, add paclitaxel solution into it, stir magnetically until it is completely mixed evenly, and remove ethanol by rotary evaporation, rapidly under vigorous stirring conditions cool down. After drying under vacuum overnight, the solid dispersion was added to 97 ml of aqueous human serum albumin (4.5% w / v). The mixture was premixed by a high-speed disperser (XHF-1, Shanghai Jinda Biochemical Instrument Factory) for 1 minute to form a coarse milk, and then transferred to a high-pressure homogenizer (EmulsiFlex-05, Avestin, Canada). Emulsified at 10,000-40,000 lbs / in 2 Carried out under the conditions of the above conditions, the emulsion was repeatedly circulated at least 6 times to obtain a prot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com