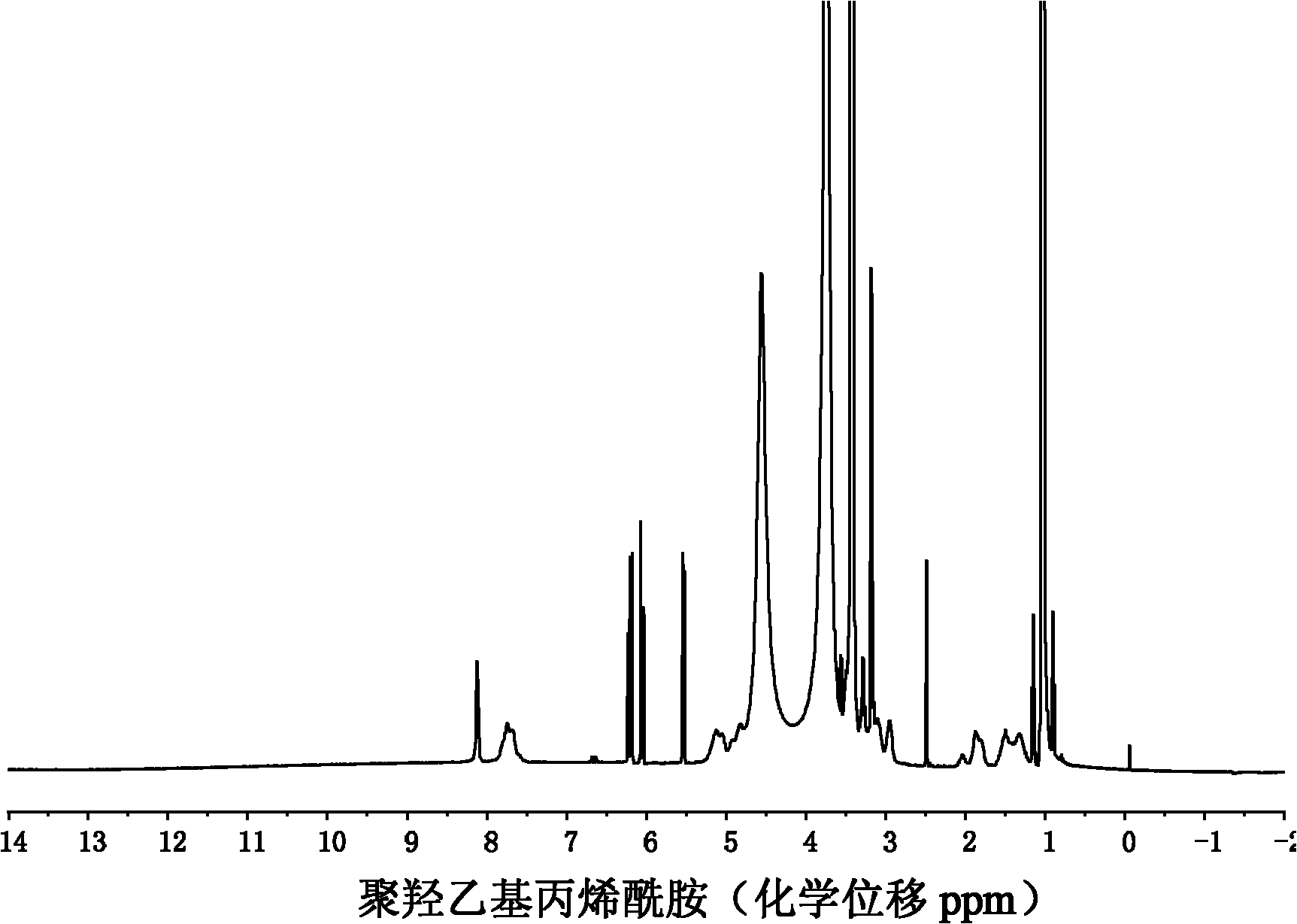
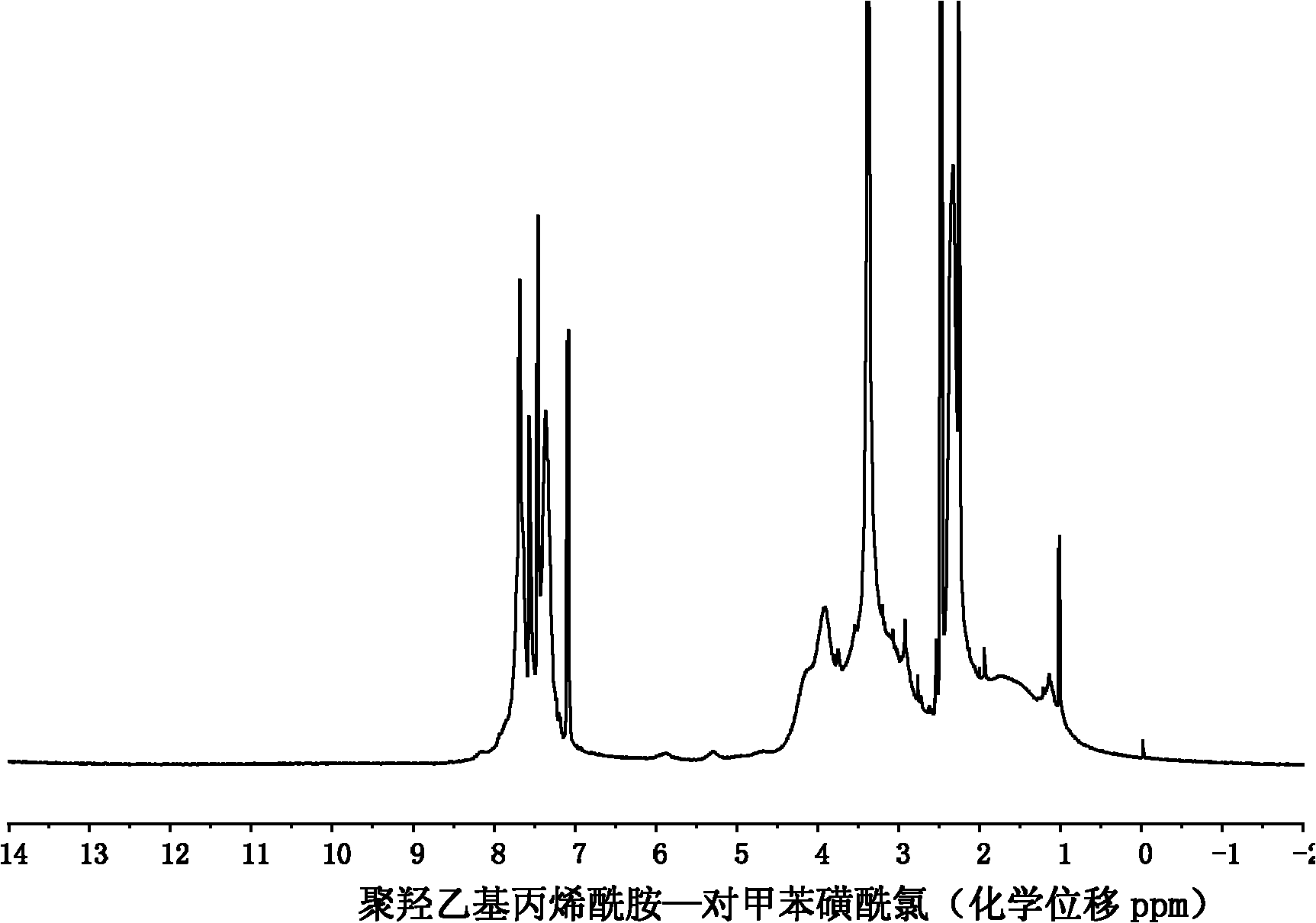
A modified polyhydroxyethylacrylamide transgenic carrier and its preparation method and application
A technology of polyhydroxyethylacrylamide and transgenic vectors, which is applied in the direction of using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, etc., and can solve the problems of low biodegradability, low transfection efficiency, toxicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Monomer HEAA (5 mmol, 575.5 mg) and catalyst CuCl (9.9 mg, 0.1 mmol) were added to a Schlenk tube and dissolved with 5 mL of ethanol / water. Freezing with liquid nitrogen, degassing, then dissolving and blowing nitrogen gas, repeated freezing and thawing three times to remove oxygen in the reaction system. Initiator PMDETA (21 ml, 0.1 mmol) and ligand EBMP (15 ml, 0.1 mmol) were dissolved in 1 ml ethanol / water solution and transferred to a Schlenk tube with a syringe under nitrogen protection. After the reaction mixture was repeatedly frozen and thawed three times, it was vacuum-sealed, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 60°C for 10 hours, the reaction product was diluted with deionized water, and then dialyzed in deionized water with a dialysis bag (molecular weight cut-off 3500), and the water was changed every 8 hours , lyophilized after 5 days of dialysis. Polyhydroxyethylacrylamide (PHEAA, theoretical degree of polymerization is 50) can be obtained;
[0032] W...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Monomer HEAA (10 mmol, 1.151 g) and catalyst CuCl (9.9 mg, 0.1 mmol) were added to a Schlenk tube and dissolved with 8 mL of ethanol / water. Freezing with liquid nitrogen, degassing, then dissolving and blowing nitrogen gas, repeated freezing and thawing three times to remove oxygen in the reaction system. Ligand PMDETA (21 ml, 0.1 mmol) and initiator EBMP (15 ml, 0.1 mmol) were dissolved in 1 ml ethanol / water solution, and transferred to a Schlenk tube with a syringe under nitrogen protection. After the reaction mixture was repeatedly frozen and thawed three times, it was vacuum-sealed, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 60°C for 10 hours, the reaction product was diluted with deionized water, and then dialyzed in deionized water with a dialysis bag (molecular weight cut-off 3500), and the water was changed every 8 hours , lyophilized after 5 days of dialysis. Polyhydroxyethylacrylamide (PHEAA, theoretical degree of polymerization is 100) can be obtained;
[0038]...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Monomer HEAA (15 mmol, 1.7265 g) and catalyst CuCl (9.9 mg, 0.1 mmol) were added to a Schlenk tube and dissolved with 11 mL of ethanol / water. Freezing with liquid nitrogen, degassing, then dissolving and blowing nitrogen gas, repeated freezing and thawing three times to remove oxygen in the reaction system. Ligand PMDETA (21 ml, 0.1 mmol) and initiator EBMP (15 ml, 0.1 mmol) were dissolved in 1 ml ethanol / water solution, and transferred to a Schlenk tube with a syringe under nitrogen protection. After the reaction mixture was repeatedly frozen and thawed three times, it was vacuum-sealed, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 60°C for 10 hours, the reaction product was diluted with deionized water, and then dialyzed in deionized water with a dialysis bag (molecular weight cut-off 3500), and the water was changed every 8 hours , lyophilized after 5 days of dialysis. Polyhydroxyethylacrylamide (PHEAA, theoretical degree of polymerization is 150) can be obtained;
[004...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com