Method for rapid detection and authenticity identification of fatty acid of racy camellia oil by near infrared transmission spectroscopy (NITS)
A transmission spectrum and near-infrared technology, applied in the field of edible vegetable oil quality analysis, can solve the problem of relatively few researches on tea oil adulteration detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
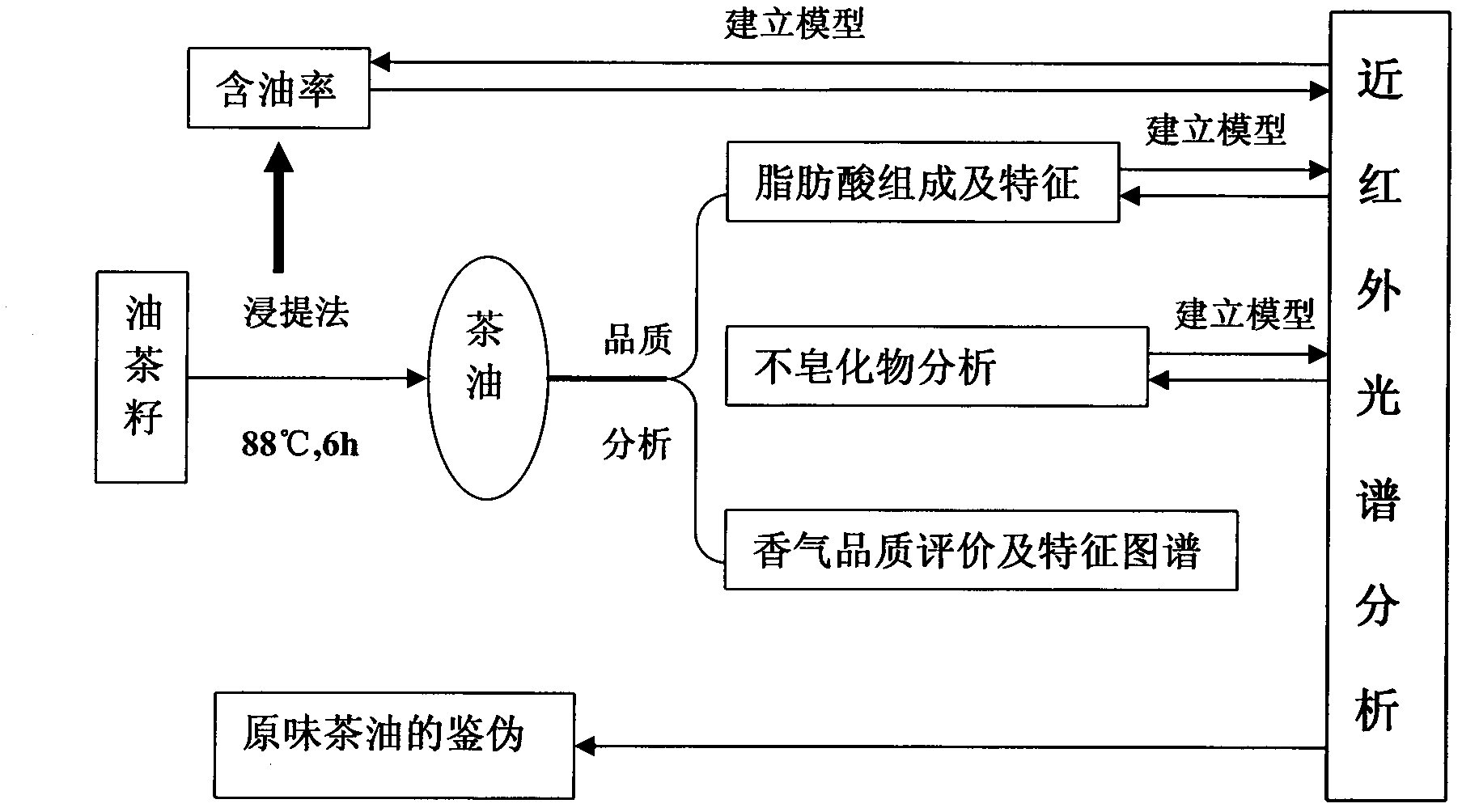
[0053] A near-infrared transmission spectrum (NITS) rapid detection of original tea oil fatty acids and a counterfeit method, characterized in that the Fourier transform near-infrared transmission spectrum analysis technology to determine oleic acid, linoleic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid in different varieties of tea oil acid and total unsaturated fatty acid content, and rapid identification of tea oil mixed with other edible vegetable oils, consists of the following steps:
[0054] The first step is the selection of high-quality Camellia oleifera varieties
[0055] Select high-quality varieties with an oil content of 30%-60% from more than 130 camellia seed varieties, including 65%-85% oleic acid, 5%-20% linoleic acid, and 3%-15% palmitic acid , stearic acid content 1%-5%;
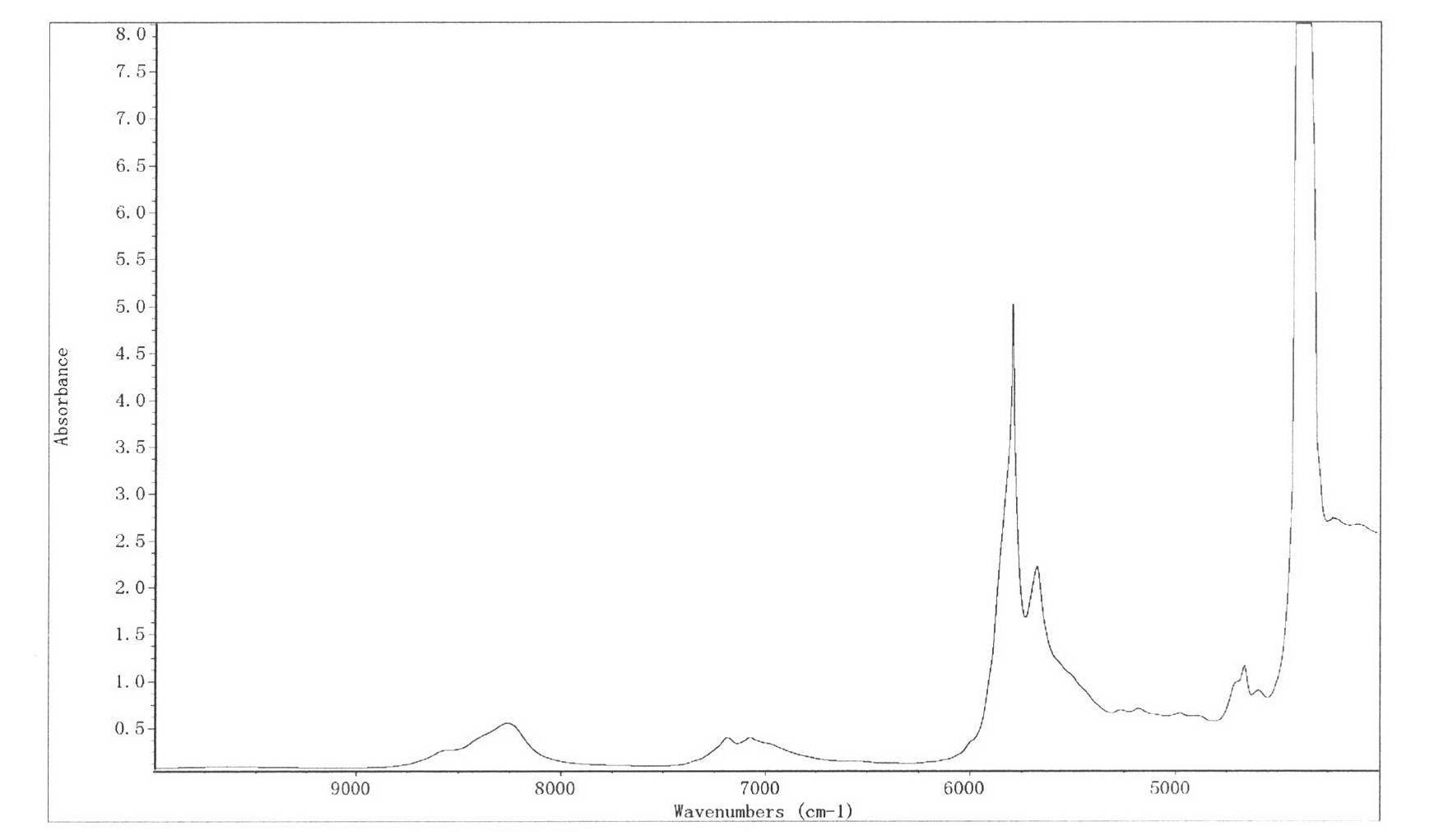
[0056] The second step is the establishment of the NITS model of each fatty acid in camellia oil
[0057] Collect 90-140 different camellia oil samples, such as 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, and 140 samp...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The determination of the oil content of different varieties of Camellia oleifera seeds in embodiment 2
[0070] Grind the dried Camellia oleifera seeds into powder (with seed husks, the water content of the sample is less than 10%), weigh a certain amount of Camellia oleifera seed powder, and record the weight m 0 . Put it into the filter paper tube, insert the absorbent cotton into the upper part, compress the sample, and put it into the extractor. Add 180mL of petroleum ether (60°C-90°C) into the extraction bottle, extract at 80°C for 6h, evaporate the extract to empty and concentrate the solvent to obtain camellia oil, weigh the oil in m 1 . Calculate the oil content w=m of the corresponding variety 1 / m 0 .
[0071] This embodiment selects different varieties in Yunnan, Jiangxi, Zhejiang and other places, and the results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 5 . There are 26 varieties of Camellia oleifera seeds whose oil content is below 30%, 27 varieties of 30% t...
Embodiment 3
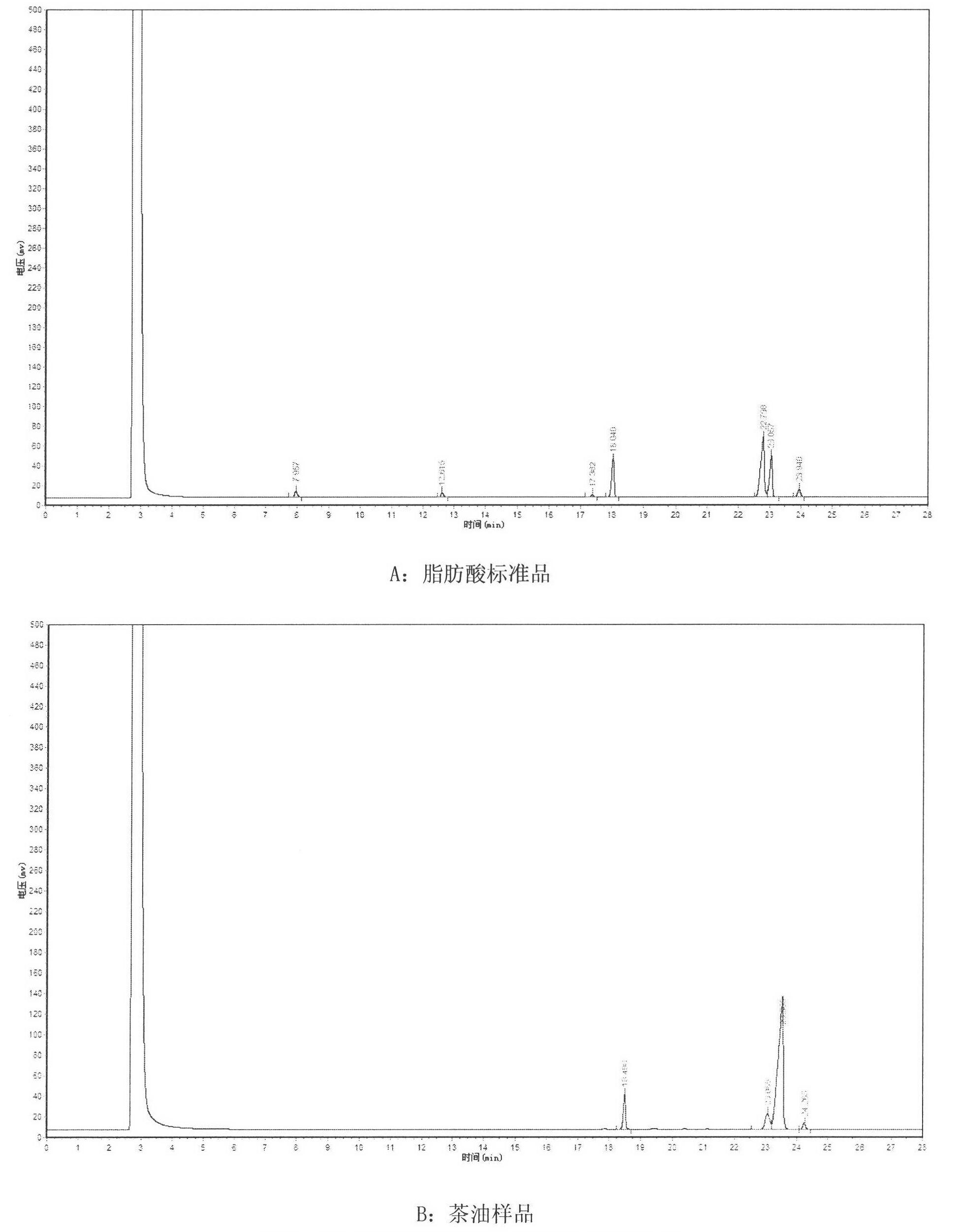
[0072] The composition of fatty acid in the different kinds of camellia oils measured by gas chromatography in embodiment 3
[0073] According to the sample prepared in Example 2, the sample was pretreated with methyl esterification. The varieties selected in this example include Guangxi (Lingyun, Liuzhou Rongshui, Fangchengdongzhong, Baise, Fengshan, Rong'an, Tianyang, Nandan, common Camellia oleifera), white camellia oil, safflower camellia oil, Yunnan Funingyan 129 samples including 1-120 samples from North Korea and Jiangxi (as shown in Table 2), and 9 samples of Camellia oleifera from Tengchong, Yunnan. Take a small amount of camellia oil sample and drop it in a 10mL test tube, add 2mL 0.5mol / L NaOH-CH 3 OH, shake well, put it in a 60°C water bath for methyl esterification for 30min, take it out and add 5mL of n-hexane, shake well, take out the supernatant after standing still, and carry out GC chromatographic analysis.
[0074] GC analysis conditions: chromatographic c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com