Blueberry mycorrhizal fungi (coprinus micaceus) and separation method and application thereof
A mycorrhizal fungus and blueberry technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as soil damage, reduce the damage of pests, and improve the effect of resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
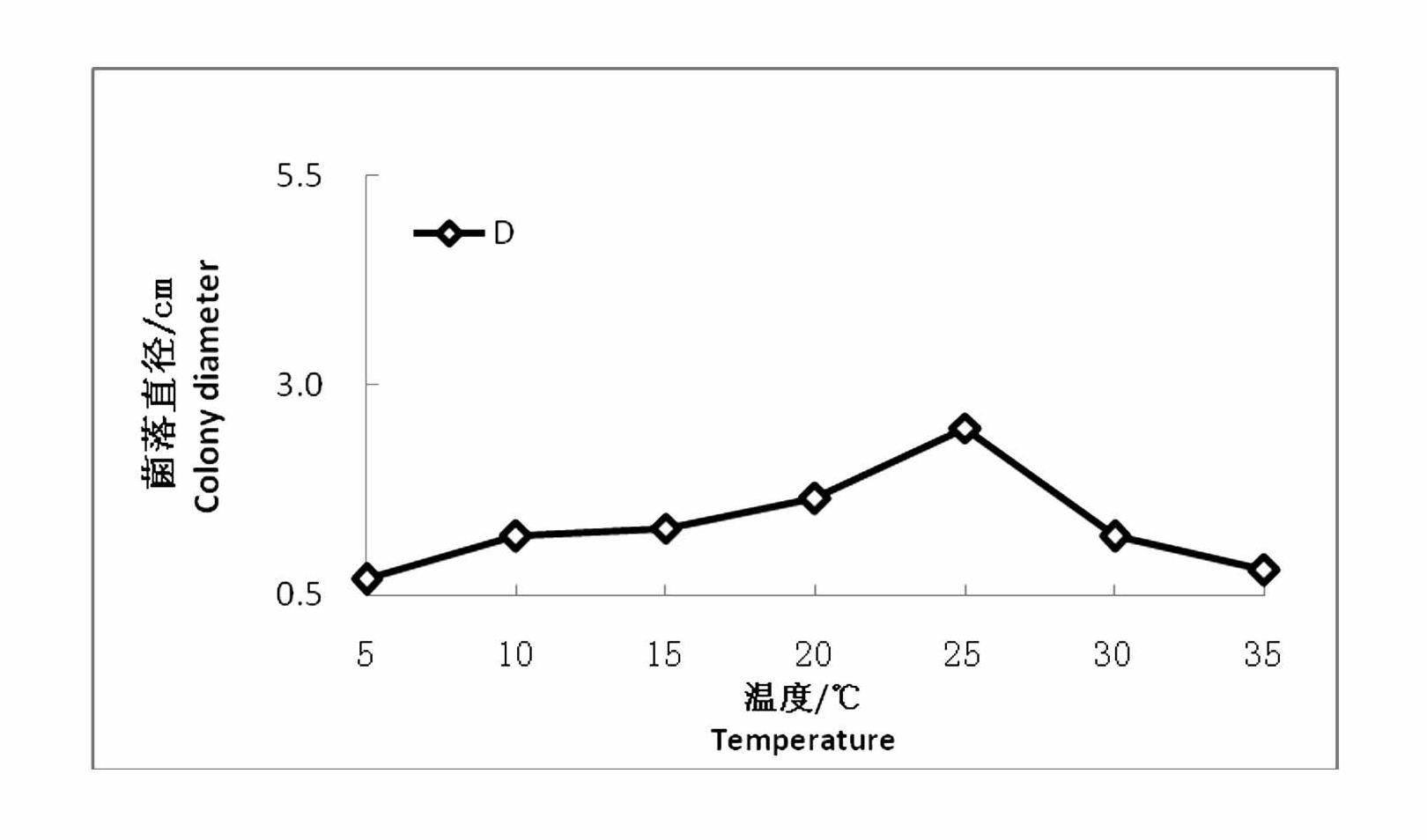
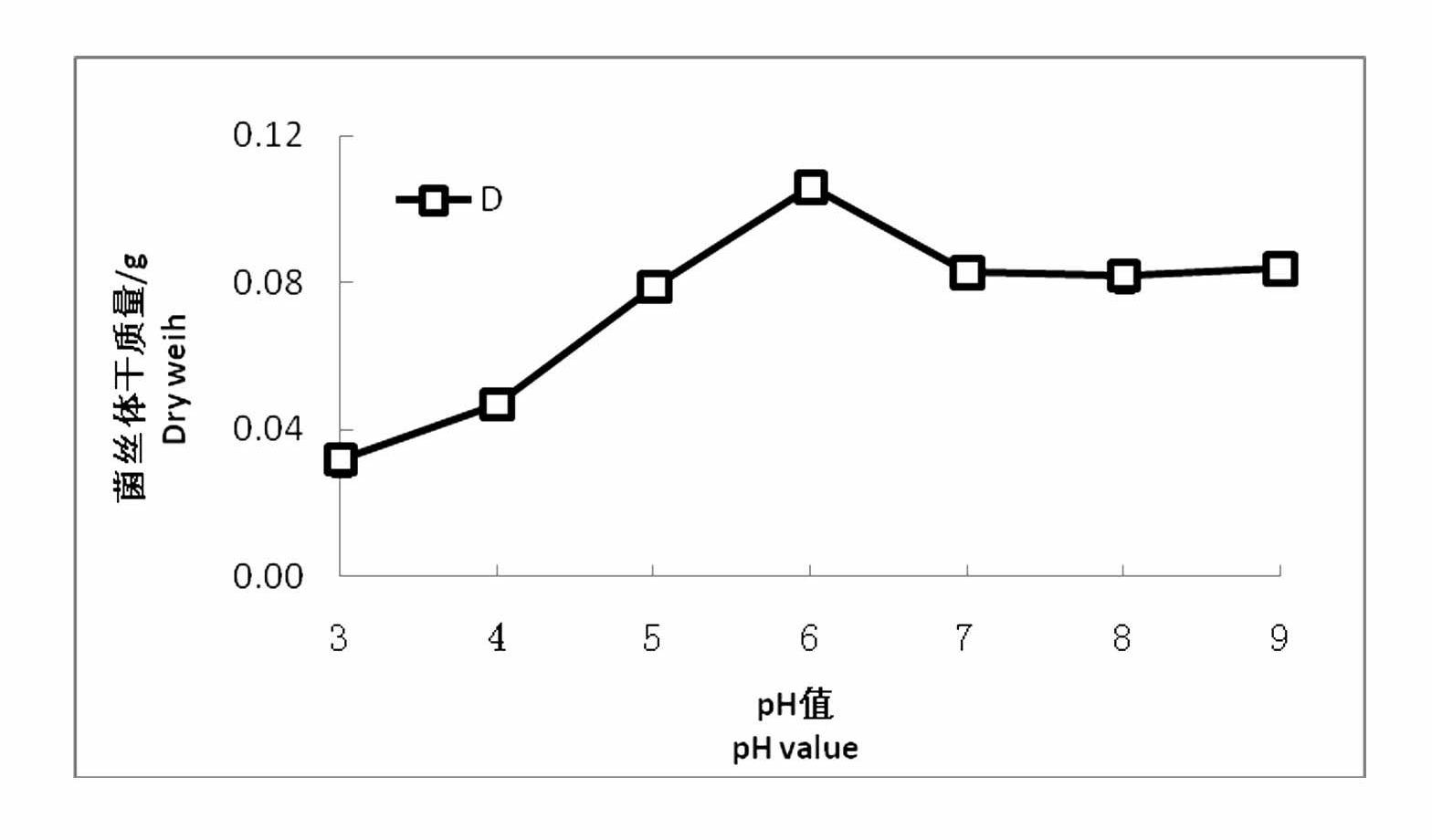
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] A method for separating blueberry mycorrhizal fungi, which is characterized in that the mycorrhizal fungi are obtained from the rhizosphere of wild bilberry plants, and the steps are as follows:
[0085] (1) Washing: Take fresh and complete roots of healthy wild blueberries, rinse them with tap water for one hour, then rinse with sterile water 3 times, and transfer the roots to sterile glass plates for later use.
[0086] (2) Disinfection: Put the roots to be used in step (1) in 70% alcohol solution for 30 seconds, rinse with sterile water 3 times, and then disinfect with 0.1% mercury solution for 2 minutes, rinse 3 times, and then immediately put it into a 1% by mass sterile sodium sulfide aqueous solution for 2 minutes, rinse with sterile water 3 times, and absorb the sterile filter paper for use.
[0087] (3) Cultivation: Cut the roots to be used after disinfection in step (2) into 0.8cm-long sections, place them on a PDA medium plate, invert the culture at a constant tempe...
Embodiment 2
[0093] A method for separating blueberry mycorrhizal fungi, which is characterized in that the mycorrhizal fungi are obtained from the rhizosphere of wild bilberry plants, and the steps are as follows:
[0094] (1) Washing: Take fresh and complete roots of healthy wild blueberries, rinse them with tap water for one hour, then rinse with sterile water twice, and transfer the roots to a sterilized glass dish for later use.
[0095] (2) Disinfection: Put the roots to be used in step (1) in 70% alcohol solution for 20 seconds, rinse with sterile water 3 times, and then disinfect with 0.1% mercury solution for 1 min, rinse 3 times, and then immediately put it in a 1% by mass sterile sodium sulfide aqueous solution for 3 minutes, rinse with sterile water 3 times, and absorb dry with sterile filter paper for later use.
[0096] (3) Cultivation: Cut the roots to be used after disinfection in step (2) into 0.5cm-long sections, place them on a PDA medium plate, and invert the culture at a cons...
Embodiment 3
[0102] A method for separating blueberry mycorrhizal fungi, which is characterized in that the mycorrhizal fungi are obtained from the rhizosphere of wild bilberry plants, and the steps are as follows:
[0103] (1) Washing: Take fresh and complete roots of healthy wild blueberries, rinse them with tap water for one hour, then rinse with sterile water 4 times, and transfer the roots to a sterilized glass plate for later use.
[0104] (2) Disinfection: Put the roots to be used in step (1) into 70% alcohol solution for 40 seconds, rinse with sterile water 3 times, and then disinfect with 0.1% mercury solution for 3 minutes, rinse 3 times, and then immediately put it into 1% by mass sterile sodium sulfide aqueous solution for 1 min, rinse with sterile water 3 times, and absorb dry with sterile filter paper for later use.
[0105] (3) Cultivation: Cut the to-be-used roots in step (2) into 1 cm long sections, place them on a PDA medium plate, invert the culture at a constant temperature at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com