Method for preparing tomato strains containing transgene sites
A transgenic and tomato technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve problems such as inability to integrate, achieve the effects of improving safety, avoiding gene silencing, and reducing interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
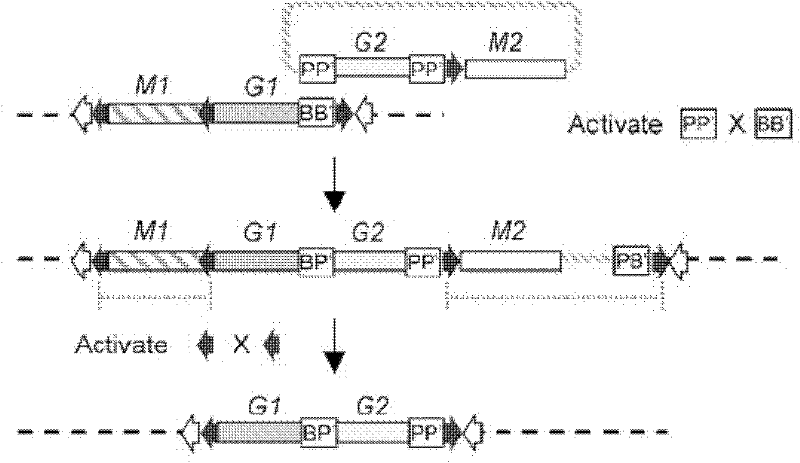
[0057] A method for preparing a tomato target gene strain containing a specific transgenic site, the steps of which are:
[0058] (1) Sterilize tomato seeds in 75% (v / v) alcohol for 28-34s, then pour out the alcohol.
[0059] (2) Transfer the seeds to a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask with tweezers, and sterilize with NaClO for 10-14min.
[0060] (3) Pour out the NaClO and wash it with sterilized distilled water for 3 to 4 times. Inoculate in 1 / 2MS medium and culture for 8-9 days.
[0061] (4) The cotyledons are fully stretched, and the tomato tender seedlings whose true leaves have not yet grown are spread on the filter paper of a large petri dish (the filter paper is moistened with sterilized water in advance). Cut off the hypocotyl and root with a razor blade, then cut off the cotyledon with a small petiole, and cut off the tip, leaving a wound for bacterial infection. Then use tweezers to transfer the cut cotyledons to the 0.2Z pre-medium (MS medium added with 2 μg / ml zeati...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The extraction of tomato genome DNA, its step is:
[0074] (1) Collect 50-100 mg tomato young leaves.
[0075] (2) Prepare freshly prepared DNA extraction solution and preheat it in a 65°C water bath.
[0076] (3) The leaves were ground in liquid nitrogen, then transferred to a 2 ml centrifuge tube, and 800 μl of DNA extraction solution was added. Water bath at 65°C for 30-120 minutes, shaking occasionally during the period.
[0077] (4) Add 600 μl of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), mix well, shake up and down 50-100 times, and centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes.
[0078] (5) Pipette the aqueous phase into a new centrifuge tube and repeat step (4) once.
[0079] (6) Pipette the water phase into a new centrifuge tube, add 2 / 3-1 times the volume of pre-cooled isopropanol, and turn it upside down until the DNA precipitates.
[0080] (7) Immediately centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes, pour out the isopropanol, and add 70% (v / v) alcohol to wash.
[0081] (8) ...
Embodiment 3
[0088] PCR amplification of specific genes and loci in the tomato genome:
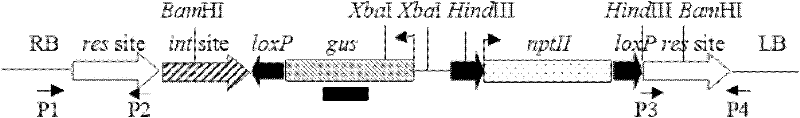
[0089] Genomic DNA is used as a template for PCR amplification, and the DNA stock solution is diluted 100 times, and T 0 Transformed seedlings and F 1 The primers selected for individual screening are the upstream primers designed in the 35S promoter, and the downstream primers designed in the nptII gene (35Sd-F and nptII-R primer pair) (Tm=57°C):
[0090] 35Sd-F: 5′-CCCAAGCTTCCCAGATTAGCCTTTTCAATTTC-3′
[0091] nptII-R: 5′-TCGATCCGAACCCCAGAGTC-3′
[0092] The PCR program is: 94°C, 5min; 94°C, 30s, 57°C, 30s; 72°C, 1min; 72°C, 8min. 16°C hold.
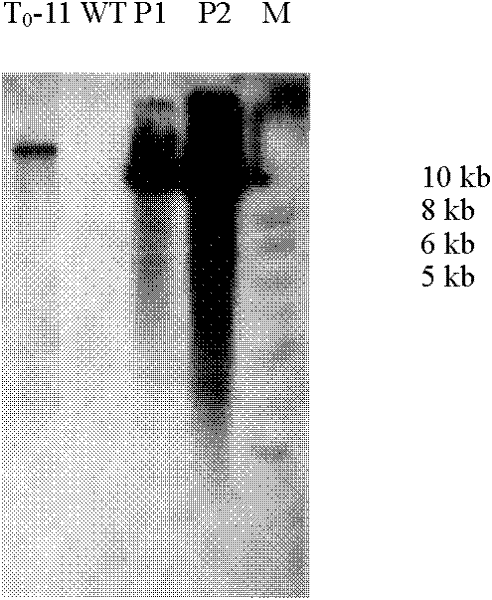
[0093] f 1 Integrity detection of T-DNA insertion in generation individuals, the primer pair on the left border is P1 and P2 (Tm=55°C); the primer pair on the right border is P3 and P4 (Tm=54°C). Figure 6 Shown are the detection results for the right boundary.
[0094] The primer pair sequences for PCR detection are as follows:
[0095] P1: 5′-TAAACGCTC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com