Method for indirectly synthesizing dimethyl carbonate by CO gas phase oxidative coupling and decarbonylation
A technology of dimethyl carbonate and oxidative coupling, applied in the preparation of carbonate/haloformate, chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, etc., can solve the problem of propylene oxide dependence and disadvantageous synthesis of dimethyl carbonate Promotion and development, shortage of crude oil resources, etc., to achieve the effects of mild reaction conditions, low prices, and reduced production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
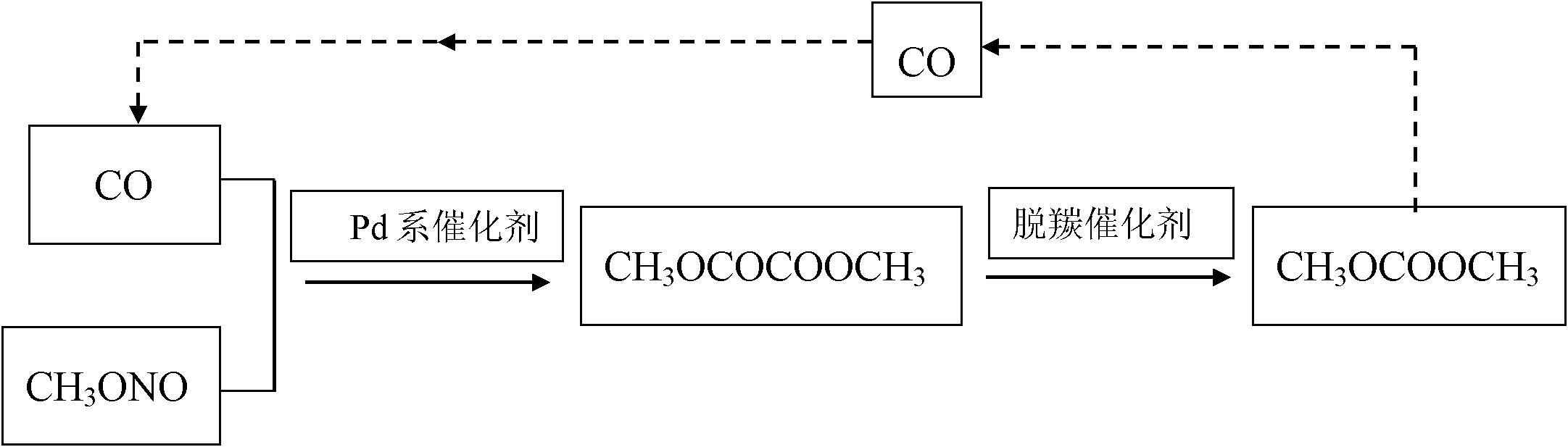
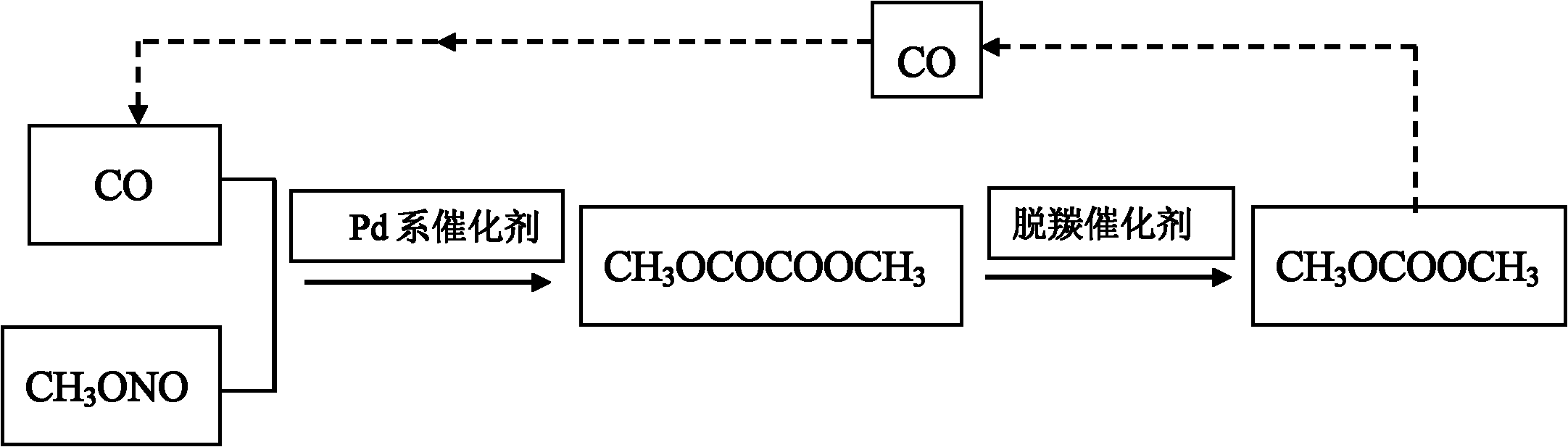
[0031] Preparation of Pd-based catalyst: mix palladium chloride, hydrochloric acid and deionized water to make an impregnation solution, the mass percentage of Pd in the impregnation solution is 1.5%, the volume ratio of the impregnation solution to the carrier is 1.5:1, take 90g of α -A1 2 o 3Dissolve in the above impregnating solution, and heat to 70°C, stir at this temperature for 2h, then impregnate at room temperature for 14h; then filter, and wash the obtained catalyst with deionized water 10 times, each time the amount of deionized water is 500ml, Then they were dried at 60°C for 6h, at 100°C for 15h, and fired at 450°C for 10h. Finally, soak the calcined catalyst in hydrazine hydrate solution at room temperature for 6 hours for reduction, and then wash it with methanol with a concentration of 100% by mass to obtain the final catalyst, which is dried in the air for use.
[0032] Oxidative coupling reaction: Take 100ml of Pd-based catalyst and place it in the constan...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The preparation method of Pd series catalyst is the same as embodiment 1.
[0036] Oxidative coupling reaction: Take 100ml of Pd-based catalyst and place it in the constant temperature zone of the fixed-bed reactor. Methyl ester passes through a reactor bed containing a palladium-based catalyst at a temperature of 135°C and a pressure of 0.3 MPa, and is oxidatively coupled to form dimethyl oxalate with a purity of more than 99%, which is used as a raw material for the subsequent decarbonylation reaction.
[0037] Decarbonylation reaction: take 100g decarbonylation catalyst Na 2 CO 3 Put it in a stainless steel reaction kettle, add 1000g dimethyl oxalate, raise the temperature to 110°C under normal pressure, keep the temperature for 4 hours, take out the liquid phase product after reaction, determine the component composition and content by gas chromatography analysis, and calculate the oxalic acid The conversion rate of dimethyl ester and the selectivity of dimethyl c...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The preparation method of Pd series catalyst is the same as embodiment 1.
[0040] Oxidative coupling reaction: Take 100ml of Pd-based catalyst and place it in the constant temperature zone of the fixed-bed reactor. Methyl ester passes through a reactor bed containing a palladium-based catalyst at a temperature of 150°C and a pressure of 0.5 MPa, and is oxidatively coupled to form dimethyl oxalate with a purity of more than 99%, which is used as a raw material for the subsequent decarbonylation reaction.
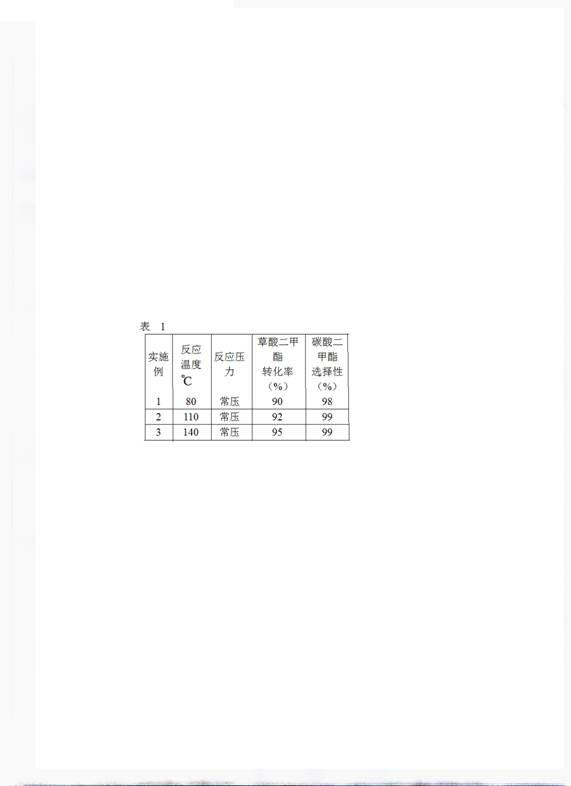
[0041] Decarbonylation reaction: take 100g decarbonylation catalyst PPh 4 Cl is placed in a stainless steel reaction kettle, 1000g of dimethyl oxalate is added, the temperature is raised to 140°C under normal pressure, and the temperature is kept at a constant temperature for 5 hours. The conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate and the selectivity of dimethyl carbonate, the results are shown in table 1.
[0042]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com