Preparation method of low-oxygen MHC alloy and application of low-oxygen MHC alloy
A technology of alloying and mixing raw materials, applied in metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, non-light-emitting electrode manufacturing and other directions, can solve the problem of high oxygen content in MHC alloys, and achieve the effects of strong normal temperature toughness, remarkable strengthening effect and stable performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
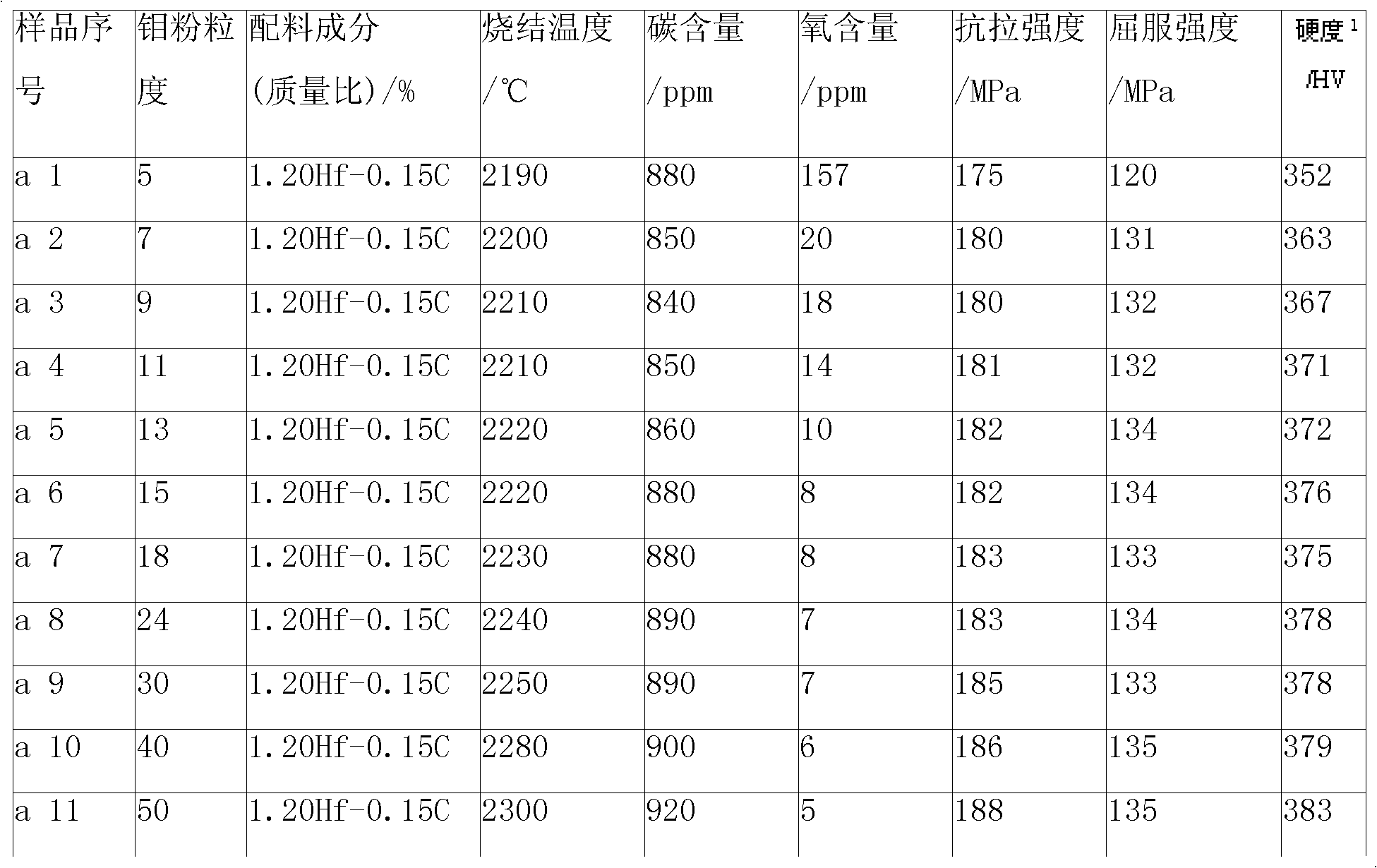
Embodiment a
[0027] 1) Raw material selection
[0028] Take the industrial molybdenum powder with the Fischer particle size of 5 μm, 7 μm, 9 μm, 11 μm, 13 μm, 15 μm, 18 μm, 24 μm, 30 μm, 40 μm, and 50 μm, and the hafnium hydride powder with the Fischer particle size of 3 μm to 10 μm, and the Fischer particle size of 0.1 μm ~3 μm carbon black. The added mass of hafnium hydride powder is 1.20%, the added mass of carbon black powder is 0.15%, and the rest is molybdenum powder. Mix the selected molybdenum powder, hafnium hydride powder and carbon black powder evenly.
[0029] 2) Raw material molding
[0030] The raw materials uniformly mixed in the step 1) are subjected to static pressure molding under a pressure of 220 MPa to 300 MPa to obtain a blank, and the size of the blank is Φ120mm×130mm.
[0031] 3) Raw material sintering
[0032] Sinter the shaped billet in a hydrogen protective atmosphere. The sintering temperature is shown in the table below. The size of the billet after sinteri...
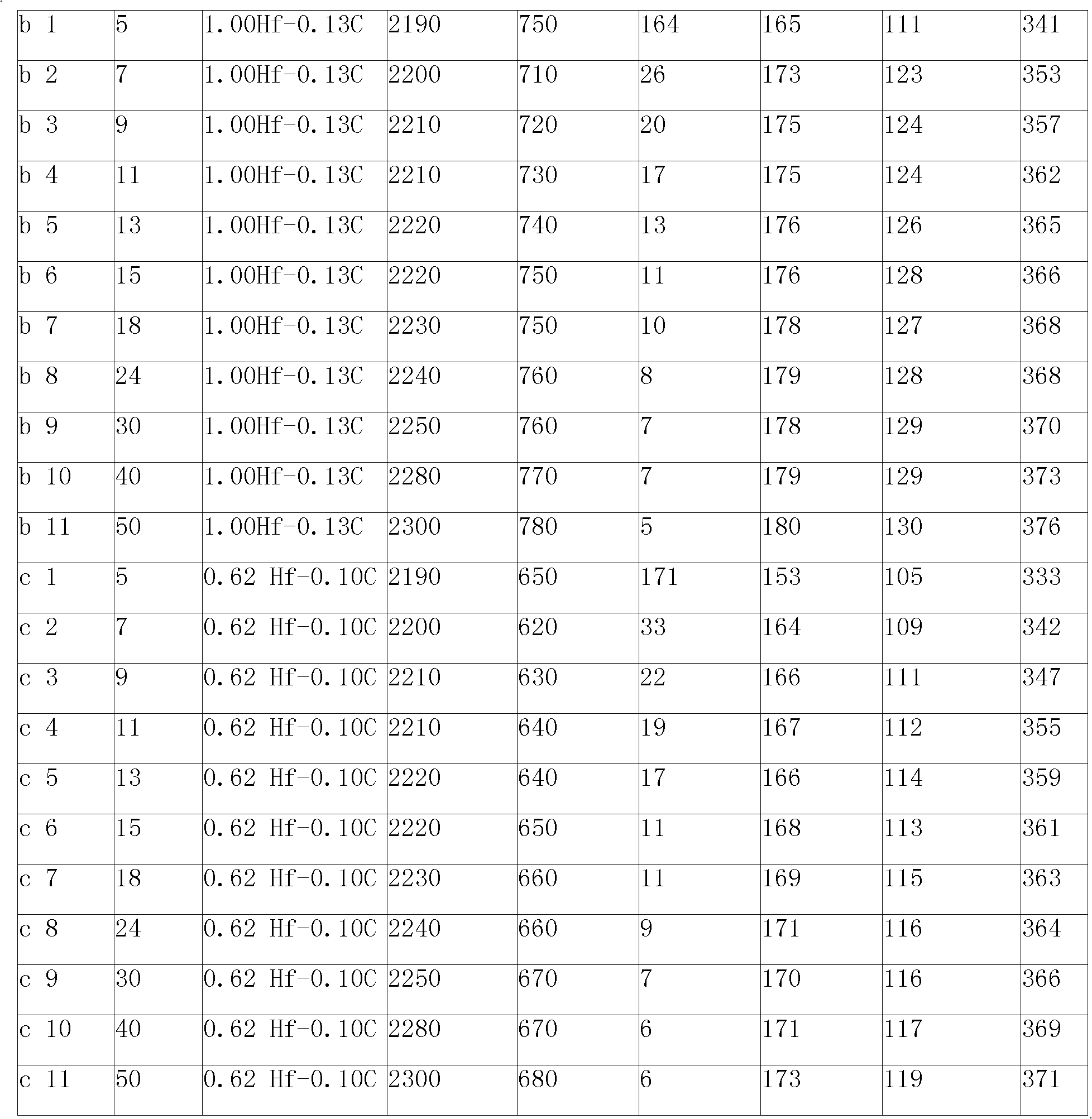
Embodiment b
[0035] 1) Raw material selection
[0036] Take the industrial molybdenum powder with the Fischer particle size of 5 μm, 7 μm, 9 μm, 11 μm, 13 μm, 15 μm, 18 μm, 24 μm, 30 μm, 40 μm, and 50 μm, and the hafnium hydride powder with the Fischer particle size of 3 μm to 10 μm, and the Fischer particle size of 0.1 μm ~3 μm carbon black. The added mass of hafnium hydride powder is 1.00%, the added mass of carbon black powder is 0.13%, and the rest is molybdenum powder. Mix the selected molybdenum powder, hafnium hydride powder and carbon black powder evenly.
[0037] 2) Raw material molding
[0038] The raw materials uniformly mixed in the step 1) are subjected to static pressure molding under a pressure of 220 MPa to 300 MPa to obtain a blank, and the size of the blank is Φ120mm×130mm.
[0039] 3) Raw material sintering
[0040] Sinter the shaped billet in a hydrogen protective atmosphere. The sintering temperature is shown in the table below. The size of the billet after sinteri...
Embodiment c
[0043] 1) Raw material selection
[0044] Take the industrial molybdenum powder with the Fischer particle size of 5 μm, 7 μm, 9 μm, 11 μm, 13 μm, 15 μm, 18 μm, 24 μm, 30 μm, 40 μm, and 50 μm, and the hafnium hydride powder with the Fischer particle size of 3 μm to 10 μm, and the Fischer particle size of 0.1 μm ~3 μm carbon black. The added mass of hafnium hydride powder is 0.62%, the added mass of carbon black powder is 0.10%, and the rest is molybdenum powder. Mix the selected molybdenum powder, hafnium hydride powder and carbon black powder evenly.
[0045] 2) Raw material molding
[0046] The raw materials uniformly mixed in the step 1) are subjected to static pressure molding under a pressure of 220 MPa to 300 MPa to obtain a blank, and the size of the blank is Φ120mm×130mm.
[0047] 3) Raw material sintering
[0048] Sinter the shaped billet in a hydrogen protective atmosphere. The sintering temperature is shown in the table below. The size of the billet after sinteri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com