Bicomponent fibers, textile sheets and use thereof
A bicomponent fiber and sheet technology, applied in textile, textile and papermaking, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of narrow bonding temperature window of PLA fiber, loss of biodegradability or compostability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] By melt spinning bicomponent fibers with a core-shell structure and forming a basis weight of 15 g / m in a pilot plant 2 spunbonded materials to produce nonwovens. The weight of the core is 75% and that of the shell is 25%. The core is made of PLA and the shell is made of polypropylene. The core contained 10% by weight calcium carbonate (Omyalene 102M), based on the weight of the core. The shell contained 3% by weight of biodegradation enhancing adjuvant (Addiflex HE), based on the weight of the shell.
Embodiment 2
[0073] According to the operation of embodiment 1, but production basis weight is 26g / m 2 of spunbond.
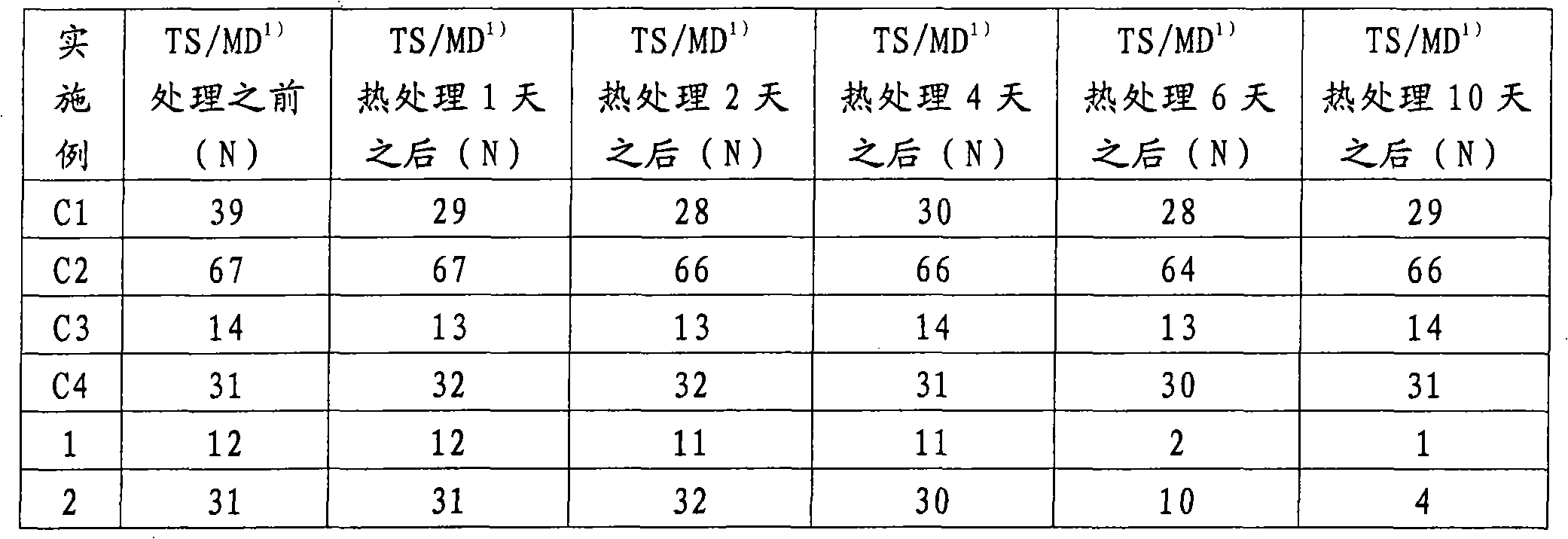
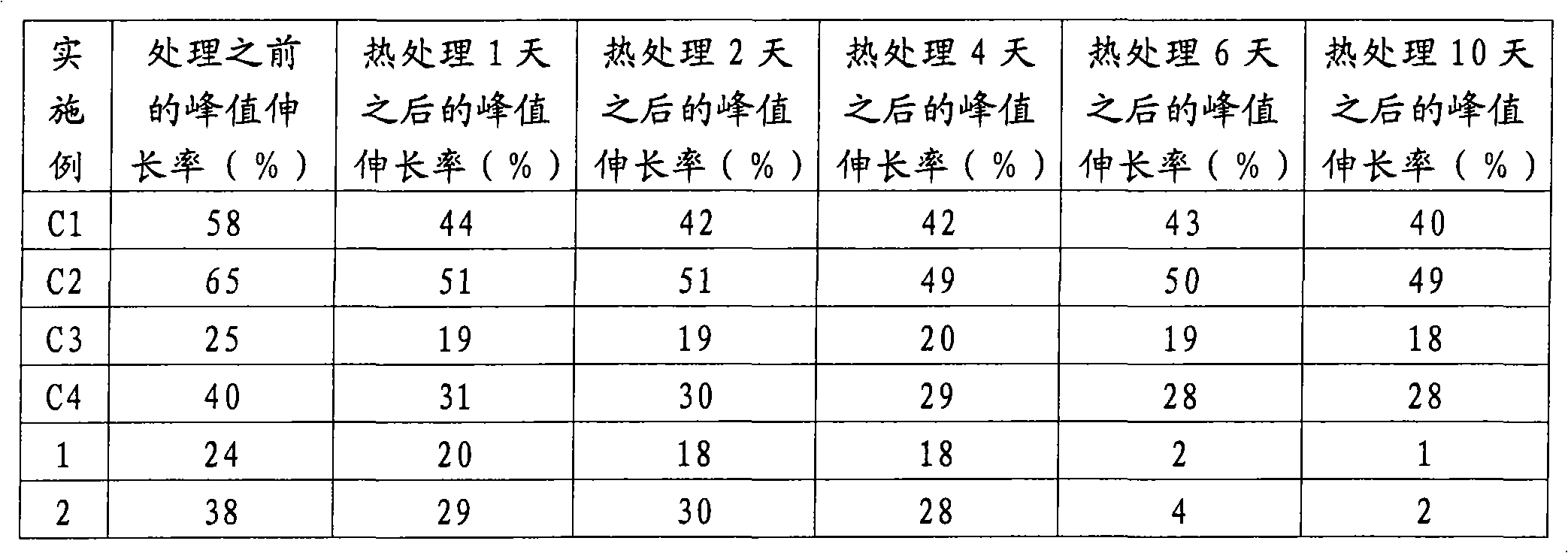
[0074] Details of the spunbonds produced in Comparative Examples 1-4 and Examples 1-2 are summarized in the table below.
[0075] Example
nuclear additive 1) (%b.wt.)
shell material
shell additive 2) (%b.wt.)
Basis weight g / m 2
C1
PLA
-
PP
-
15
C2
PLA
-
PP
-
26
C3
PLA
PP
-
15
C4
PLA
PP
-
26
1
PLA
PP
Degradation Accelerator (3)
15
2
PLA
PP
Degradation Accelerator (3)
26
[0076] 1) Omyalene 102M (Omya)
[0077] 2) Addiflex HE(Add-X)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com