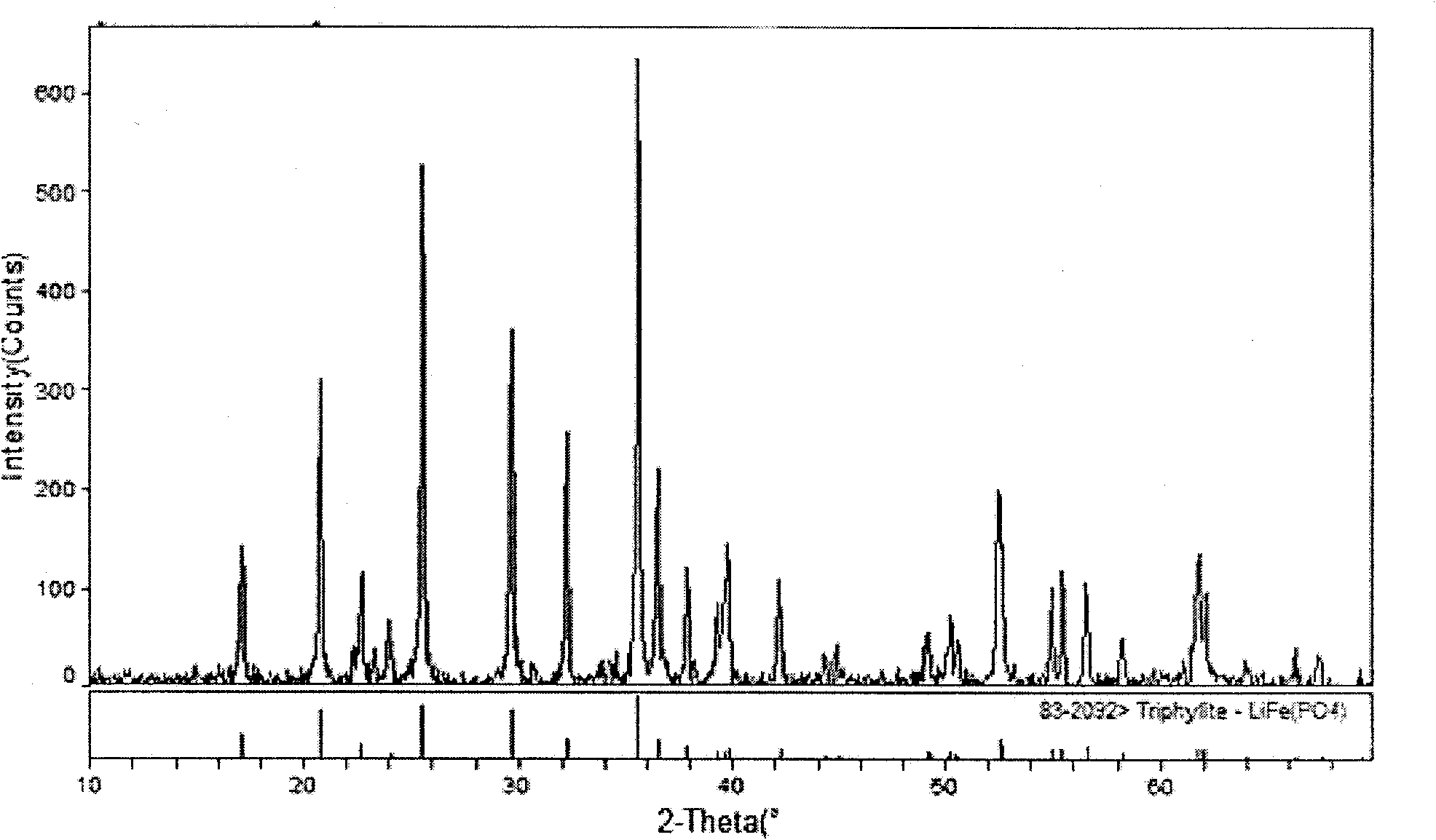
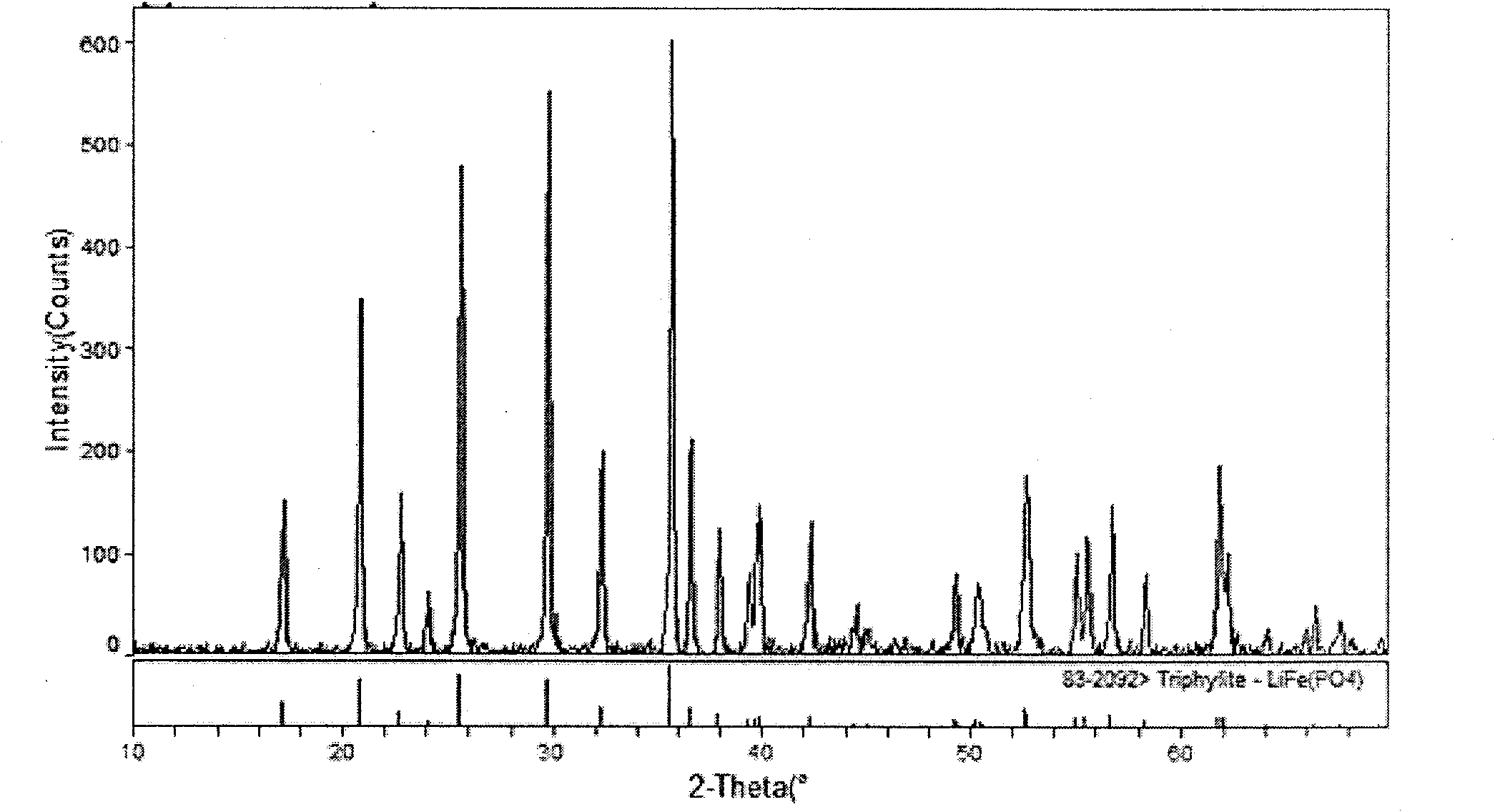
Method for preparing sub-micrometer lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4)
A lithium iron phosphate, sub-micron technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of increased lithium iron phosphate trivalent iron content, danger, difficulty in process operation, etc., to achieve environmental benefits. protection, excellent electrochemical performance, and the effect of improving economic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] In this example, LiFePO 4 and LiFePO 4 The processing steps of the / C preparation method are as follows:
[0038] (1) Ingredients to synthesize LiFePO 4
[0039] Iron source: FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 55.61 grams or 0.2 mol of iron;
[0040] Phosphorus source: (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 26.40 grams or 0.2 mol of phosphorus;
[0041] Lithium source: LiOH·H 2 O 7.98 grams or lithium 0.19mol;
[0042] Compounds containing dopant ions: NH 4 VO 3 1.17 grams is the doping ion vanadium 0.01mol
[0043] The operation is:
[0044] FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O plus 50mL deionized water to prepare iron source solution, LiOH·H 2 O adds 50mL deionized water to be mixed with lithium source solution, (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 and NH 4 VO 3 Add 150mL of deionized water to prepare phosphorus and doping ion source solution, then drop the phosphorus and doping ion source solution into the lithium source solution at room temperature, normal pressure, and stir, and then add the iron source solution to the lithium ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] In this example, LiFePO 4 and LiFePO 4 The processing steps of the / C preparation method are as follows:
[0051] (1) Ingredients to synthesize LiFePO 4
[0052] Iron source: FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 55.61 grams or 0.2 mol of iron;
[0053] Phosphorus source: (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 26.40 grams or 0.2 mol of phosphorus;
[0054] Lithium source: LiOH·H 2 O 7.55 grams or lithium 0.18mol;
[0055] Compounds containing dopant ions: MgSO 4 · 7H204.94g is doped ion magnesium 0.02mol
[0056] Organic solvent: ethylene glycol 200mL.
[0057] The operation is basically the same as that of Example 1, except that the timing is started when the reaction temperature reaches 190° C., and the temperature is kept at 190° C. for 10 hours.
[0058] (2) Calcination
[0059] The LiFePO prepared in step (1) 4 Weigh 20 grams, add 2 grams of sucrose, and use a ball mill to grind LiFePO 4 Mix well with sucrose, then LiFePO 4 The mixture with sucrose was placed in a tube furnace and heated to 6...
Embodiment 3
[0061] In this example, LiFePO 4 and LiFePO 4 The processing steps of the / C preparation method are as follows:
[0062] (1) Ingredients to synthesize LiFePO 4
[0063] Iron source: Fe(Ac) 2 4H 2 O 46.74 grams or iron 0.19mol;
[0064] Phosphorus and lithium sources: LiH 2 PO 4 10.393 grams, that is, 0.2 mol of phosphorus and 0.2 mol of lithium;
[0065] Compounds containing dopant ions: Mn(Ac) 2 4H 2 O 2.45 grams that is doped ion manganese 0.01mol
[0066] Organic solvent: tetraethylene glycol 250mL.
[0067] The operation is:
[0068] Fe(Ac) 2 4H 2 O and Mn(Ac) 2 4H 2 O is added 50mL deionized water to prepare iron source and doping ion source solution, LiH 2 PO 4 Add 100mL deionized water to be mixed with lithium source solution, iron source-doping ion source solution and lithium source solution are added in 250mL tetraethylene glycol under stirring to form the mixed solution containing lithium, iron, phosphorus and dopant ion; The stirring speed was set...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tap density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com