Manufacturing method and mould of tissue engineering tubular scaffold with hierarchical porous structure
A tissue engineering and production method technology, which is applied in the production and mold fields of tissue engineering tubular stents with multi-level pore structure, can solve unseen problems and achieve the effects of small batch difference, low cost and good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
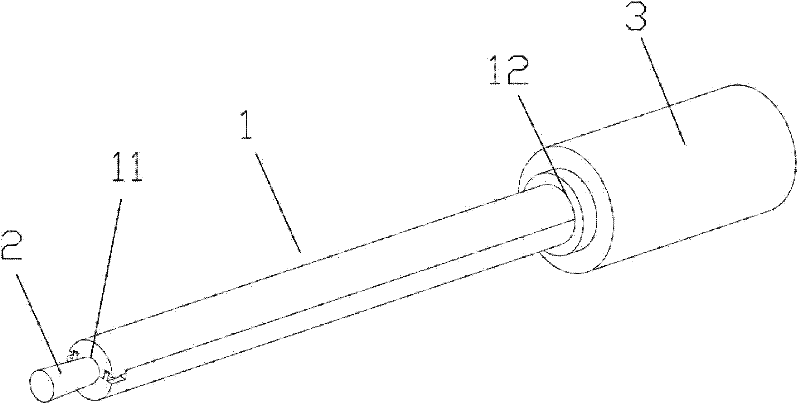
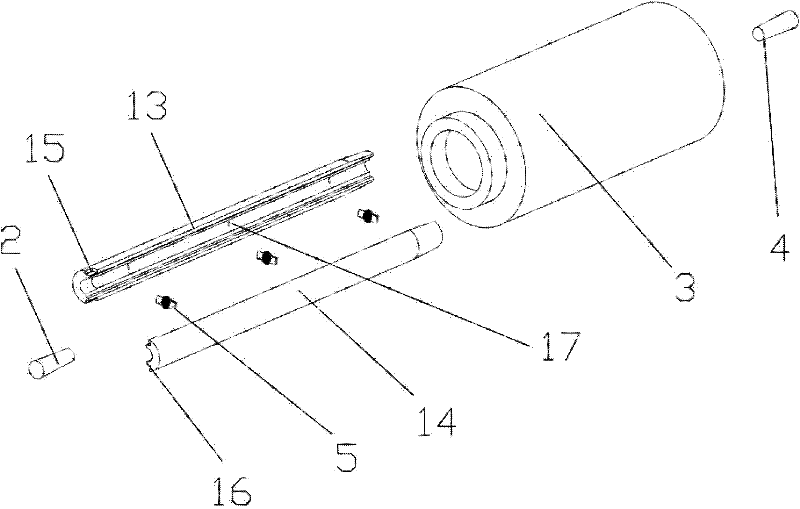
[0045] The mold for preparing tissue engineering tubular scaffolds of the present invention has a simple structure, and is easy to manufacture and use; it has wide adaptability to raw materials; Bracket; Secondly, because the outside of the cavity is a circular tube with uniform wall thickness, the mold body is isotropic in cross section, and has high sensitivity to temperature selection, temperature change range and trend, and heat transfer direction. Good adaptability, controllability, and small batch differences; in addition, the internal setting of the orifice plate with a gap at the edge, the material and size parameters of each component of the mold, and the distribution of grooves on the inner cavity for fixing the orifice plate , The distribution of holes and gaps on the orifice plate and the number of orifice plates can be adjusted according to the application requirements, and the scalability is good.
[0046] A method for making a tissue engineering tubular support wi...
Embodiment 1
[0060] a) dissolving L-polylactic acid in tetrahydrofuran to prepare a solution with a mass volume concentration of 20 mg / mL;
[0061] b) Assemble the mold and place it in a temperature environment of 50°C so that there is no temperature difference between the various parts of the mold;
[0062] c) injecting the polymer solution into the mold, cooling to 20°C, and quenching after the polymer solution in the mold cavity becomes gel;
[0063] d) Demoulding, soaking in a large amount of water at 4° C. for 3 days, and freeze-drying to obtain a tubular scaffold of L-polylactic acid tissue engineering with a nanofiber microstructure.
Embodiment 2
[0065] a) dissolving polycaprolactone in ethyl acetate to prepare a polymer solution with a mass volume concentration of 40 mg / mL;
[0066] b) Assemble the mold and place it in a temperature environment of 0°C so that there is no temperature difference between the various parts of the mold;
[0067] c) The volume added to the cavity of the mold is about 2mm 3 The sodium chloride needle crystal porogen;
[0068] d) injecting the polymer solution into the mold, cooling to -90°C, and quenching after the polymer solution in the mold cavity is solid;
[0069] e) Demoulding, high vacuum freeze-drying to remove ethyl acetate, water to filter out the sodium chloride porogen, and freeze-drying again to obtain an internal volume of about 2mm 3 Needle-like Microporous Polycaprolactone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com