Pb-free solder compositions and PCB and electronic device using same
A printed circuit board, lead-free solder technology, applied in the directions of printed circuit, printed circuit manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the basic performance of solder, i.e. decrease in bondability, increase the influence of slag and discoloration, increase melting temperature and other problems , to achieve the effect of improving bondability, improving mechanical properties and preventing oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0065] This embodiment provides a lead-free solder composition and a PCB and an electronic device using the lead-free solder composition, the composition includes silver from 0.1wt%-4.0wt%, copper from 0.1wt%-2wt%, 0.001wt%-0.05wt% of silicon, 0.001wt%-0.01wt% of cobalt, and the balance of tin.
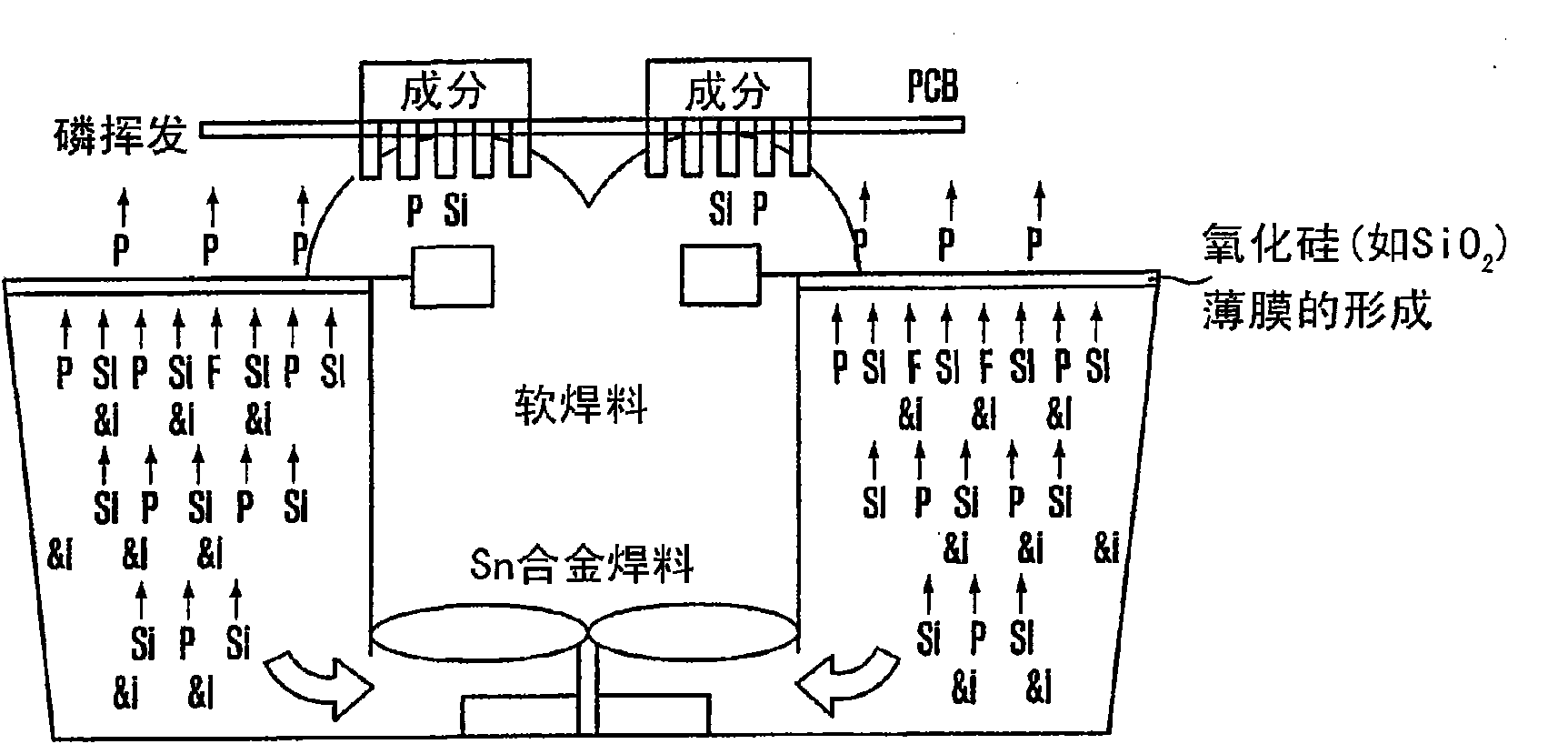
[0066] The following will refer to figure 1 Explain the role of the composition of silicon and cobalt in preventing oxidation.
[0067] figure 1
[0068]
[0069] (Amount of oxidation: amount of oxide; oxidation rate: oxidation rate; comparative example: comparative example; example: embodiment; after 1 hour: after 1 hour; after 2 hours: after 2 hours; after 3 hours: after 3 hours.)
[0070] figure 1 Experimental data of the amount of oxides measured by the following method are exemplified. Silicon and cobalt are added to the intended base alloy. The resulting alloy is melted to make a solder composition. The solder composition was heated to 260° C. on a hot plate in a 160 m...
Embodiment 2
[0318] The high temperature lead-free solder compound according to the present embodiment may include tin (Sn), copper (Cu), silicon (Si), and cobalt (Co).
[0319] The effect of the silicon and cobalt components on the prevention of oxidation will be described below with reference to FIG. 16 .
[0320] Figure 16 illustrates experimental data for the amount of oxides measured by the following procedure. A tin-copper based alloy is prepared and co-melted with either or both silicon and cobalt in a high frequency melting furnace to form a solder compound. After sampling the solder compound, its melting temperature was measured using DSC analysis at 5°C / min. Thereafter, in order to measure the amount of oxide, 3 kg of solder was heated to 420° C. in a SUS crucible having a diameter of 160 mm on a hot plane. Then, the solder compound was stirred at 60 rpm using a stirrer having a diameter of 140 mm for 1 hour, 2 hours, and 3 hours, and oxides were extracted therefrom each time a...
Embodiment 3
[0399] The lead-free solder compound for dilution according to the present embodiment may include nickel (Ni), silicon (Si), phosphorus (P), cobalt (CO), and tin (Sn).
[0400] The effect of the silicon and cobalt components on preventing oxidation will be described below with reference to FIG. 20 .
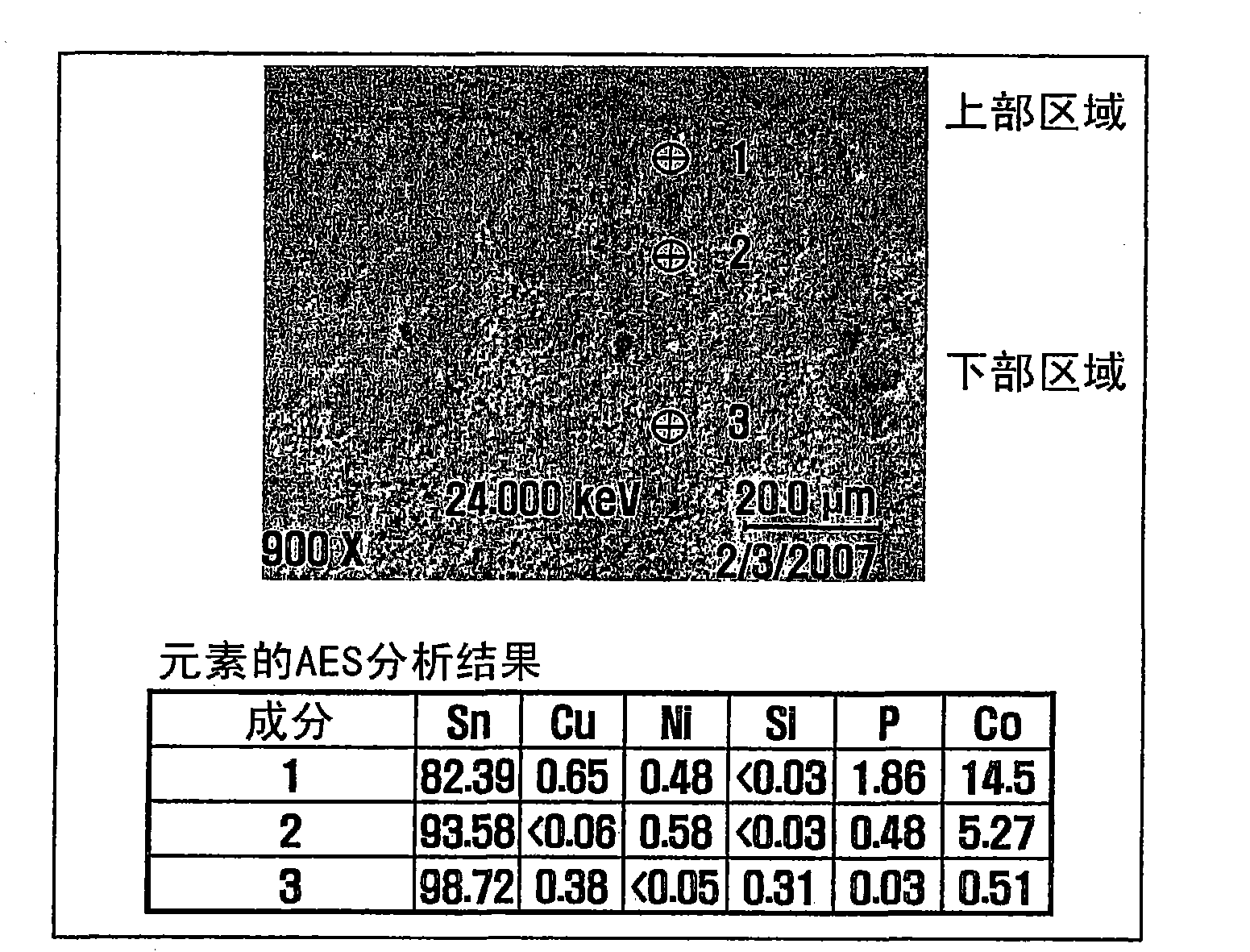
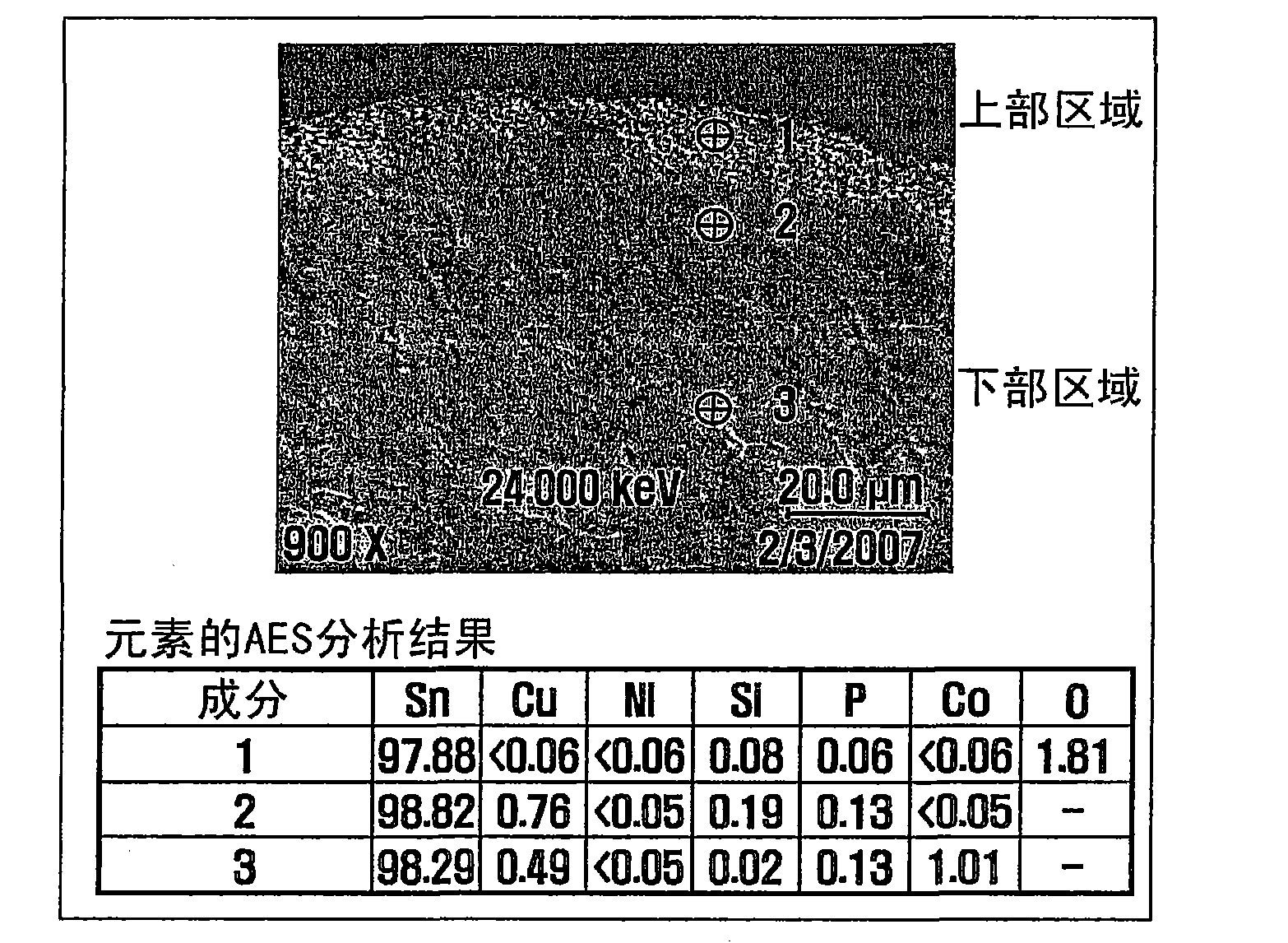
[0401] Figure 20 illustrates experimental data for the amount of oxides measured by the following procedure. Silicon and cobalt are added to the Sn-Ni-P based alloy. The resulting alloy is melted to produce a solder compound. On a hot plane, the solder compound was heated to 260° C. in a SUS crucible with a diameter of 160 mm. Then, the solder compound was stirred at 60 rpm using a stirrer having a diameter of 140 mm for 1 hour, 2 hours, and 3 hours, and oxides were extracted therefrom each time and weighed.
[0402] Thereafter, the solder was allowed to solidify, and then a solder sample was cut from the solder. Polish the cut surface of the solder sample. Then, the composi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com