Method for extracting tungsten trioxide and molybdenum trioxide by pretreating tungsten-molybdenum concentrates with concentrated acid
A technology of tungsten trioxide and molybdenum trioxide, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of failure to achieve the leaching purpose, large loss of tungsten and molybdenum, low tungsten grade, etc., and achieves a short process, high recovery rate and simple process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
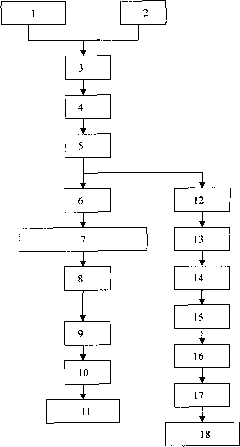
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: the present invention makes MoO 3 The technological process includes four steps of concentrated acid pretreatment, leaching, molybdenum precipitation, and roasting. The process is as follows:
[0021] A. Concentrated acid pretreatment: In an acid-resistant enamel kettle, put 100kg of tungsten-molybdenum ore powder containing 3.5% molybdenum and 3.5% tungsten trioxide, and add 1.5-3.5 times the theoretical amount of acid to completely react with the contained calcium molybdate. Concentrated acid (HCl or HNO 3 ) or mixed acid, stir evenly, and pretreat at room temperature for 0.5-2.5 hours.
[0022] B. Leaching: After the mineral powder is pretreated with concentrated acid, the solid-to-liquid ratio is controlled at 1:2, the pH value of the solution is 0.1-0.5, the reaction temperature is 15°C-95°C, and the reaction time is 0.5h-5.5h. After the reaction, the solid and liquid were separated, and the solid obtained was 36 kg of tungsten concentrate with impr...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: This invention makes MoO 3 The process includes four steps of concentrated acid pretreatment, leaching, molybdenum precipitation, and roasting. The process is as follows:
[0027] A. Concentrated acid pretreatment: Put 100kg of tungsten-molybdenum ore powder containing 8% molybdenum and 8% tungsten trioxide into an acid-resistant enamel kettle, and add a little water to moisten the ore powder. Add concentrated acid (HCl or HNO) that is 1.5 to 2.5 times the theoretical amount of acid and calcium molybdate reaction 3 ) or mixed acid, stirred evenly, and pretreated at room temperature for 1.5h.
[0028] B. Leaching: After concentrated acid pretreatment, control the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3, adjust the pH value of the solution to 0.25, the reaction temperature is 50-85°C, and the reaction time is 4h. After the reaction, the solid and liquid were separated, and the solid obtained was 34 kg of tungsten concentrate with improved grade, the liquid contained ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: This invention makes MoO 3 The process mainly includes four steps of concentrated acid pretreatment, leaching, molybdenum precipitation and roasting. The process flow is as follows:
[0033] A. Concentrated acid and pretreatment: Put 100kg of tungsten-molybdenum ore powder containing 12% molybdenum and 12% tungsten trioxide into an acid-resistant enamel kettle, and add 2 to 4 times the theoretical amount of acid and calcium molybdate reaction while stirring. Concentrated acid (HCl or H 2 SO 4 ) or mixed acid, pretreatment for 1.5h after adding concentrated acid.
[0034] B. Leaching: After concentrated acid pretreatment, control the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3.5, adjust the pH of the solution to 0.1, the reaction temperature is 70°C, and the reaction time is 6h. Stirring, solid-liquid separation after leaching, the obtained solid is 33kg of tungsten concentrate with improved grade, the liquid contains 34.1g / L of molybdenum, and the molybdenum leaching ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com