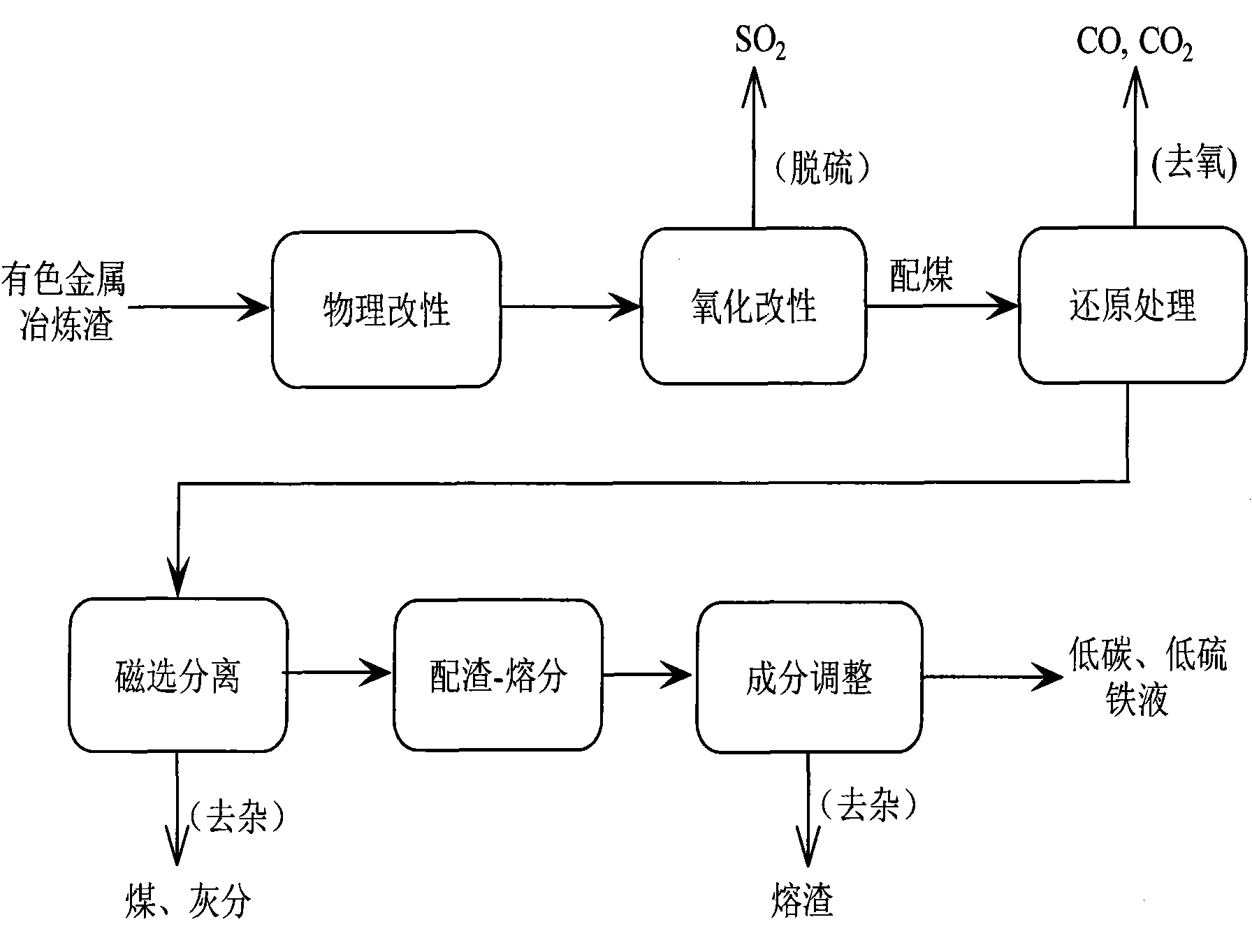
Method for extracting valuable elements from slag of melted high-iron high-silicon nonferrous metal
A technology of non-ferrous metals and valuable elements, applied in the field of metallurgical materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
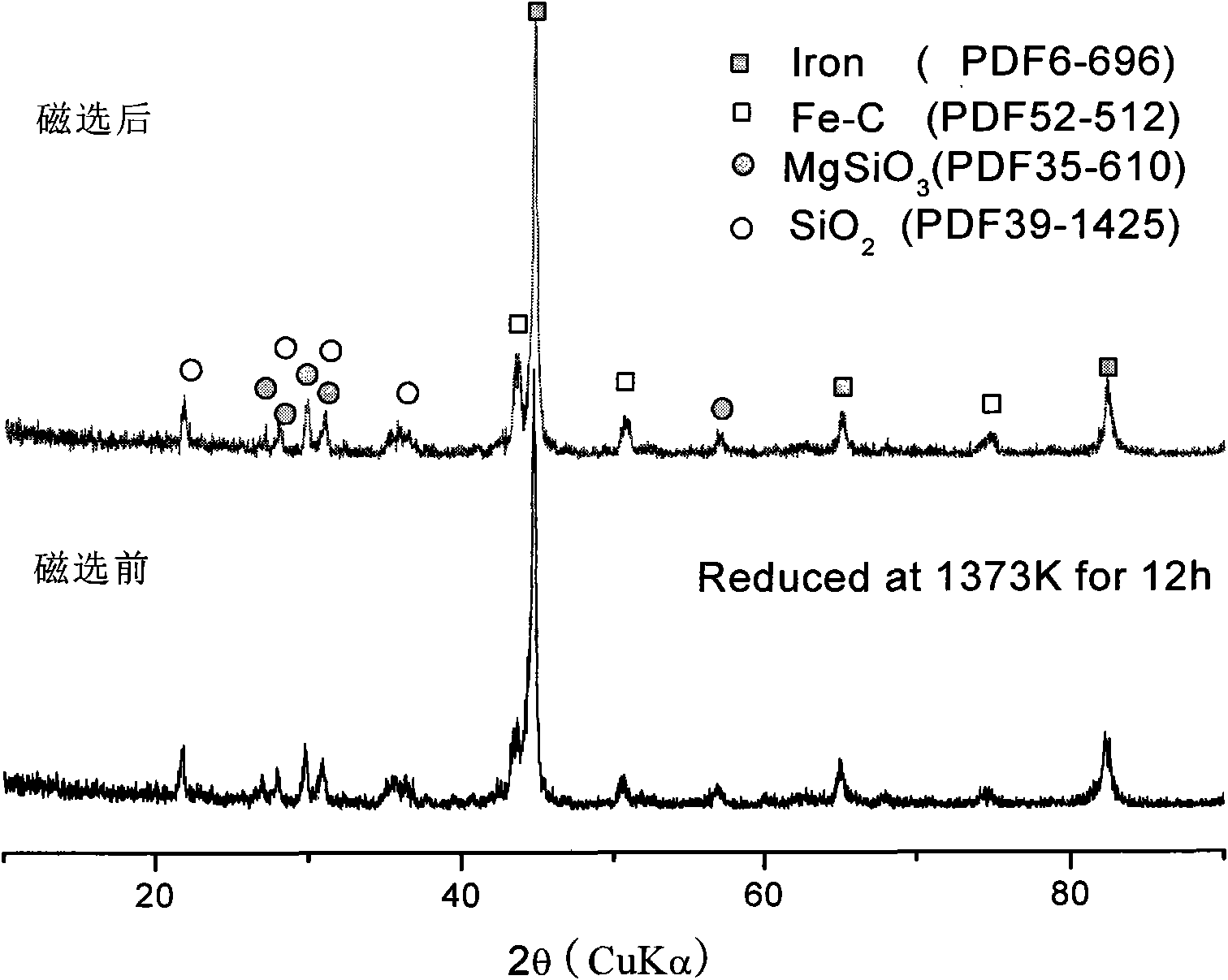
[0040] Choose a non-ferrous metal smelting slag, its chemical composition is shown in Table 1. Take 2kg of non-ferrous metal smelting slag, break it into a particle size smaller than 0.074mm for physical modification; put it into a φ120×160mm corundum crucible, pass air from the bottom at a flow rate of 1L / min in the resistance furnace, and carry out chemical modification at 1373K. The XRD curve after chemical modification for 5h, such as figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that fayalite is almost completely converted into hematite and quartz.
[0041] Take the non-ferrous smelting slag after chemical modification, grind and mix in the sample maker for 5 minutes after coal blending, the coal blending ratio is based on the theoretical oxygen content of valuable elements: carbon blending amount = 1: 1.1 (atomic ratio), and put it into φ120× Put the 160mm corundum crucible into the resistance furnace for reduction treatment. In order to prevent surface oxidation from burying a su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com