A kind of forensic medicine diatom test method
An inspection method and a forensic technology, applied in the field of forensic inspection, can solve the problems of increasing centrifugal speed, polluting the environment, and missing detection of micro diatoms, and achieve the effects of improving the recovery rate, simplifying the processing process, and reducing the loss of diatoms.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment one, experimental embodiment of the present invention
[0045] 1. Experimental materials and equipment
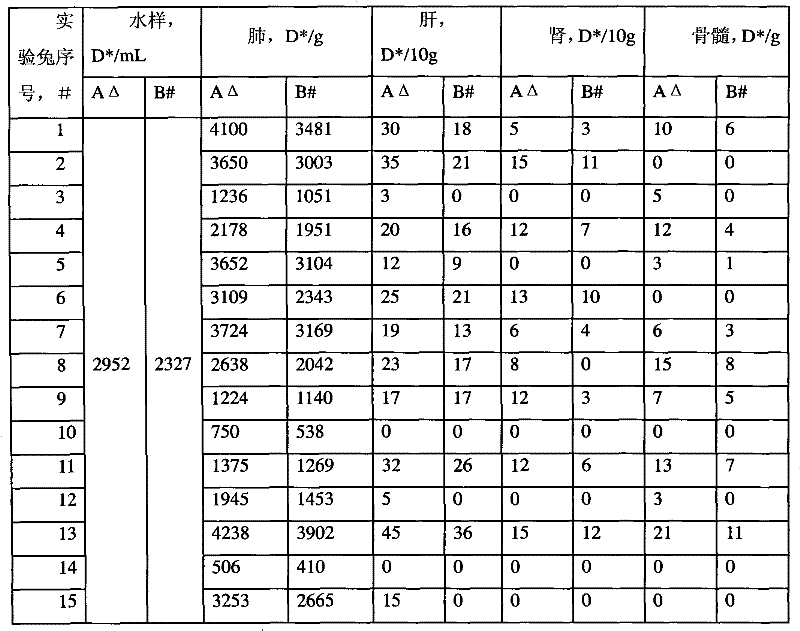
[0046] 30 New Zealand white rabbits, male or female, weighing 1.0-3.0 kg, were provided by the Animal Experiment Center of Guangdong Province, and were randomly divided into two groups: drowning group (n=15) and postmortem submersion group (n=15). The central location of Haizhu Bridge in Guangzhou City on the Pearl River was selected as the experimental site. Put the rabbits in the drowning group in a rabbit cage, sink them into the water at 0.5m, lift them out of the water after 1min, and sink them back into the same water depth after 30s, repeat several times to slowly drown the white rabbits, soak them in water for 30min after death, and put them into the water after death The experimental rabbits in the group were killed by air embolism, placed in the same place and soaked at the same depth for 30 minutes, and then taken out. Extract the lung, liver,...
Embodiment 2
[0122] Typical criminal case 1: A 3-year-old girl named Xie disappeared, and her body was found in a cistern in a residential area 3 months later. Due to the high degree of corruption of the corpse, it is difficult to determine the cause of death and the nature of the case after the autopsy. The diatom test was digested by nitric acid ethanol method and observed by optical microscope. As a result, the same type of diatoms as in the reservoir was detected from the lungs, the content was 550 / 10g lung tissue, and the diatom test in liver and kidney tissues was negative. The MW-VF-Auto SEM method was used to detect the same type of diatoms from the lungs, liver, and kidneys of the deceased as in the water samples of the reservoir, and the contents were 720 / 10g lung tissue and 3 / 10g liver tissue respectively. , 2 / 10g kidney tissue, so the cause of death was diagnosed as drowning. Combined with other investigation results, it was finally confirmed that the deceased died by accident...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Typical criminal case 2: The victim Huang was kidnapped and extorted 1 million yuan. His highly decomposed body was found in a lake in the suburbs 10 days later. In order to confirm whether the deceased was thrown into the water before death or was thrown into the water after death, the lung, liver and kidney tissues were collected after autopsy and digested with nitric acid ethanol. , only the same type of diatoms as in the on-site water samples were detected in the lungs, the content was 2030 / 10g lung tissue, and the diatoms in the liver and kidney tissues were negative, so a clear diagnosis of drowning could not be made. Afterwards, the MW-VF-Auto SEM method was used to detect the same type of diatoms as the on-site water samples from the lungs and livers. The content of diatoms in the lung tissue was 2580 per 10g of lung tissue, and the content of diatoms in the liver tissue It was 5 / 10g liver tissue, and according to the conclusion of this test, the cause of death...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com