Application of nickel-molybdenum carbide in production of anode of microbial fuel cell
A fuel cell, nickel-molybdenum carbide technology, applied in biochemical fuel cells, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of strict conditions and complex preparation methods, and achieve the effects of short operation time, simple production process and strong stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Step 1: Catalyst Preparation
[0039] Nickel Molybdenum Carbide
[0040] 1. Mix molybdic acid and NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O (molar ratio Ni:Mo=1:3) was dissolved in ethylene glycol and stirred vigorously at 60°C until NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O is completely dissolved. Then, starch was added to the mixture at a molar ratio of Mo:C=1:3.5. When the starch is heated and dissolved, the solvent is stirred and concentrated into a viscous solvent at about 130°C, and then the viscous solvent is heated to 190°C to form matrix fragments.
[0041]2. The fragments were placed in a graphite boat and annealed in an alumina tube furnace at a temperature of 900°C, under the protection of Ar, and the annealing time was 2 hours. Cool to room temperature to obtain dark blue powder, which is nickel molybdenum carbide.
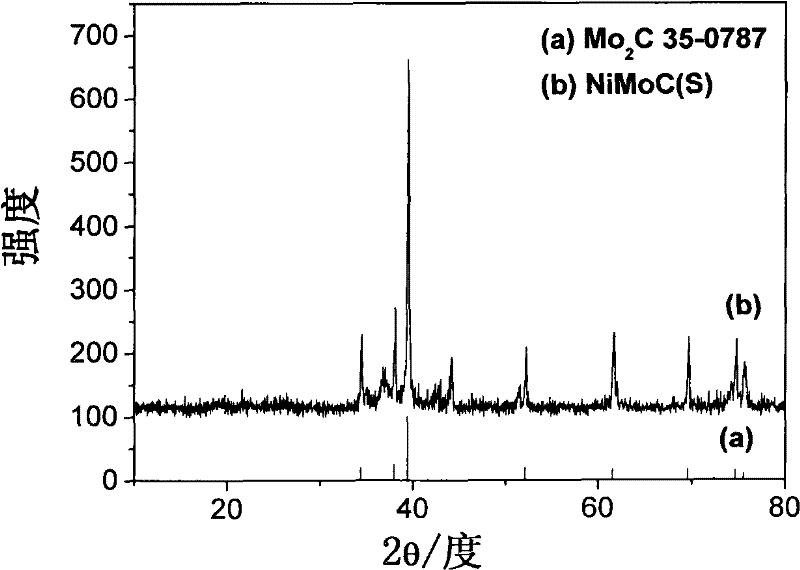
[0042] The comparison of the obtained nickel-molybdenum carbide sample (S) XRD pattern and the XRD standard collection of patterns (a) of molybdenum carbide is as follows figure 1 shown. ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Step 1: Catalyst Preparation
[0054] 1. Mix molybdic acid and NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O (Ni:Mo=1:3) was dissolved in ethylene glycol and stirred vigorously at 60°C until NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O is completely dissolved. Then, glucose was added to the mixture at a molar ratio of Mo:C=1:2 to prepare precursor G. After the glucose is heated and dissolved, the solvent is stirred and concentrated into a viscous solvent at about 130°C, and then the viscous solvent is heated to 190°C to form matrix fragments.
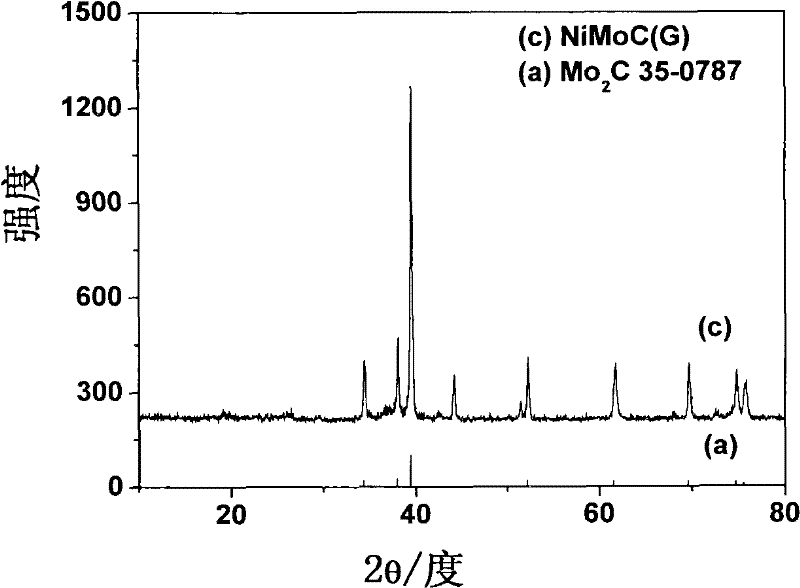
[0055] 2. The fragments were placed in a graphite boat and annealed in an alumina tube furnace at a temperature of 900°C, under the protection of Ar, and the annealing time was 2 hours. Cool to room temperature to obtain dark blue powder. The comparison of the XRD standard collection of illustrative plates (a) of the nickel-molybdenum carbide sample (G)XRD pattern and molybdenum carbide obtained is as follows figure 2 shown.
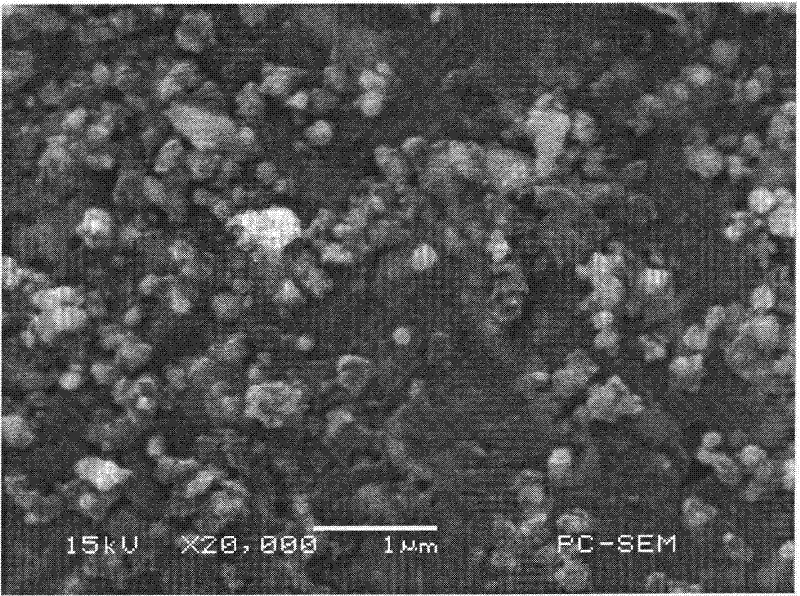
[0056] Step 2: Physical Characterization
[0057] Ste...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Step 1: Catalyst Preparation
[0069] 1. Mix molybdic acid and NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O (Ni:Mo=1:1) was dissolved in ethylene glycol and stirred vigorously at 80°C until NiCl 2 ·6H 2 O is completely dissolved. Then, sucrose was added to the mixture at a molar ratio of Mo:C=1:4 to prepare the precursor s. When the sucrose is heated and dissolved, the solvent is stirred and concentrated into a viscous solvent at about 100°C, and then the viscous solvent is heated to 150°C to form matrix fragments.
[0070] 2. The fragments are placed in a graphite boat and annealed in an alumina tube furnace at a temperature of 800°C, under the protection of Ar, and the annealing time is 4h. Cool to room temperature to obtain dark blue powder.
[0071] Step 2: Physical Characterization
[0072] Step is as embodiment 1
[0073] Step 3: Preparation of the base electrode
[0074] Step is as embodiment 1
[0075] Step 4: Preparation of Pt / C cathode
[0076] Step is as embodiment 1
[0077] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com