ELISA detection method of red-tide algae toxin okadaic acid (OA)
A red tide algae toxin and detection method technology, applied in the field of ELISA detection of red tide algae toxin halicic acid OA, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish the type and structure of the toxin, complex processing process, and inaccurate data, so as to reduce false positives, High sensitivity and good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: raw material preparation
[0025] The materials used in this example are OA standard (purchased from Taiwan Algae Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); coating antigen OA-OVA, OA monoclonal antibody, enzyme-labeled secondary antibody HRG-goat anti-mouse IgG (purchased from Shanghai Dingguo Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); newborn bovine serum, 1% gelatin, ovalbumin (OVA), bovine serum albumin (BSA), N-hydroxysuccinimide (N-hydroxysuccinimide), N, N dicycloethane carbon di Imine (N, N-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, DCC), N, N-dimethylformamide (N, N-dimethylformamide, DMF), polyethylene glycol (polythylene glycol-4000, PEG), Freund's complete adjuvant, Freund's incomplete adjuvant, tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), MES buffer, etc. were products of Sigma; SP2 / 0 myeloma cells (from Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, National Academy of Agricultural Sciences) ); the rest were domestic analytically pure.
[0026] Preparation of coating antigen OA-OVA:
[...
Embodiment 2
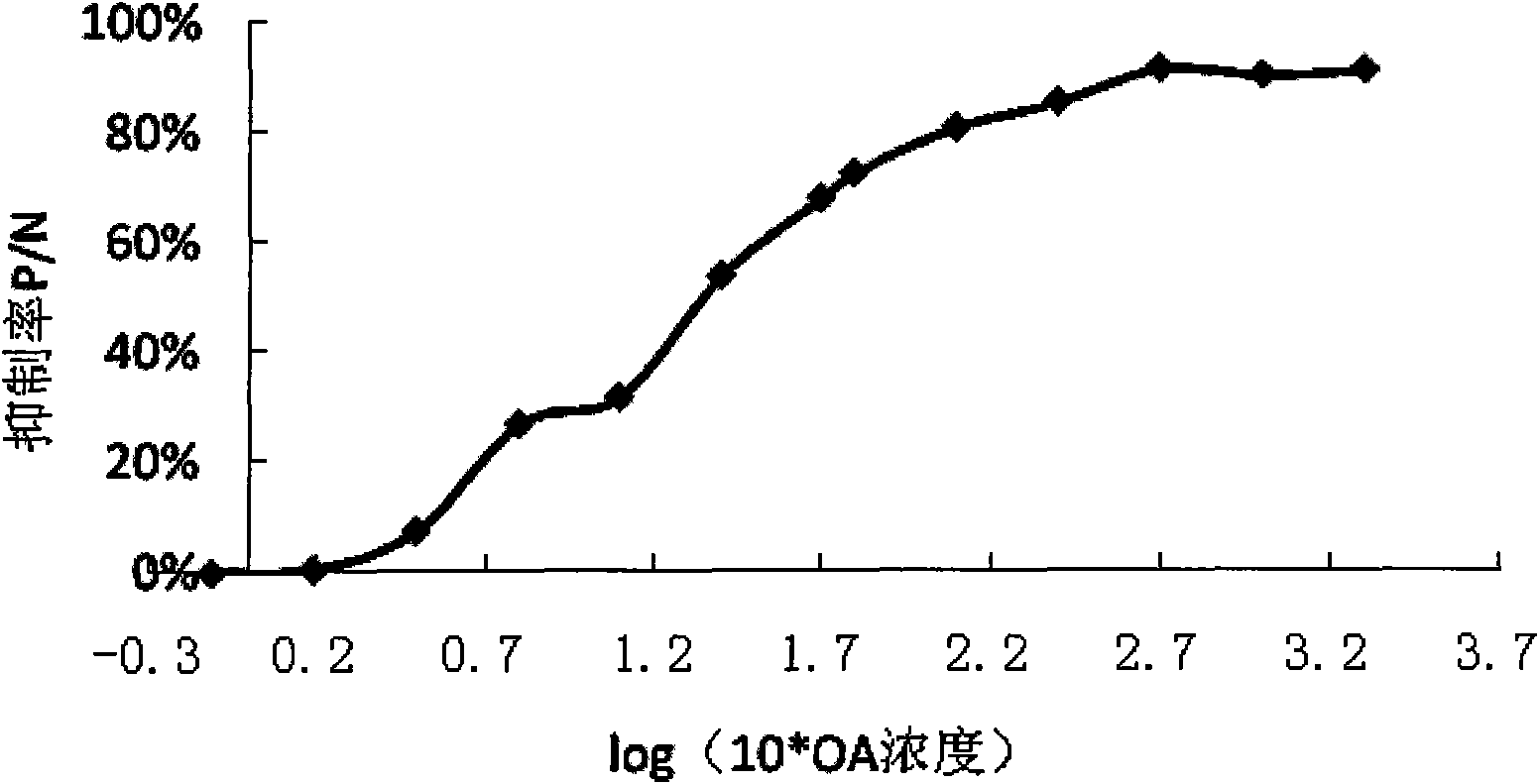
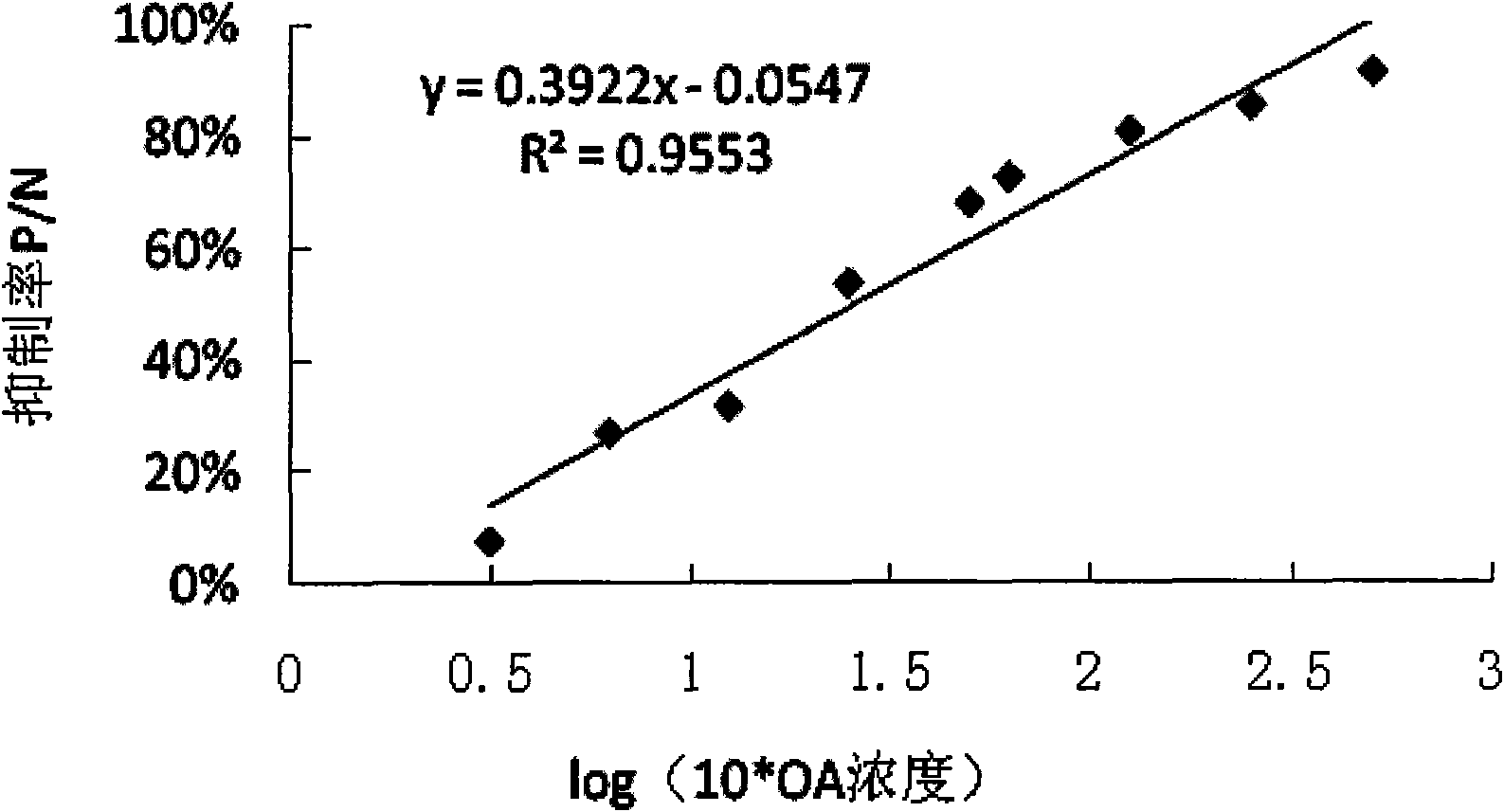
[0034] Example 2: Obtaining of OA indirect competition ELISA standard curve
[0035]The OA-OVA conjugate was used as the coated antigen, diluted with carbonate buffer to 1:2000, coated with 96-well microtiter plate, 100ul per well, overnight at 4°C; the residual solution was discarded and washed with phosphoric acid Wash the plate with salt buffer PBST (containing 0.05% Tween-20) 3 times, 200ul per hole, and then pat dry; seal the microplate plate with 1% gelatin, 150ul per hole, and incubate at 37°C for 2h; discard the blocking solution, wash plate, dilute the OA standard solution to 200, 100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 5, 2.5, 1.25, 0.625, 0.3125, 0.156, 0.078ng / ml, 0ng / ml (blank control) with PBST, respectively Shake and mix an equal volume of monoclonal antibody diluted at 1:10000, that is, the final dilution of monoclonal antibody is 1:20000, add 100ul to each well, and incubate at 37°C for 1h; discard the residual solution, wash the plate, and add ELISA II Antibody, diluted ac...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: ELISA detection of red tide algae toxin halicic acid OA
[0038] a. Sample processing:
[0039] Obtaining Shellfish Extract:
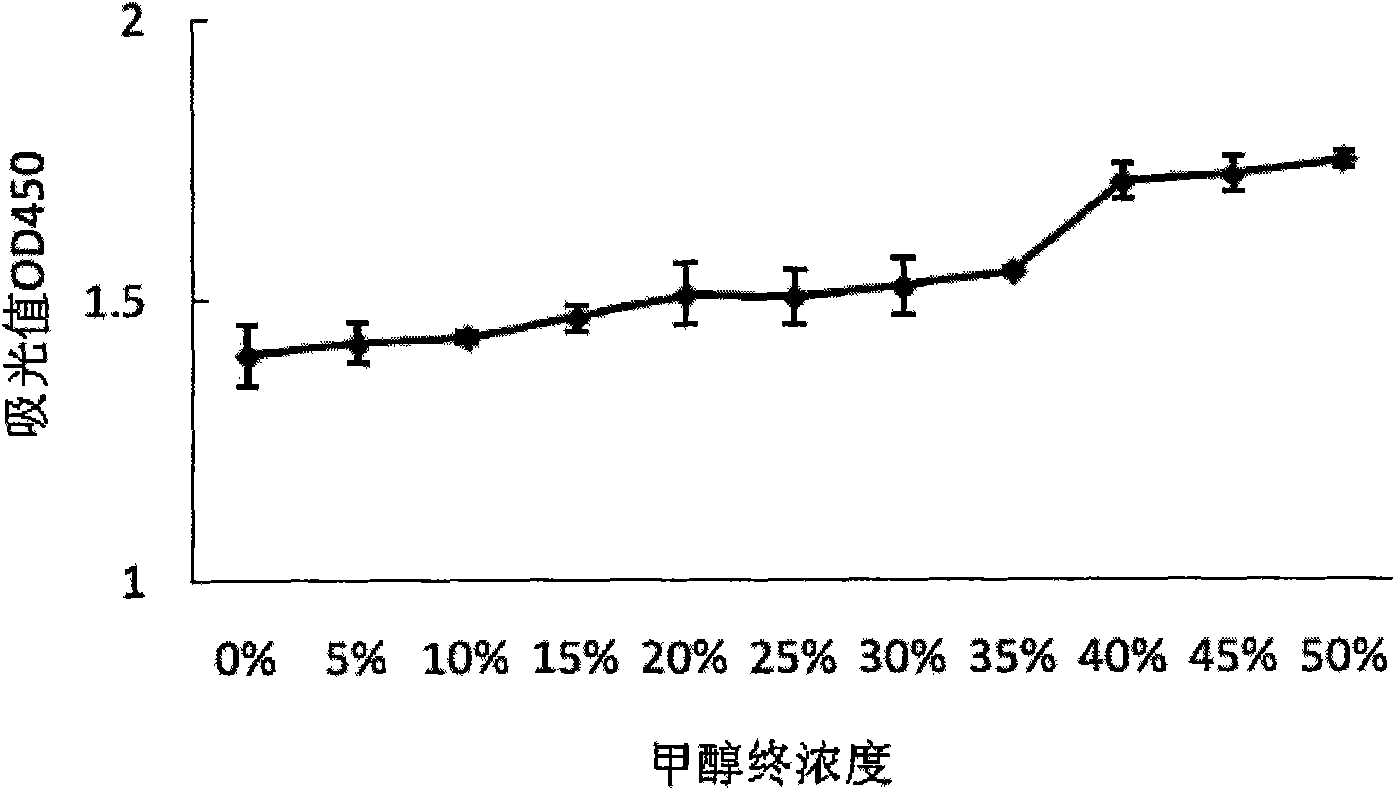
[0040] Clean the shellfish samples, remove impurities such as silt on the surface, drain after shelling, and homogenize the organisms with a high-speed dispersing homogenizer. Weigh 2 parts of homogenized shellfish meat samples, each 5g, place them in clean centrifuge tubes respectively, add weakly acidic methanol solution, add a certain amount of OA standard solution to one part, and not add to the other part (i.e. negative control). Centrifuge at 3500r / min for 10min, and take the supernatant. Add methanol and n-hexane to the supernatant in turn, vortex and mix well, and let the layers stand still. Then discard the n-hexane layer, evaporate to dryness on a rotary evaporator, then add a small amount of methanol to dissolve the attachment on the wall, and then evaporate to dryness. Finally, dissolve the residue with 100ul methanol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com