Resistive random access memory based on bismuth iron thin film system and manufacturing method thereof
A resistive random, bismuth ferrite technology, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve the problems of slow speed, high operating voltage, poor endurance, etc., and achieve good electro-resistance effect and stable resistance value , good stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
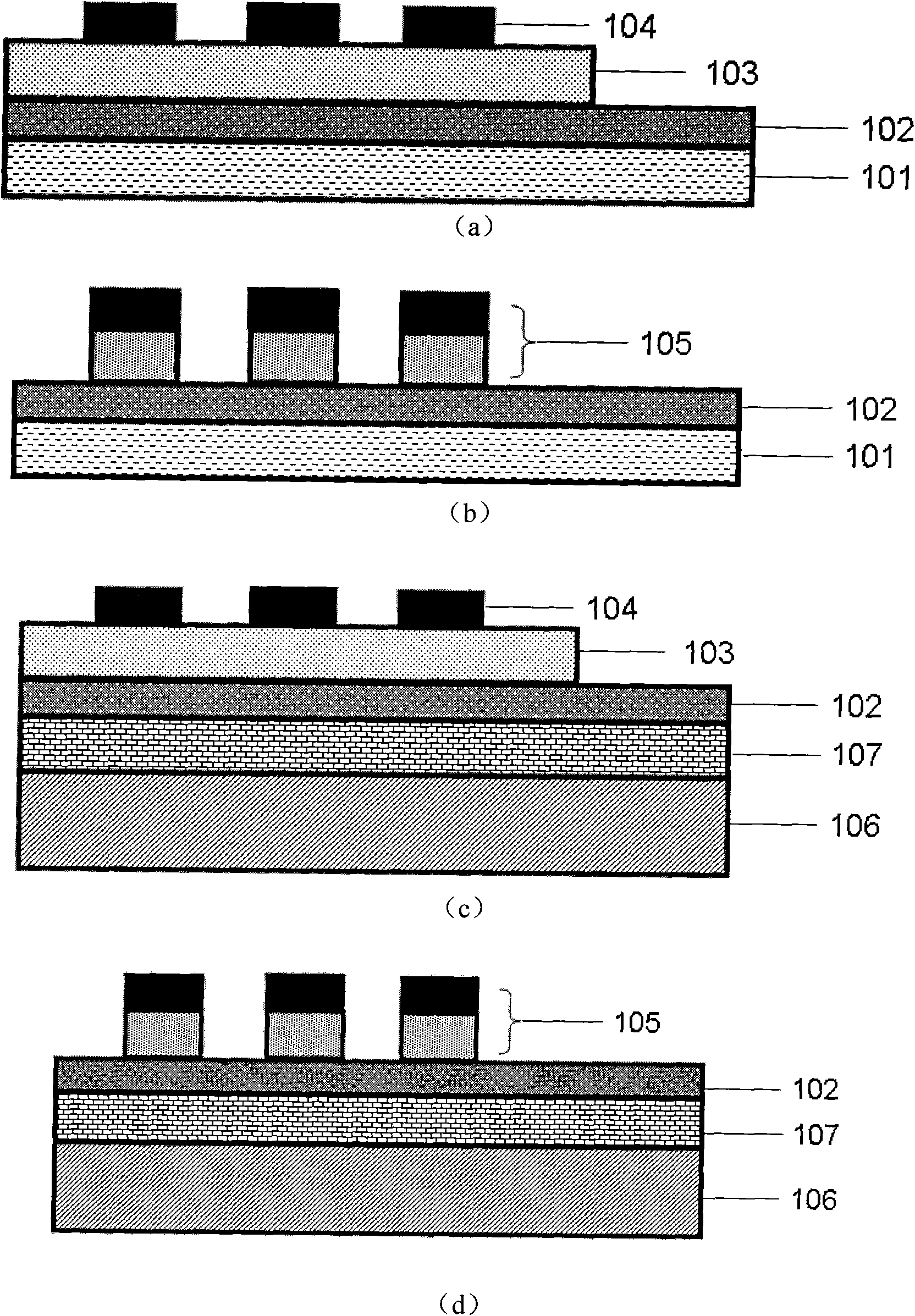
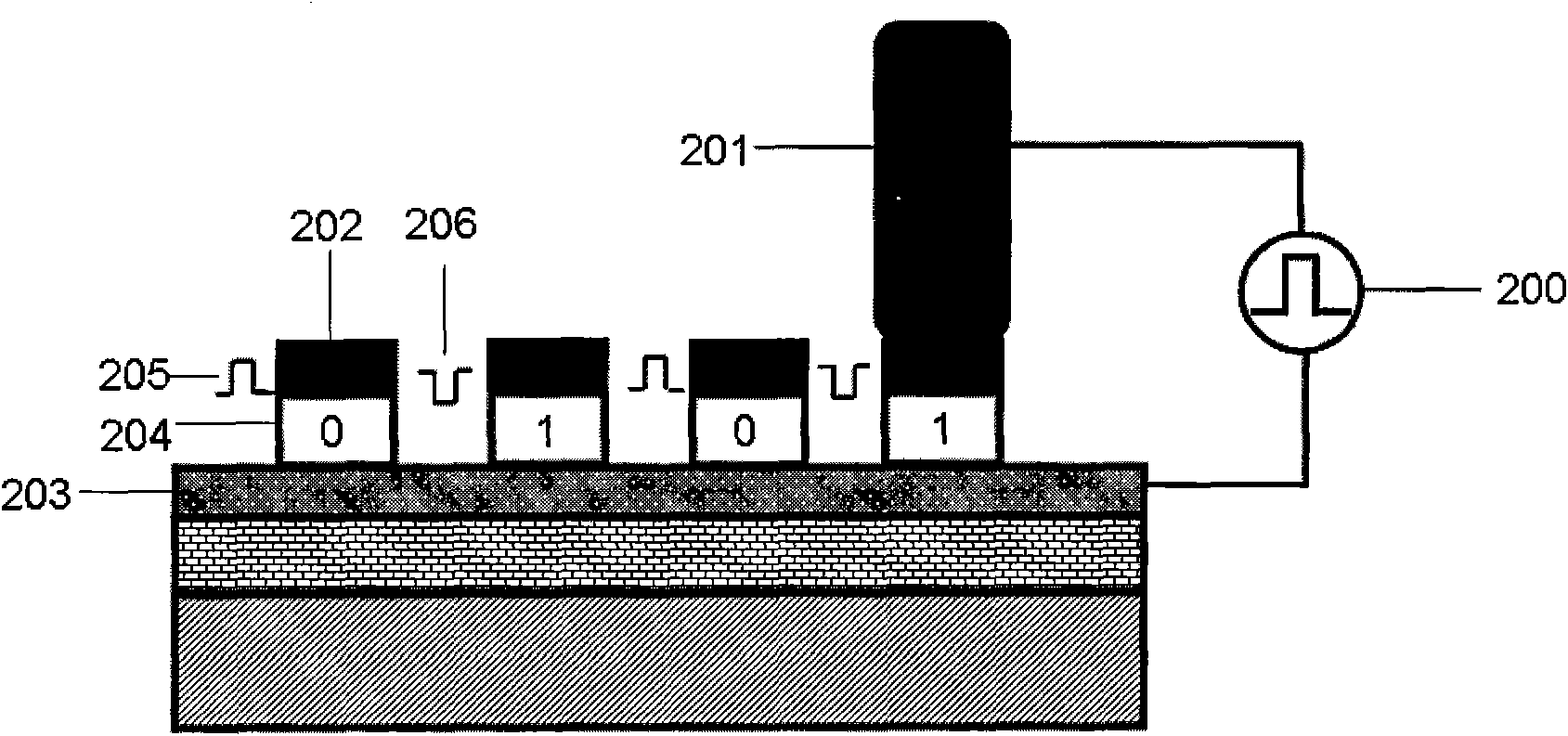
[0039] like figure 1 In (c), the silicon dioxide dielectric isolation layer 107 with a thickness of about 400nm is oxidized on the single crystal silicon base layer 106 by thermal oxidation, and the silicon dioxide dielectric isolation layer 107 is oxidized by thermal evaporation or magnetron sputtering 2 Growth Pt / Ti (the thickness of Pt is respectively 100nm, the thickness of Ti is 50nm, used as bonding layer) lower electrode 102 on dielectric isolation layer 107; Then grow bismuth ferrite thin film on lower electrode 102; Finally by electron beam evaporation, A 200 nm thick Cu upper electrode 104 is prepared by using a mask (the mask is uniformly distributed 100 μm circular holes), and the size of the electrode is 100 μm.
[0040] Among them, the bismuth ferrite thin film is prepared by the sol-gel method, and the specific process is as follows:
[0041] (1) Weigh iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O) and bismuth nitrate (Bi(NO 3 ) 3 ·5H 2 O), dissolved in ethylene glyc...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The main difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is: the recording medium used in embodiment 2 is lanthanum (La) doped BiFeO 3 Thin films in which the molar ratio of lanthanum is 5%, i.e. La 0.05 Bi 0.95 FeO 3 , the annealing temperature is 550°C.
[0048] Oxidize about 400nm thick silicon dioxide dielectric isolation layer 107 on the monocrystalline silicon base layer 106 by thermal oxidation, and grow Pt / Ti (Pt) on the silicon dioxide dielectric isolation layer 107 by thermal evaporation or magnetron sputtering Thickness is 100nm, the thickness of Ti is 50nm, as bonding layer) lower electrode 102, then grow the bismuth ferrite thin film doped with lanthanum on the lower electrode 102, finally by electron beam evaporation, adopt the method of mask plate to prepare 200nm thick The Cu upper electrode 104 has a size of 100 μm.
[0049] Wherein, the above-mentioned bismuth ferrite film is prepared by a sol-gel method, and the specific process is as follows:
...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The main difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is: the upper electrode of embodiment 3 adopts Ag electrode.
[0055] Oxidize SiO with a thickness of about 400 nm on the single crystal silicon base layer 106 by thermal oxidation 2 The dielectric isolation layer 107 is formed on SiO by thermal evaporation or magnetron sputtering 2 A lower electrode 102 of Pt / Ti (with a thickness of 100 nm / 50 nm) is grown on the dielectric isolation layer 107 .
[0056] The above-mentioned bismuth ferrite thin film is prepared by a sol-gel method.
[0057] The specific process is:
[0058] (1) Weigh iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O), bismuth nitrate (Bi(NO 3 ) 3 ·5H 2 O) and La(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O dissolved in ethylene glycol methyl ether (C 3 h 8 o 2 ) and ethylene glycol (C 2 h 6 o 2 ) in the mixed solution, and add an appropriate amount of acetic acid (C 2 h 4 o 2 ), adjust the pH value at about 2-3, so that the concentration of the bismuth ferrite sol obtain...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com