Process for recovering non-ferrous metal and noble metal from electronic waste material
A technology of electronic waste and non-ferrous metals, which is applied in the field of industrial waste resource treatment, can solve the problems of incomplete resource recovery, environmental secondary pollution, and failure to recycle, and achieve good environmental friendliness, energy saving, and good economic benefits Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
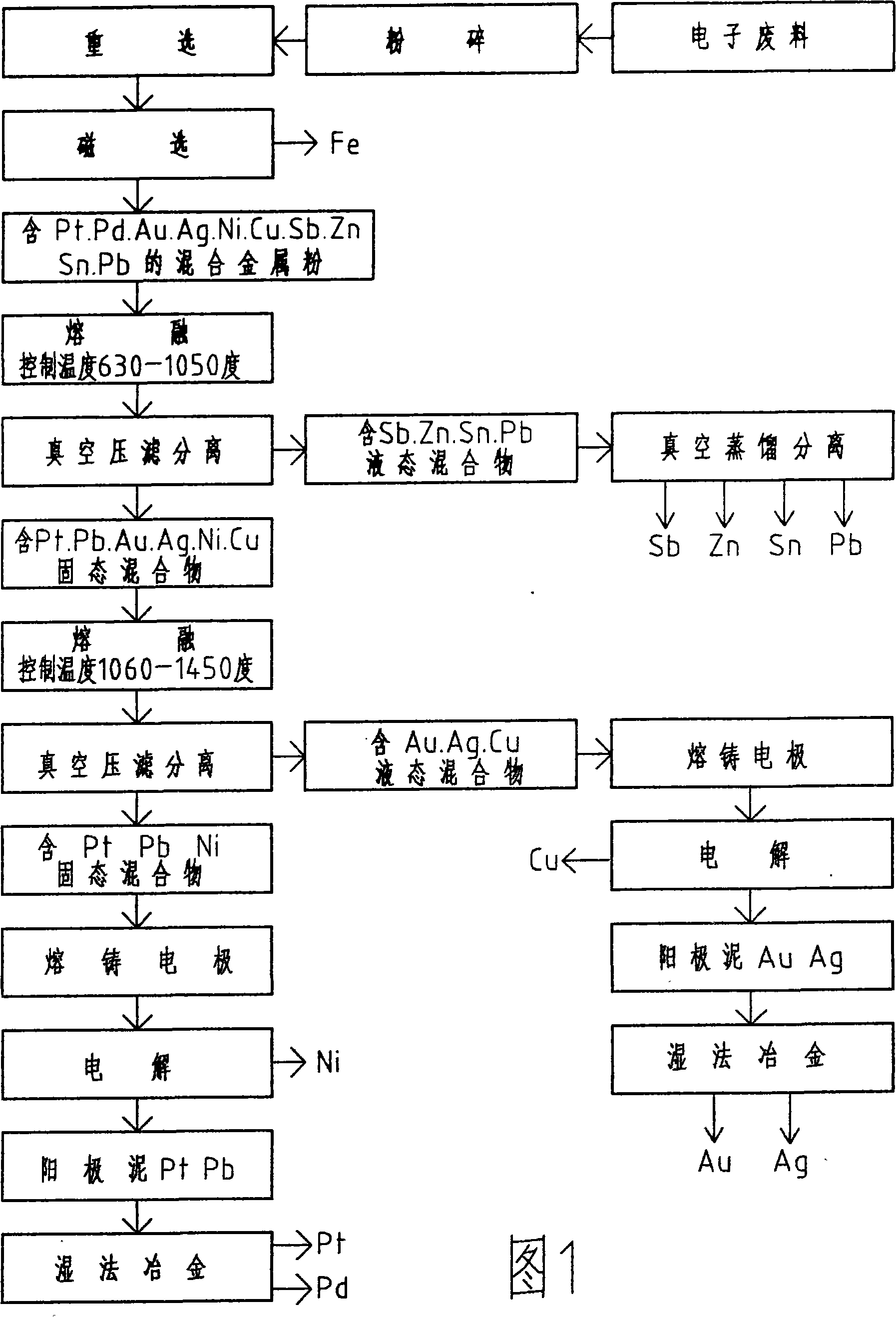
[0009] As shown in Figure 1, the electronic waste powder is re-selected and magnetically separated according to the conventional method to remove the Fe in the mixed metal powder to obtain Pt, Pd, Au, Ag, Ni, Cu, Sb, Zn, Pb, Sn Add the mixed metal powder to the melting pool of the electric melting furnace, turn on the induction heating coil, control the temperature in the melting pool to 900 ℃ and heat for 2 hours, and heat the Pb, Sn, Zn whose melting point is less than 630 ℃ , After Sb is fully melted into a liquid state, turn on the vacuum pump and keep the pressure in the liquid metal collector below the melting pool at 90 Pa, so that the molten lead Pb, tin Sn, zinc Zn, and antimony Sb are passed through with nickel The filter screen made of silk cloth enters the liquid metal collector and then is sent to the vacuum distillation separation furnace. The metal element has the characteristics of different vapor pressures at different temperatures and pressures and different cond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com