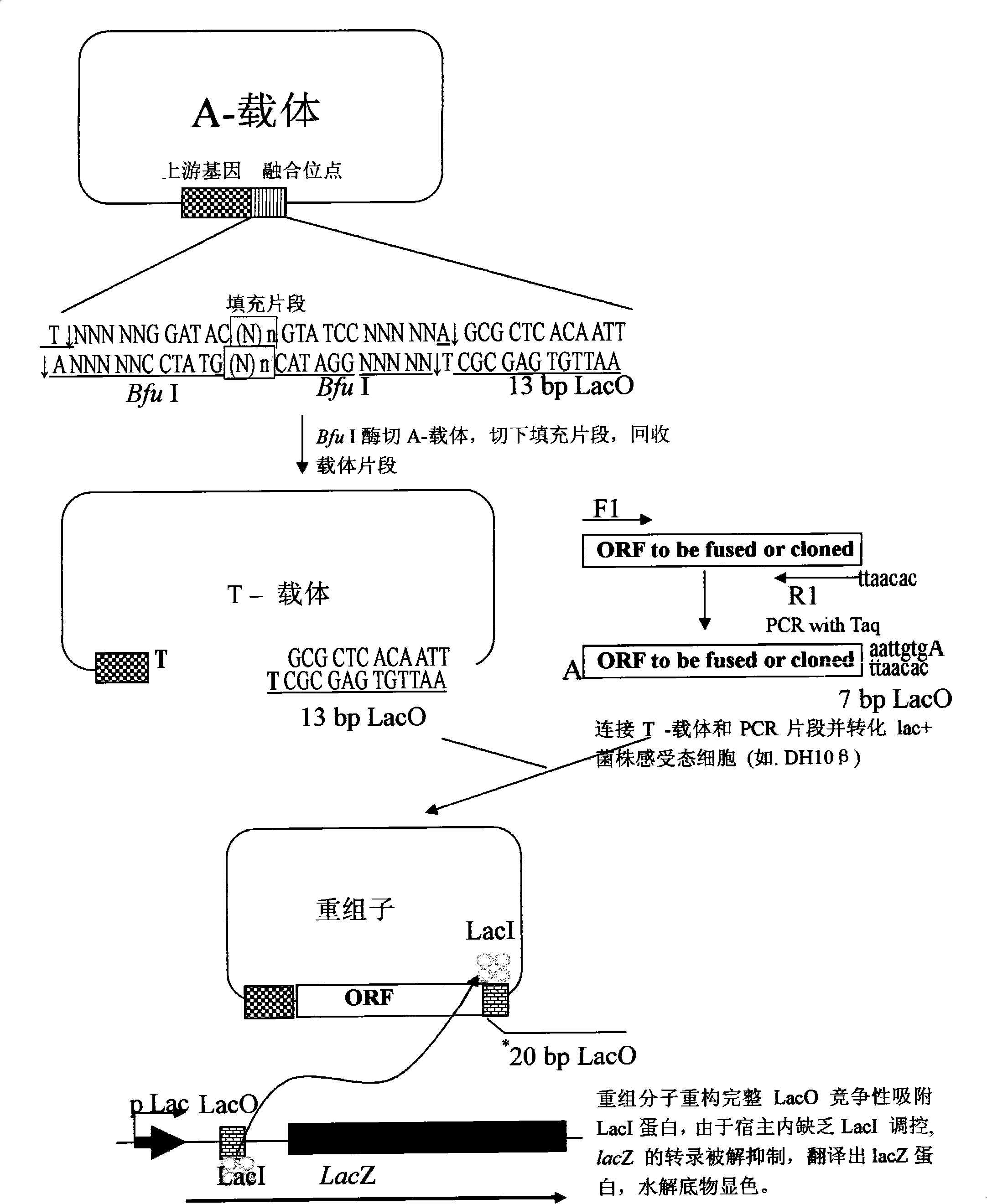
High throughput directional T carrier cloning process
A cloning method and high-throughput technology, applied in the direction of using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of low cloning efficiency, high cost of primer synthesis, and reduced cloning efficiency, so as to achieve simple and economical primer design. The effect of primer cost and strong compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The method of the invention is used to construct expression vectors for directional cloning of human liver protein genes BIRC4 and CDK9, and the genes are directly and seamlessly fused with 6×His for expression. The concrete operation of embodiment is as follows:
[0052] 1. Select the pet-23a vector, and eliminate the Bfu I site and potential LacO sequence on the vector by mutagenesis.
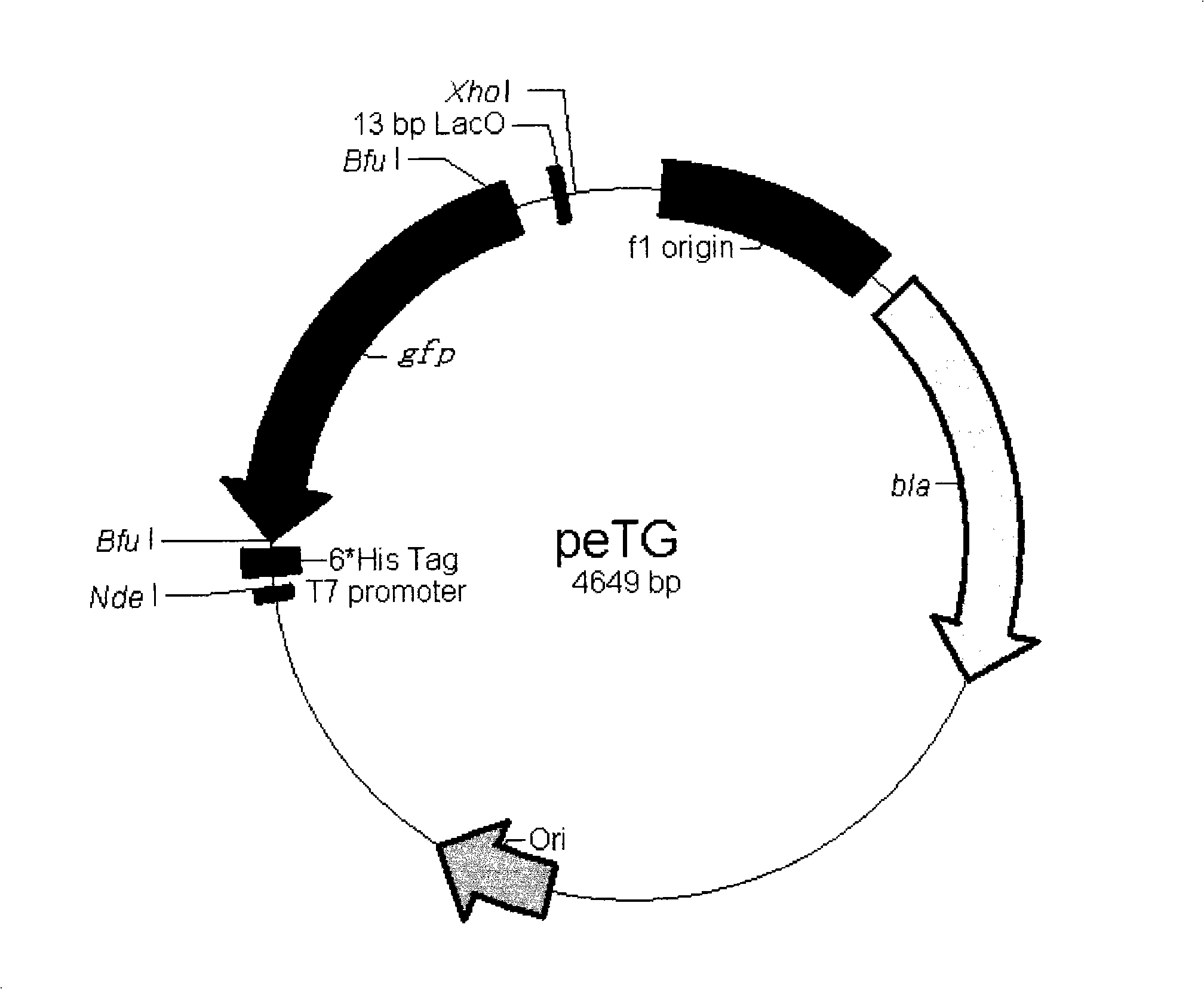
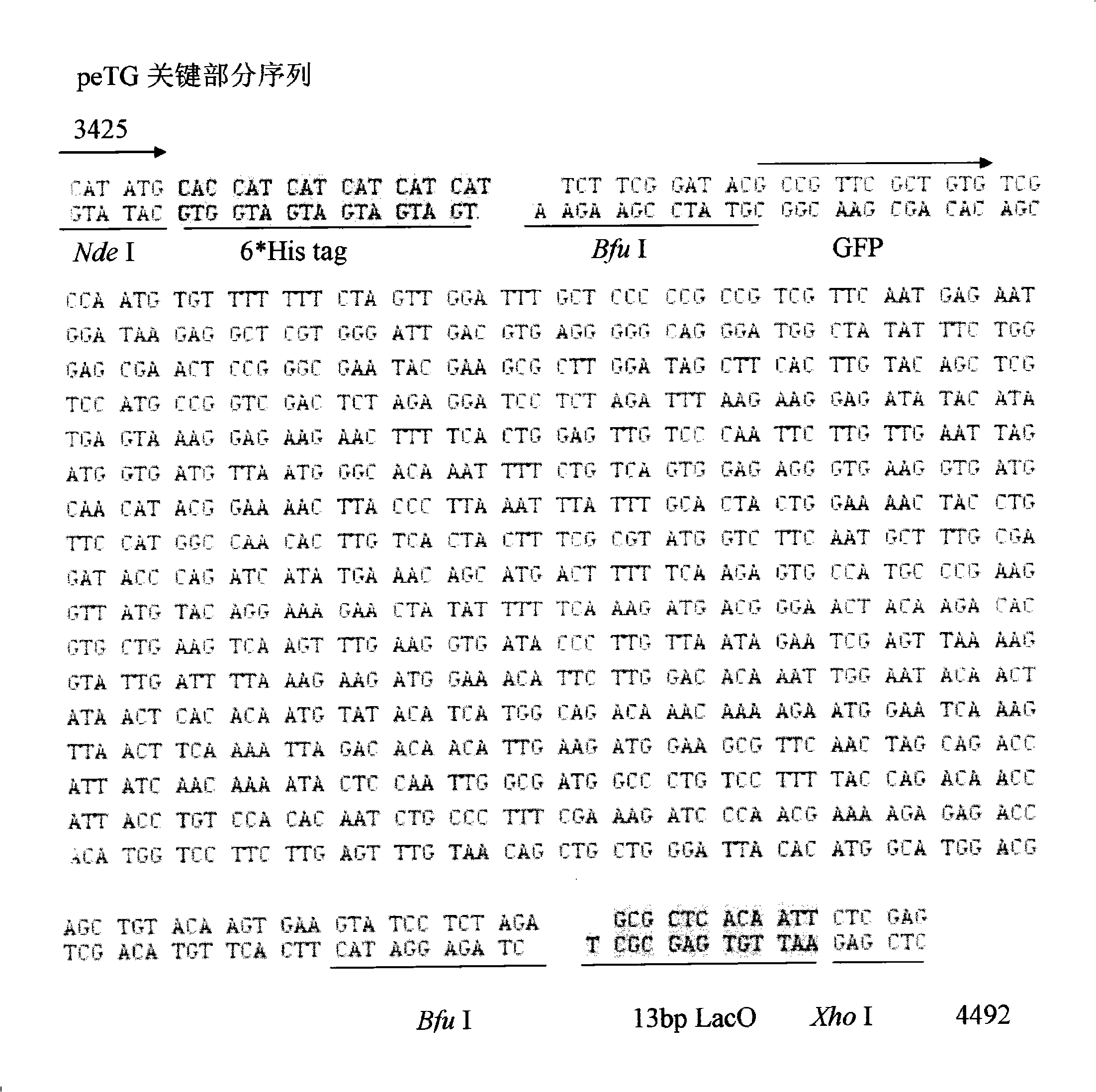
[0053] 2. The vector obtained after mutagenesis was digested with Nhe I and Xhol I, and a fragment of about 2.6 kb was recovered. A pair of primers GFPBF and GFPBR* were designed to amplify the stuffer fragment gfp. At the same time, the upstream and downstream primers respectively introduced two Bfu I sites, and the downstream introduced a 13bp part of the LacO sequence. The pair of primers was used to amplify the stuffer fragment gfp, and a fragment of about 1 kb was recovered. Recombine with the recovered vector to obtain the peTG vector (the vector map is as follows: figure 2 , ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] The method of the present invention is used to construct a mammalian two-hybrid T vector for directional fusion of ORF, clone and fuse transcription factors ICAM1 and E2F-6.
[0075] 1. Select pACT, one of the mammalian two-hybrid vectors, and eliminate the Bfu I site and potential LacO sequence on the vector by mutagenesis.
[0076] 2. After completion of the mutagenesis, insert the gfp stuffer fragment (GFPAF, GFPAR* in the primers as noted below) downstream of VP16. Similarly, two Bfu I sites are introduced into the upstream and downstream of gfp, and a 13bp partial LacO sequence is introduced downstream. Specifically, using iPCR to use pACT as a template, the carrier fragment obtained by reverse amplification of primers iPCRF and iPCRR* is recombined with the filler fragment to obtain the transformed mammalian two-hybrid vector pACTG.
[0077] 3. After digesting pACTG with Bfu I, recover about 5.5kb T vector.
[0078] 4. Design two pairs of RT-PCR primers ICAM1F, I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com