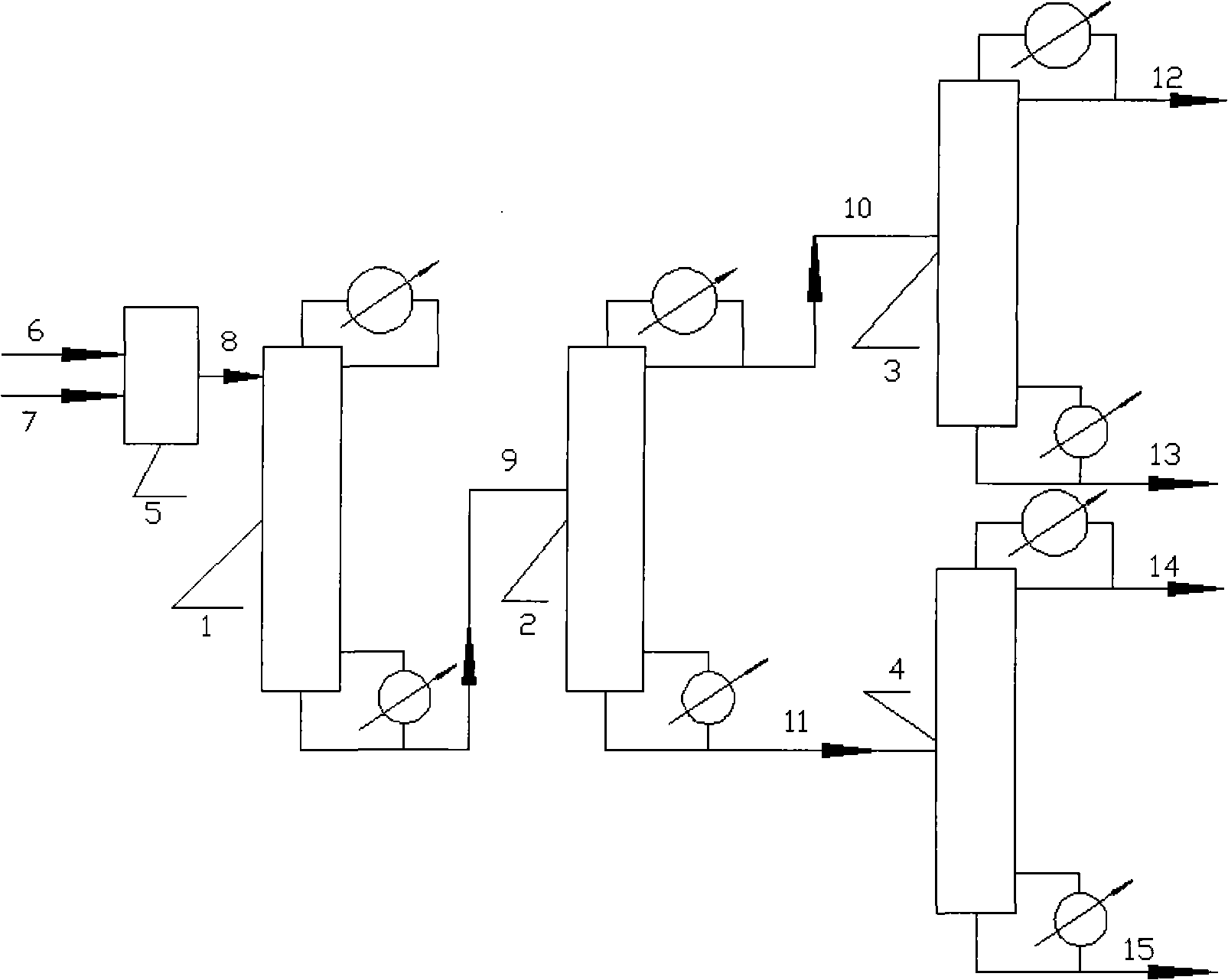
Azeotropy process for catalyzing, rectifying and hydrolyzing methyl acetate
A technology of methyl acetate and rectified water, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of carboxylate/lactone, etc., can solve the problems of complex process and high energy consumption, and reduce energy consumption of tower stills , the effect of short process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] according to figure 1 The flow shown: the number of theoretical plates of the catalytic rectification tower is 15, among which 10 theoretical plates in the upper part of the tower are filled with catalysts. Methyl acetate and water enter the catalytic rectification tower at a flow rate of 1 kg / h and 1.4 kg / h respectively, the reflux flow at the top of the tower is 8 kg / h, the temperature at the top of the tower is controlled at 87-92°C, and the output from the tower reactor enters the theoretical In a dealcoholization tower with 50 plates, the feeding position is the 30th theoretical plate, the reflux ratio is 2, the temperature at the top of the tower is 80-85°C, the distillate at the top of the tower is aqueous methanol, and the output from the tower is aqueous acetic acid. The methanol aqueous solution enters the alcohol refining tower, the number of theoretical plates is 15, the feeding position is the 10th tray, the reflux ratio is 6, the temperature at the top of ...
Embodiment 2
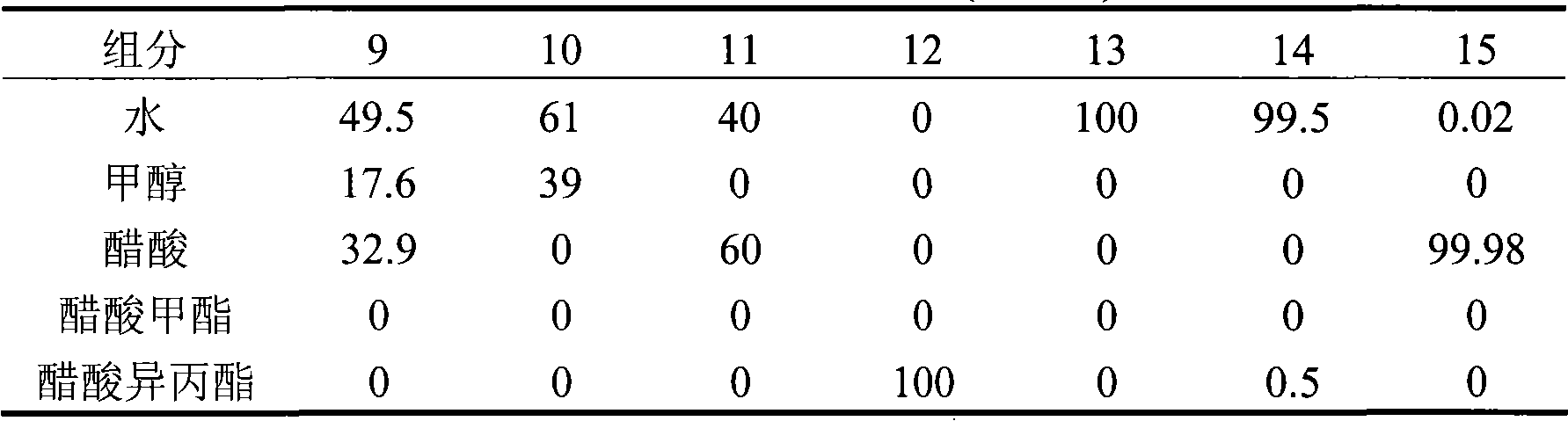
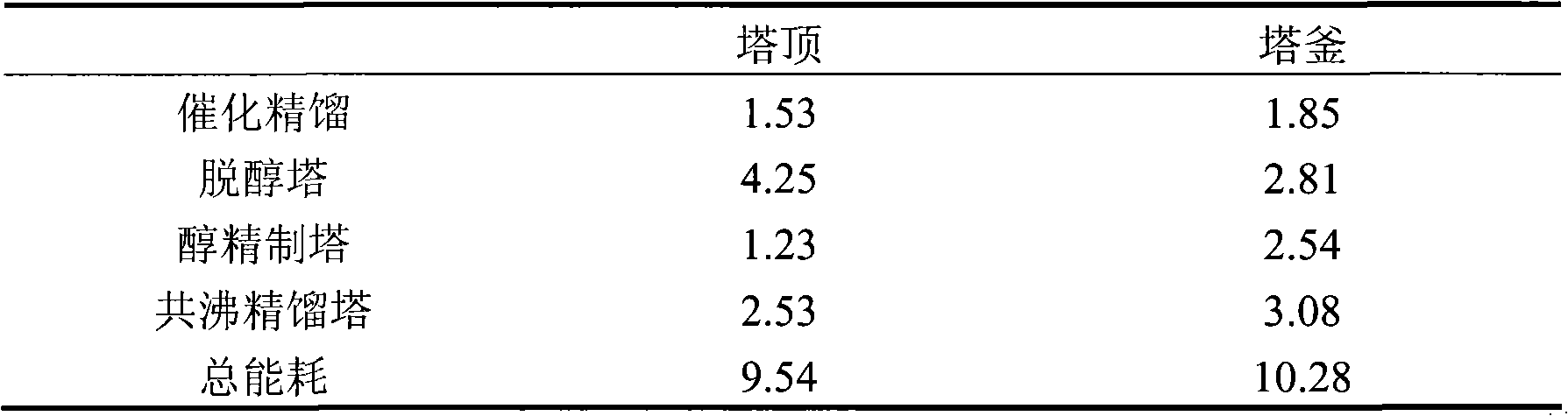
[0019] The number of theoretical plates in the catalytic rectification tower is 45, of which 12 theoretical plates in the upper part of the tower are filled with catalysts. Methyl acetate and water enter the catalytic rectification tower at a flow rate of 1 kg / h and 1.2 kg / h respectively, the top reflux flow rate is 2 kg / h, and the temperature at the top of the tower is controlled to be 87-92°C. The operating parameters are as in Example 1, and the analysis results of each stream and the energy consumption of each tower are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.
[0020] The analysis result (mass %) of each stream of table 3
[0021]
[0022] The energy consumption of each tower of table 4 (megajoules / hour)
[0023]
Embodiment 3
[0025] Only change the condition of dealcoholization tower, other each condition is as embodiment 1. The theoretical plate number of the dealcoholization tower is 10, the feeding position is the sixth theoretical plate, the reflux ratio is 8, and the temperature at the top of the tower is controlled at 80-85°C. After stable operation, the analysis results of each stream and the temperature of each tower The energy consumption is shown in Table 5 and Table 6, respectively.
[0026] The analysis result (mass %) of each stream of table 5
[0027]
[0028] The energy consumption of each tower of table 6 (megajoules / hour)
[0029]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com