Carbidonitridosilicate luminescent substances
A carbon nitride silicate, luminescent material technology, applied in the field of inorganic luminescent materials, can solve problems such as lack of information on compound luminescence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] For the preparation of terbium and cerium activated carbonitride silicate Y 1.00 Si 4 N 6 C:Tb 0.99 Ce 0.01 , the metal terbium was first nitrided in a horizontal tube furnace at 1200 °C in a pure nitrogen atmosphere for 12 hours to become TbN x (x≈0.99).
[0041] Then, 34.24 g of TbN x , 17.78g metal yttrium, 0.28g metal cerium, 28.06g α-Si 3 N 4 and 8.02 g of the original material of SiC were thoroughly mixed in an agate mortar in a dry nitrogen atmosphere and put into a molybdenum crucible. This powder mixture was fired at 1600° C. in pure nitrogen for 10 hours, and then cooled to room temperature in a furnace. A green-emitting luminescent substance is obtained after removal of unreacted and loose components: Composition Y 1.00 Si 4 N 6 C:Tb 0.99 Ce 0.01 .
Embodiment 2
[0043] For the production of synthetic Gd with 5% europium activated carbonitride silicate 18 Sr 0.2 Si4N 6.2 C 0.8 , the pure metal strontium and metal europium were nitridated in a horizontal tube furnace at 850 °C in a pure nitrogen atmosphere for 2 hours to become the precursor Sr 3 N 2 and EuN. Then, 56.61g of metal gadolinium, 2.91g of Sr 3 N 2 , 1.66g of EuN, 29.93g of α-Si 3 N 4 and 6.42g of SiC were thoroughly mixed in a dry nitrogen atmosphere, and placed in a heat-resistant crucible. The ignition of the mixture was carried out at 1750° C. for 24 hours in a nitrogen-hydrogen atmosphere (90:10). Efficient red-emitting luminescent substances were obtained after appropriate sample reprocessing.
[0044] The figures are generally self-evident to those skilled in the art of luminescent substances. A rationale for the illustrated factual situation is given above. In the following, only some special points will be supplemented.
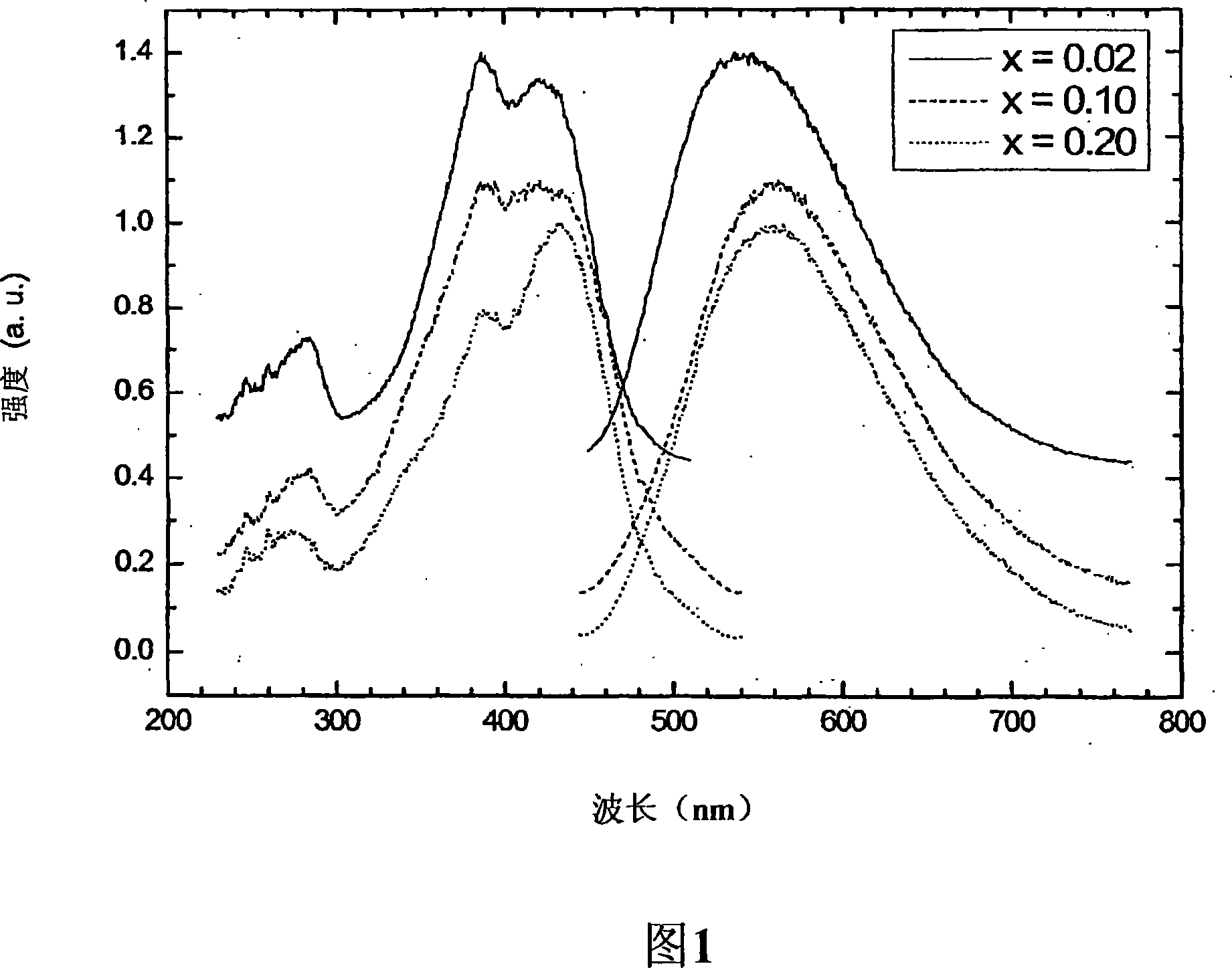
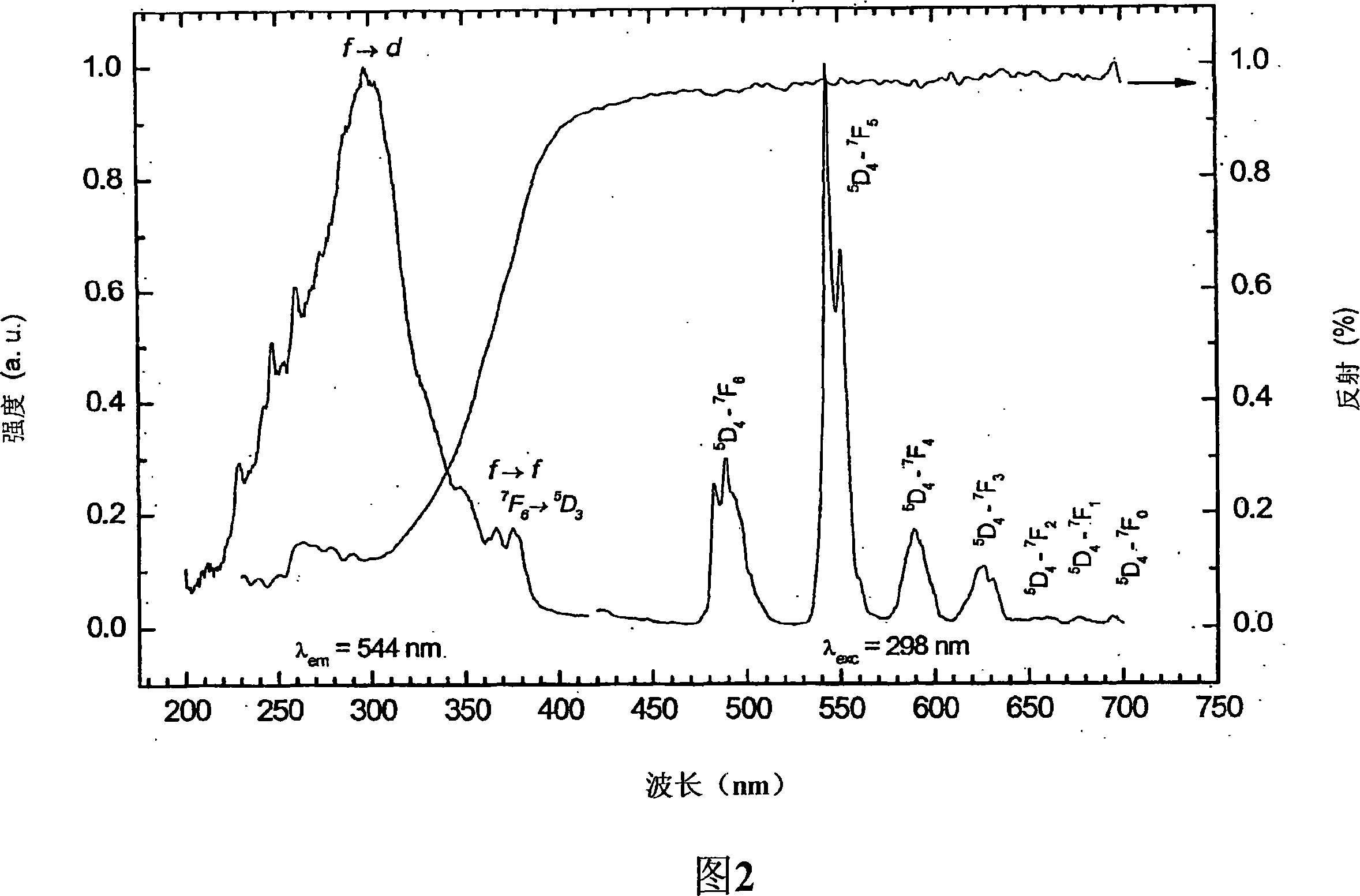
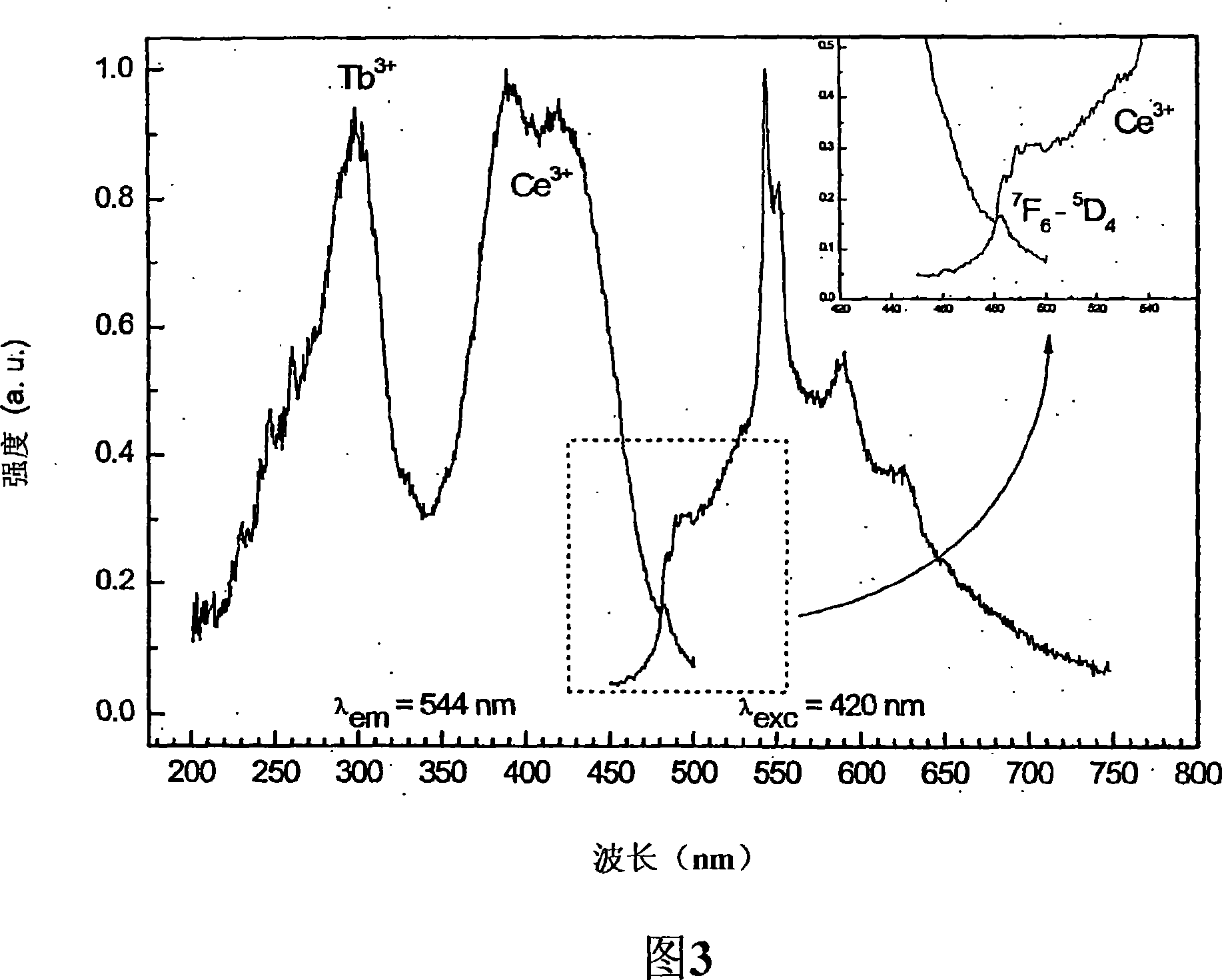
[0045] It can be seen from Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com