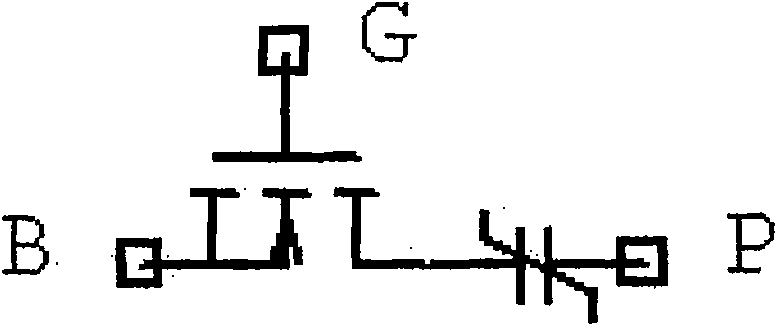A crossed iron electric memory array structure
A ferroelectric storage and array structure technology, applied in information storage, static memory, digital memory information and other directions, can solve the problem of the size and operation speed of the decoder, the inability to effectively optimize the storage array, and increase the circuit complexity and area. and other problems to achieve the effect of shortening the length, simplifying the design, and improving the reading and writing speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
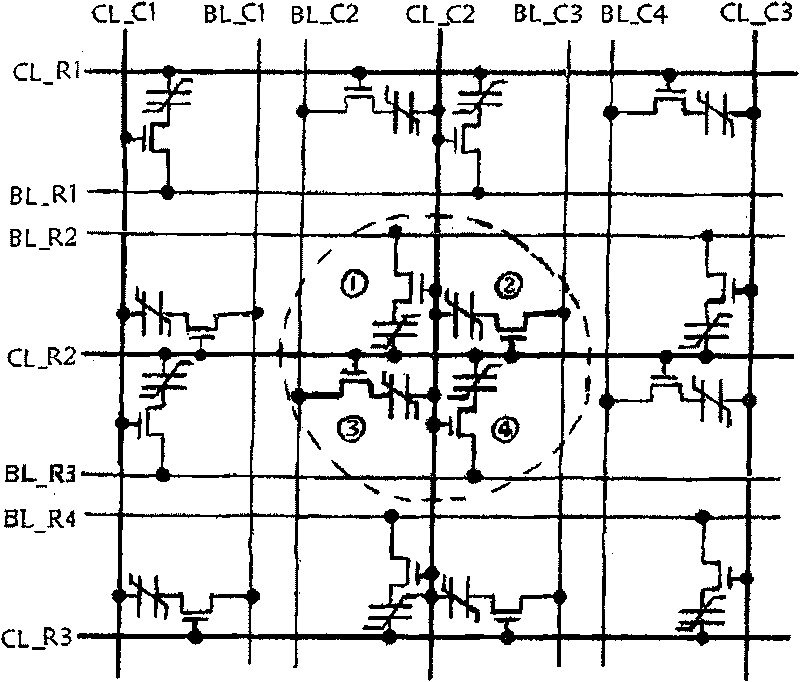
[0015] The invention designs a cross-type ferroelectric storage array structure. The cross-type ferroelectric storage array structure takes the cross-type ferroelectric storage unit as a basic component.
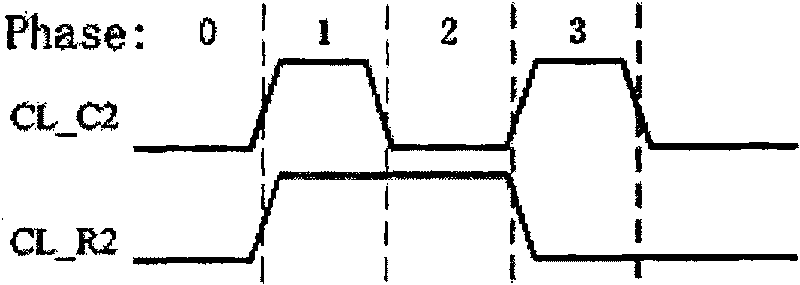
[0016] Such as figure 1 In the cross-type ferroelectric memory array structure shown, the dotted circle in the figure represents the cross-type FeRAM memory unit, where ① is Ce1, ② is Ce2, ③ is Ce3 and ④ is Ce4. Each ferroelectric memory cell shares the control line CL with the memory cells in the same row or column in the horizontal and vertical directions, the data signal line BL in the column direction is shared between the memory cells in the same column, and the row line is shared between the memory cells in the same row. For the upward data signal line BL, the data signal line BL is not shared between rows and columns. Specifically, it includes one row control line (CL_R2), one column control line (CL_C2), two row data lines (BL_R2, BL_R3), and two column data lines...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com