Method for testing DNA mononucleotide pleomorphism
A single nucleotide polymorphism and detection method technology, applied in the field of DNA single nucleotide polymorphism detection, can solve the problems of high cost, increased detection time, low sensitivity, etc., and achieve the effect of simple processing and no need for separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
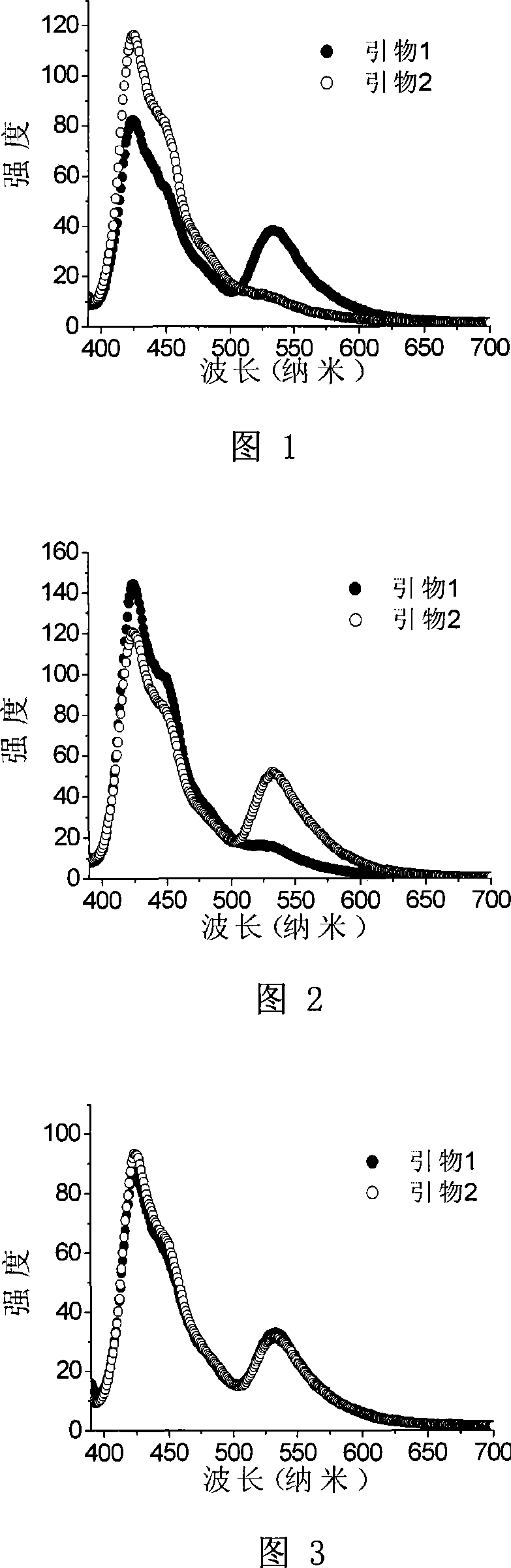
[0053] Example 1. Application of PFP1 to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms at the RS1800469 site in wild-type samples
[0054]
[0055] 1. Synthesis of PFP1
[0056] The structure of PFP1 is shown in formula (II), and the synthesis method is as follows:
[0057] Add 50mL of toluene, 5.2g of neopentyl glycol and 0.5g of p-toluenesulfonic acid to a 100mL single-necked bottle, reflux for 24 hours, evaporate the solvent and separate on a silica gel column (eluent: dichloromethane) to obtain 4.8g of 1,4- Neopentyldiboronate. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ (ppm) 7.78 (4H, s), 3.77 (8H, s), 1.02 (12H, s).
[0058] Add 5.4mL toluene and 3.6mL 2M potassium carbonate to a 25mL two-necked flask, and after bubbling nitrogen gas for 30 minutes, add 325 mg of 2,7-dibromo-9,9-bis(6-bromohexyl)fluorene, 165 mg 1,4-Neopentyldiborate and 20 mg tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium, stirred and reacted at 95°C under nitrogen for 24 hours, added chloroform and water after cooling, washe...
Embodiment 2
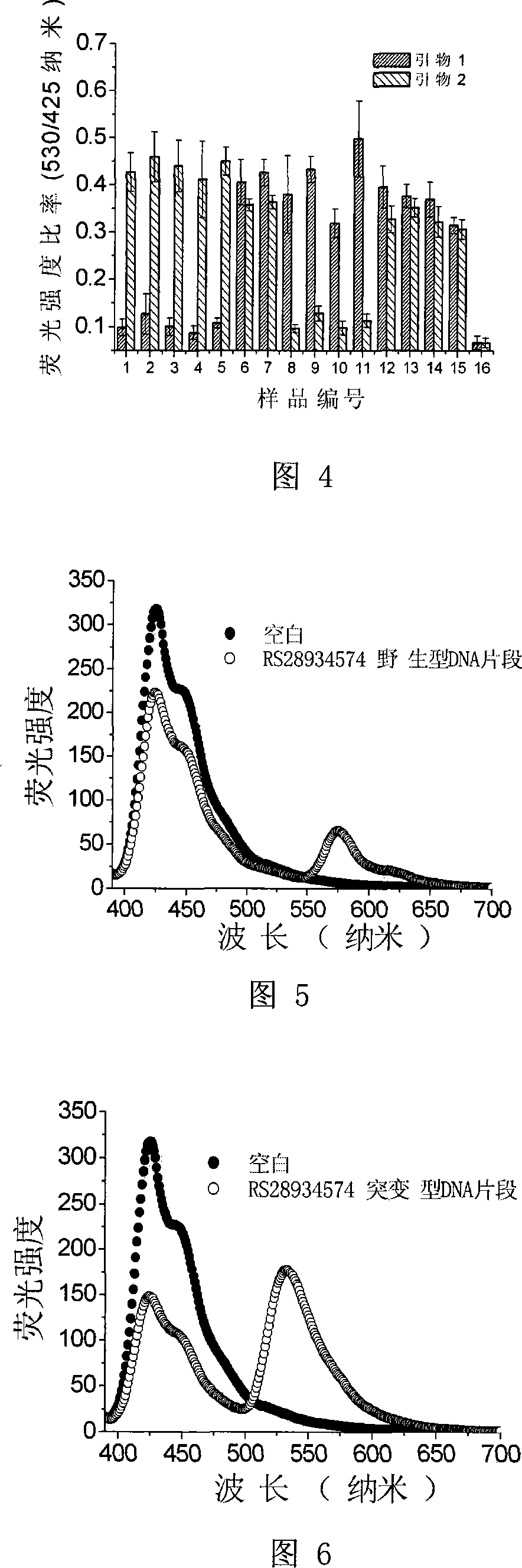
[0079] Example 2. Using PFP1 to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms at the RS1800469 site in mutant samples
[0080] 1. Synthesis of PFP1
[0081] Same as Step 1 of Example 1.
[0082] 2. Extraction of DNA from samples to be tested
[0083] Same as Step 2 of Example 1.
[0084] 3. Amplification of DNA Fragments Containing Target Sites
[0085] Same as Step 3 of Example 1.
[0086] 4. Single base extension reaction
[0087] Same as Step 4 of Example 1.
[0088] 5. Measurement of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
[0089] Same as Step 5 of Example 1.
[0090] Figure 2 shows the fluorescence spectra obtained by single-base extension with primer 1 and primer 2 respectively. When primer 2 is used, there is a significant energy transfer, but when primer 1 is used, only a background signal appears, indicating that the nucleus of the RS1800469 site of the DNA to be tested is The nucleotide is homozygous for the mutation.
[0091] 6. Result Verification
[0092] Same as Step 6 of ...
Embodiment 3
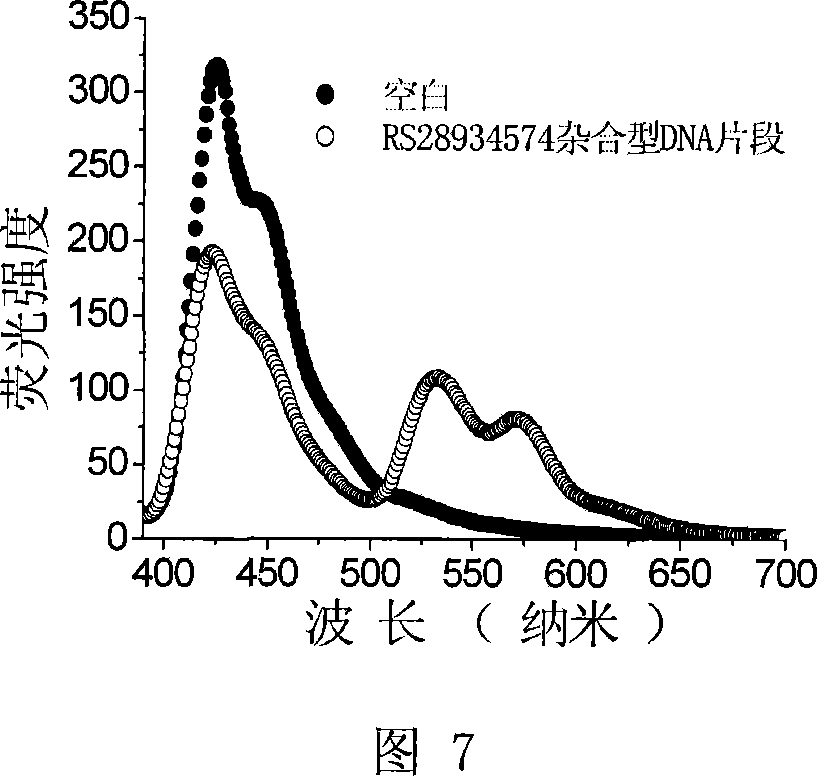
[0094]Example 3. Application of PFP1 to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms at the RS1800469 site in heterozygous samples
[0095] 1. Synthesis of PFP1
[0096] Same as Step 1 of Example 1.
[0097] 2. Extraction of DNA from samples to be tested
[0098] Same as Step 2 of Example 1.
[0099] 3. Amplification of DNA Fragments Containing Target Sites
[0100] Same as Step 3 of Example 1.
[0101] 4. Single base extension reaction
[0102] Same as Step 4 of Example 1.
[0103] 5. Measurement of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
[0104] Same as Step 5 of Example 1.
[0105] Figure 3 shows the fluorescence spectra obtained by single-base extension with primer 1 and primer 2 respectively. Significant energy transfer occurs when primers 1 and 2 are used, indicating that the nucleotide at the RS1800469 site of the DNA to be tested is a hybrid type.
[0106] 6. Result Verification
[0107] Same as Step 6 of Example 1.
[0108] The result proves that there are two kinds of PCR pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com