Microparticle and pharmaceutical composition
A technology of microparticles and polymers, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, microcapsules, and medical preparations of non-active ingredients, etc., and can solve the problems of non-biodegradable and inapplicable administration of microparticles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0129] Microparticle preparation:
[0130] 10 mg of polyethylene glycol-poly(ε-caprolactone) (molecular weight of polyethylene glycol: 5,000, molecular weight of poly(ε-caprolactone): 10,000) which is an amphiphilic polymer was dissolved in 500 μL of chloroform. This solution was added to 2 mL of a mixed solvent of hexane and chloroform (1.6 mL of hexane, 0.4 mL) to prepare a polymer solution. While stirring the polymer solution at a stirring rate of 1,600 rpm, 10-100 μL of a 25 wt % bovine serum albumin solution was added dropwise. Stirring was further performed for 5 minutes, thereby preparing microparticles. After spreading this fine particle dispersion on a silicon wafer, it was fully dried under vacuum, and platinum was vapor-deposited, and observed with a scanning electron microscope (HITACHS-4800).
[0131]
[0132] Microparticles with a diameter of several micrometers to hundreds of micrometers were observed. The particle shape observed after drying is not inconsi...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Microparticle preparation:
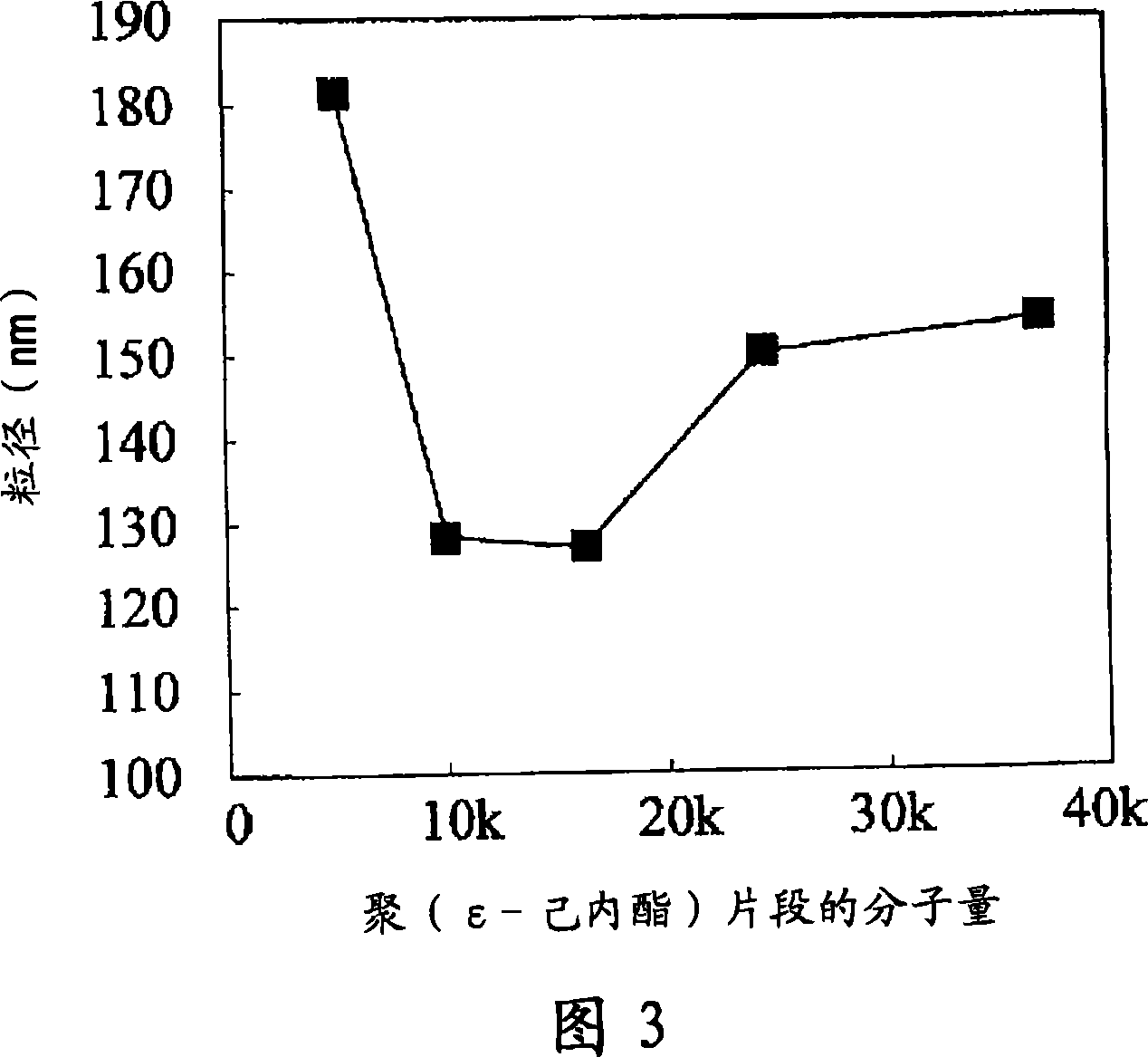
[0135] 10 mg of polyethylene glycol-poly(ε-caprolactone) (molecular weight of polyethylene glycol 5,000, molecular weight of poly(ε-caprolactone) 10,000 or 37,000) which is an amphiphilic polymer was dissolved by heating in 2 mL of acetic acid in ethyl ester. While stirring the polymer solution at a stirring rate of 1,600 rpm, 50-200 µL of a horseradish peroxidase aqueous solution (1 wt% horseradish peroxidase, 9 wt% sucrose, 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4) was added dropwise. Stirring was further carried out for 1 hour, whereby microparticles were prepared. The particle size measurement of the fine particles was carried out by a dynamic light scattering method using an apparatus Zetasizer 3000HSA (MALVERN INSTRUMENTS). The obtained data was analyzed by the CONTIN method and the histogram method, and the particle diameter was calculated.
[0136]
[0137] Microparticles with a minimum number-average particle diameter of 25.1 nm were formed (Fig....
Embodiment 3
[0139] Microparticle preparation:
[0140] Dissolve 10 mg of polyethylene glycol-poly(ε-caprolactone) (molecular weight of polyethylene glycol 5,000, molecular weight of poly(ε-caprolactone) 37,000) which is an amphiphilic polymer in 2 mL of ethyl acetate , to prepare a polymer solution. While stirring the polymer solution at a stirring rate of 1,600 rpm, 100 μL of a 1 wt % horseradish peroxidase solution was added dropwise. After further stirring for 1 hour, it was added to 10 times the amount of dioxane. After evaporating the solvent and concentrating to about 2 mL, the particle dispersion was added to a phosphate buffer solution (10 mL) containing various concentrations of Pluronic (registered trademark of BASF) F68 (PEO-PPO-PEO block polymer). The particle size measurement of the fine particles was carried out by a dynamic light scattering method using an apparatus Zetasizer 3000HSA (Malvern Instruments). The obtained data was analyzed by the CONTIN method and the histo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com