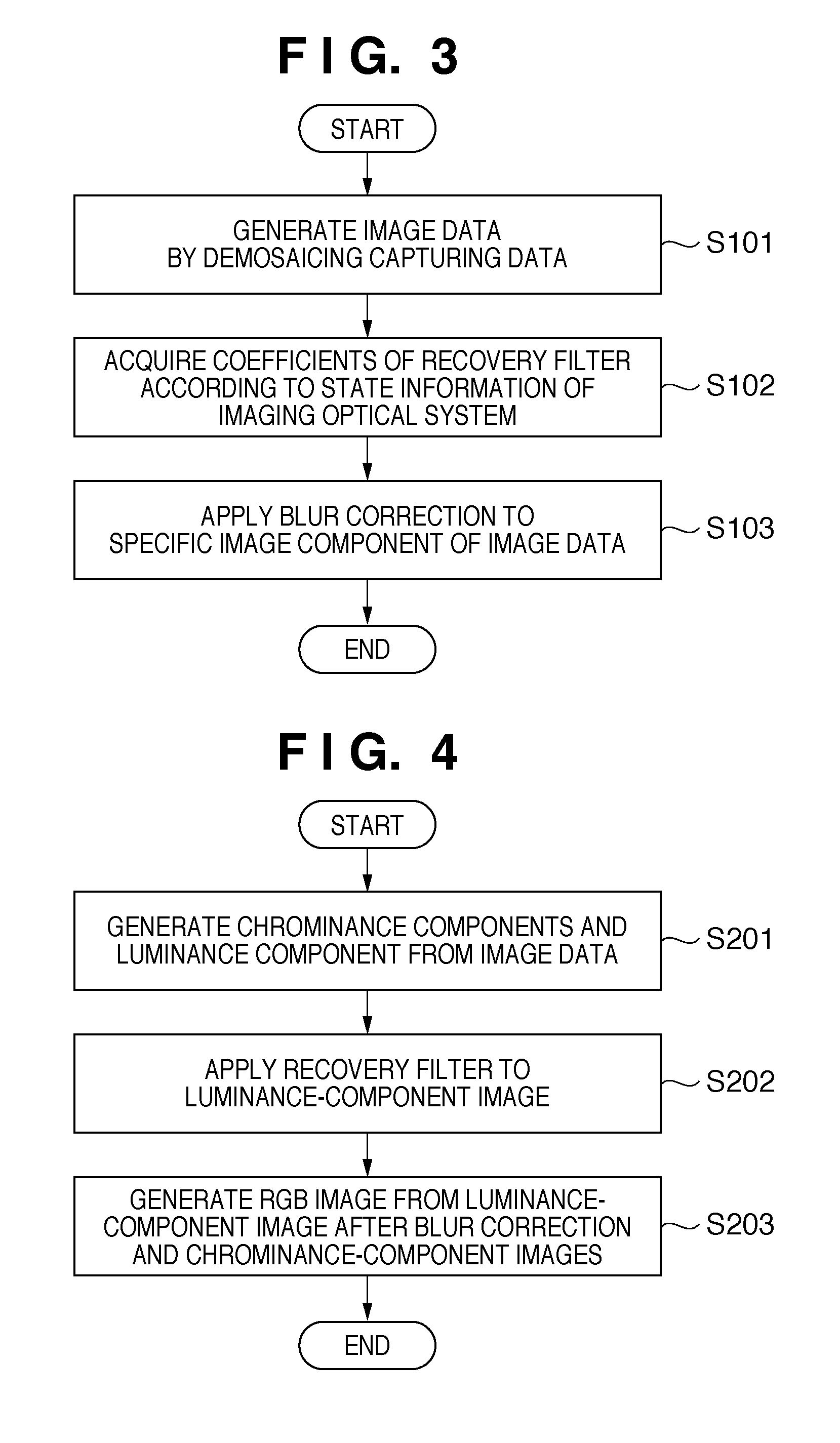
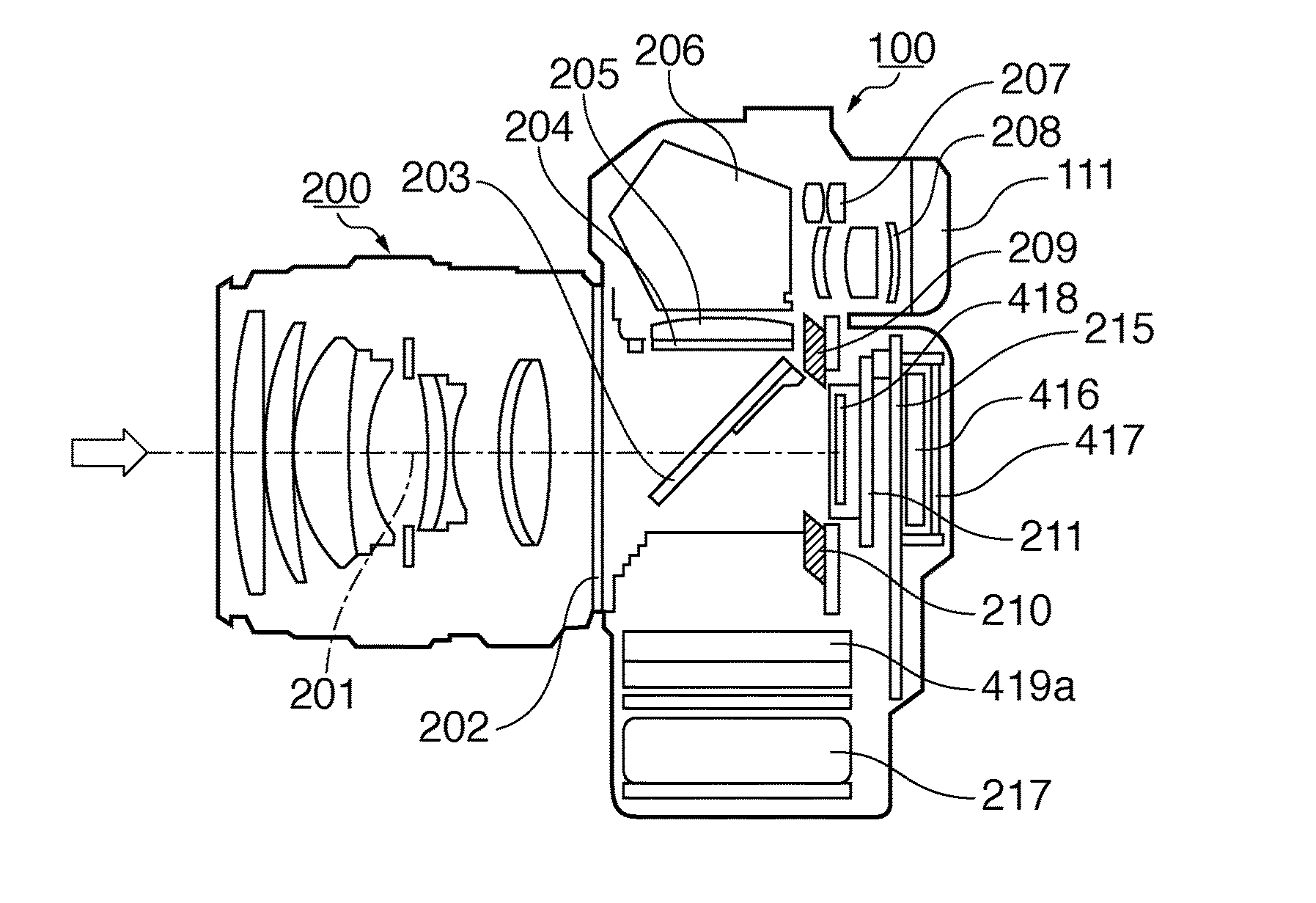
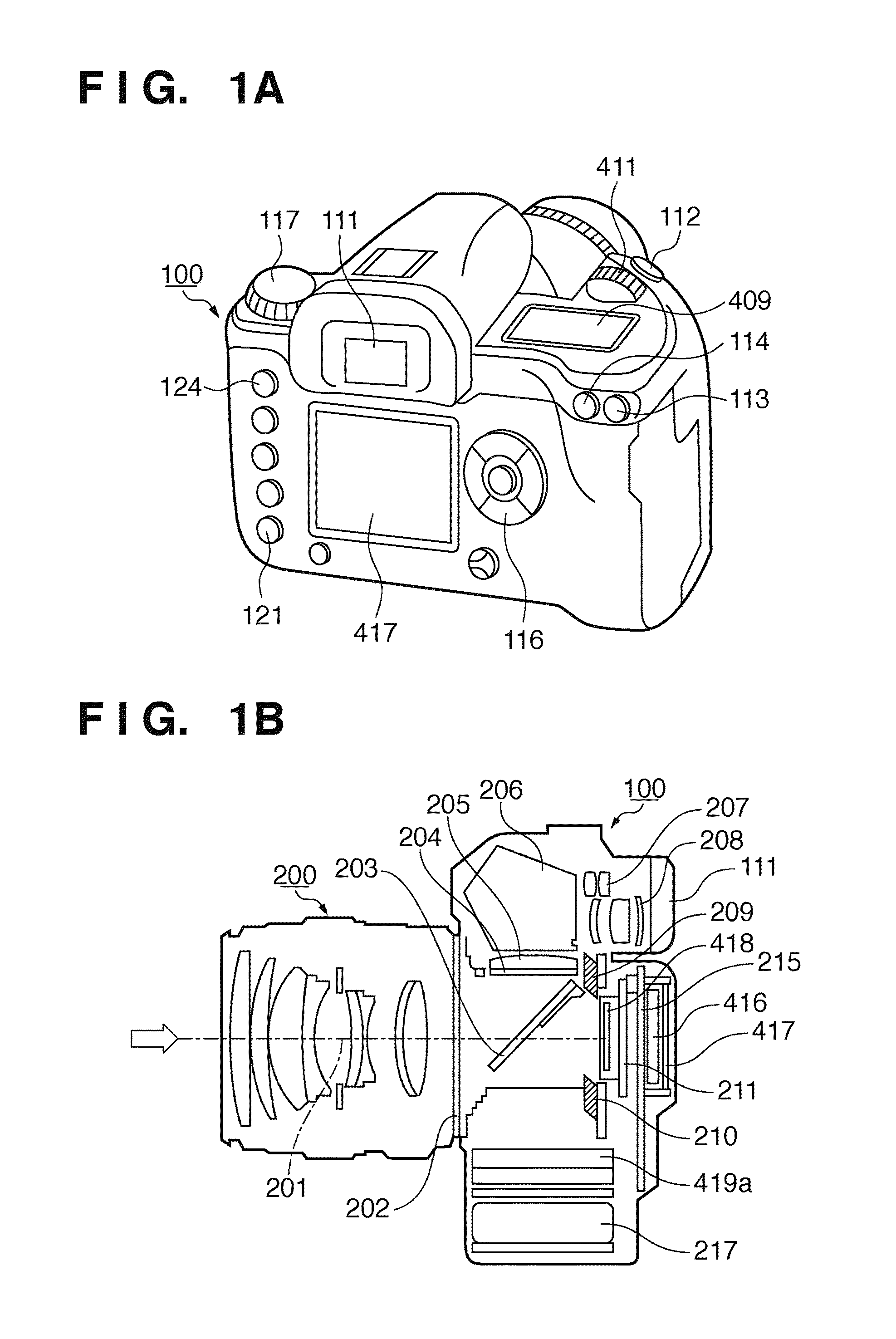
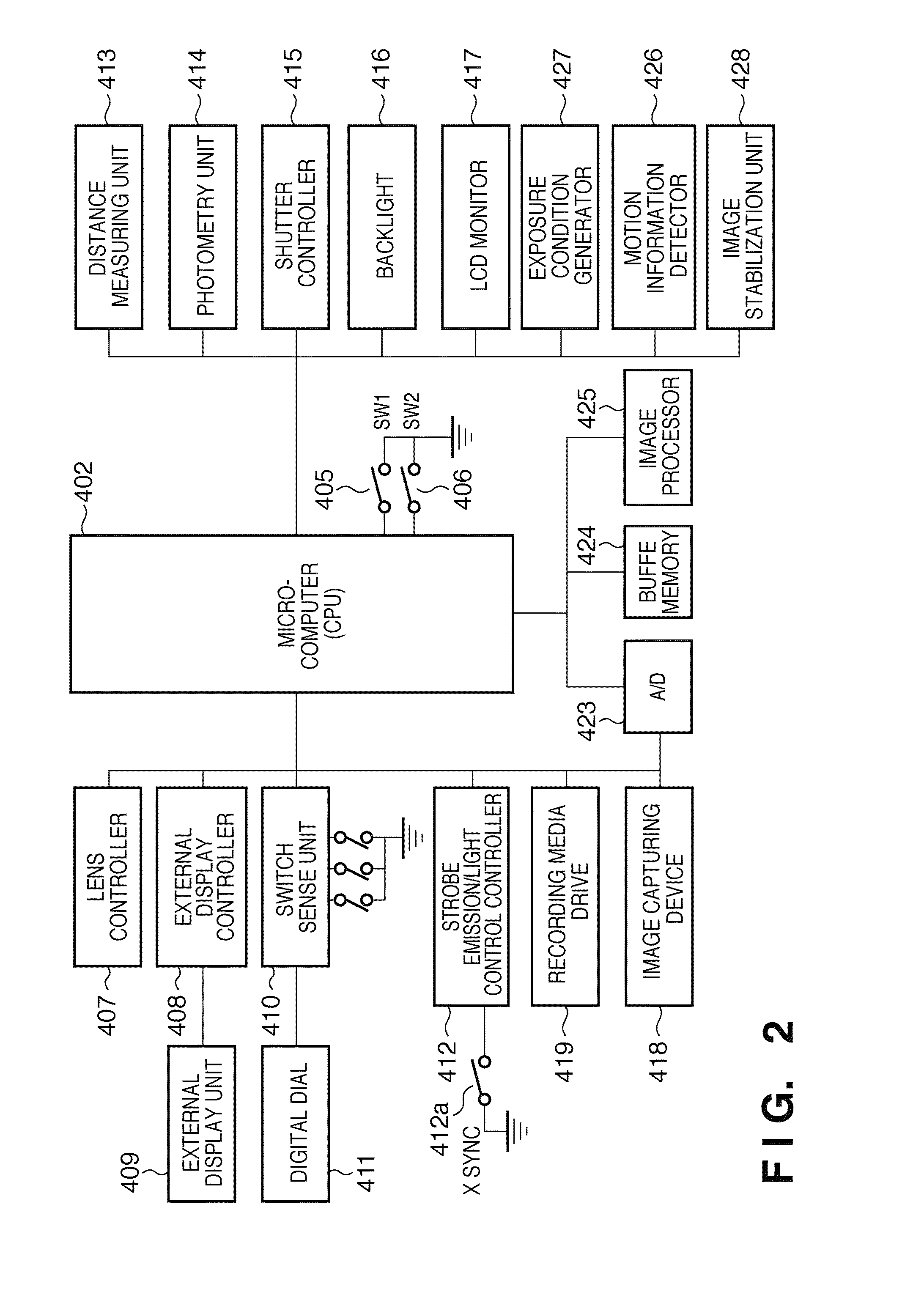
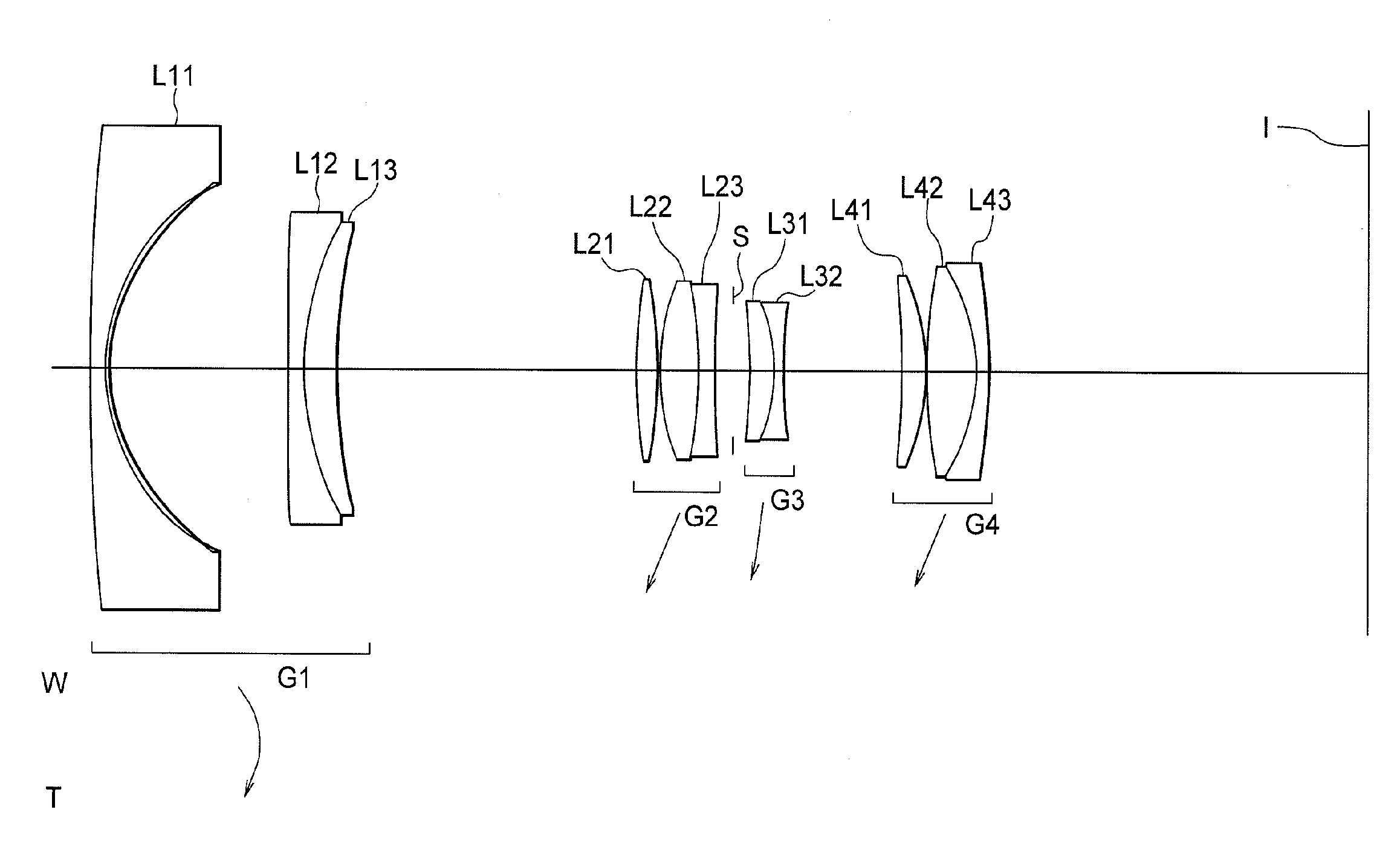
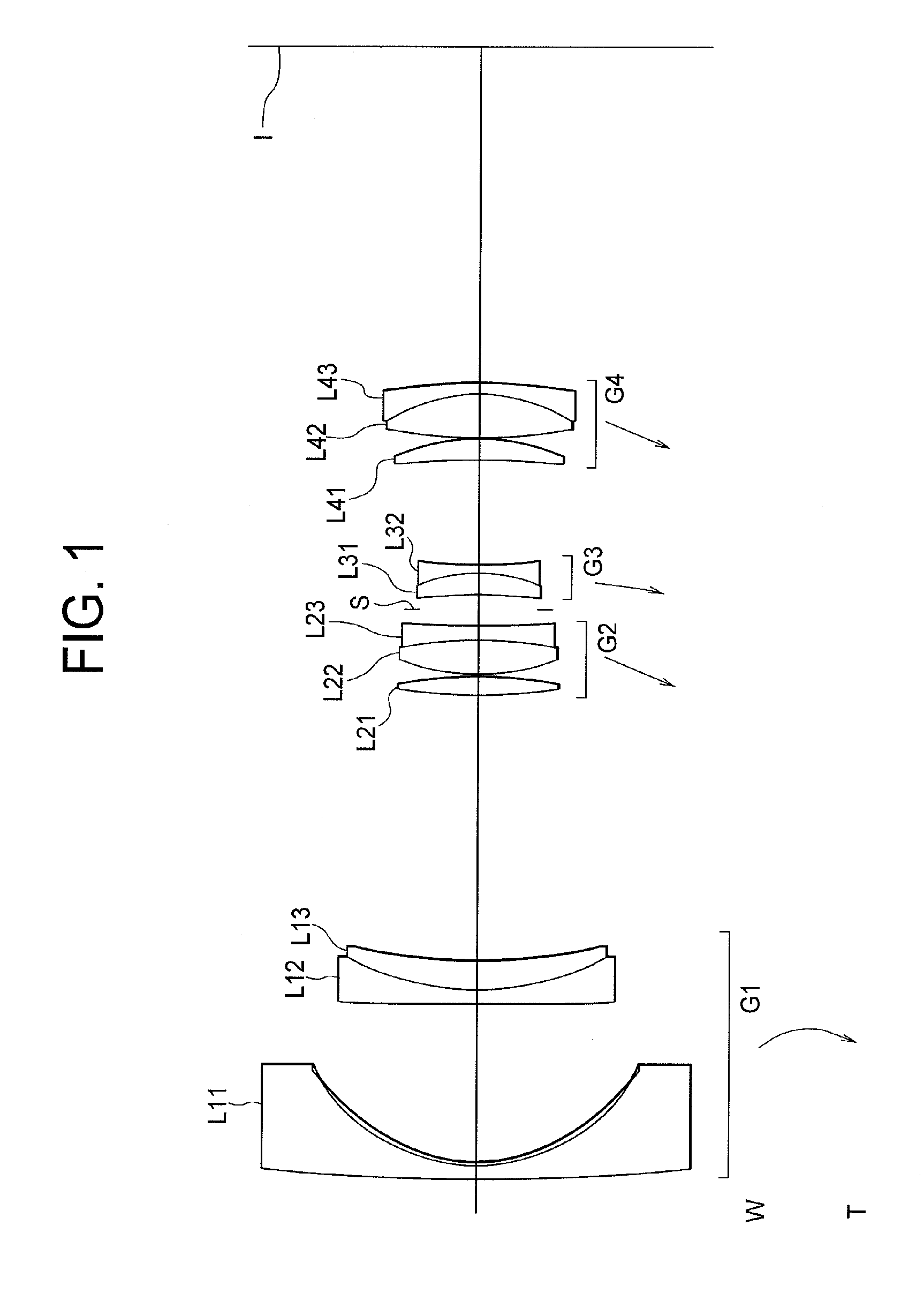
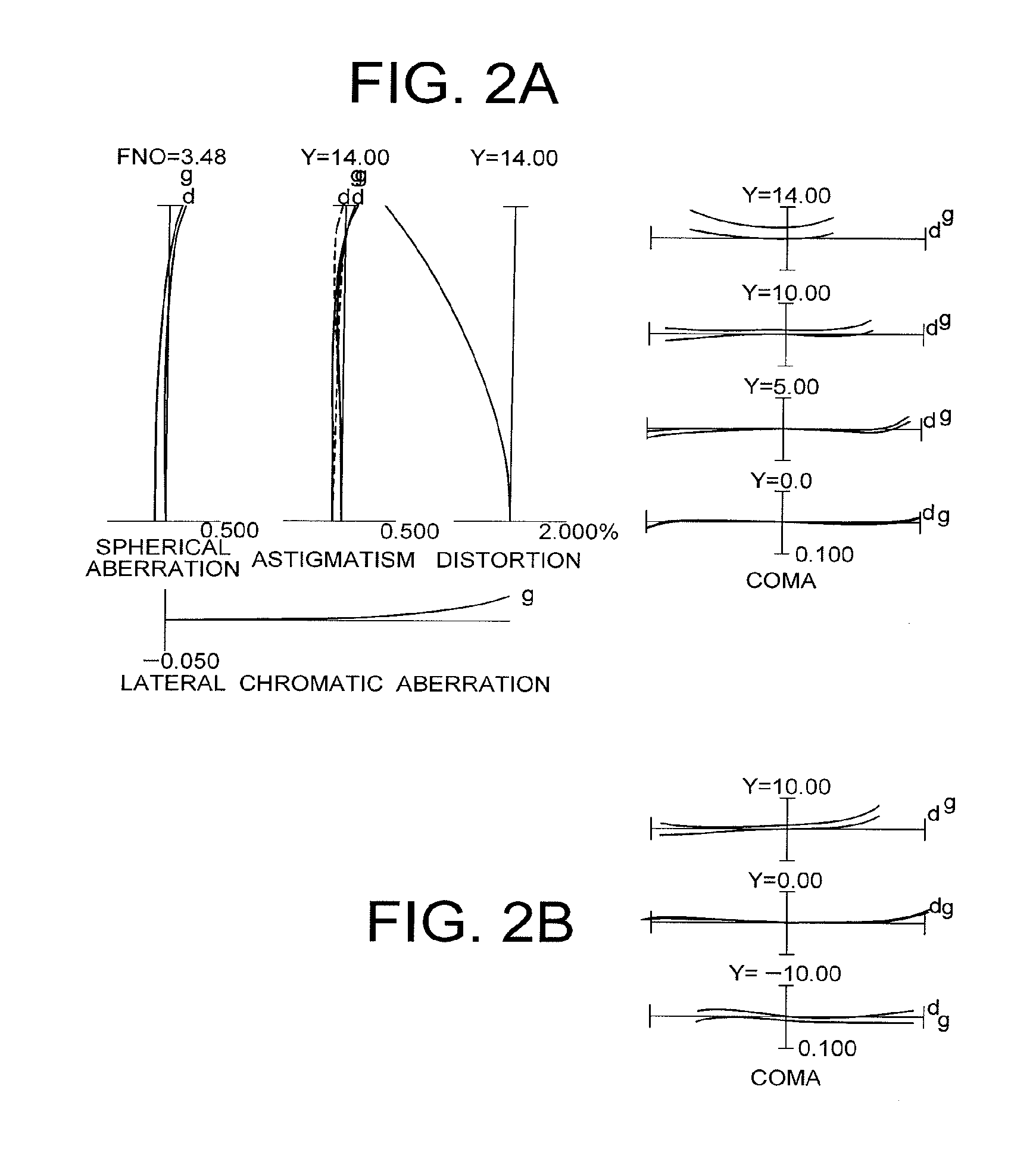
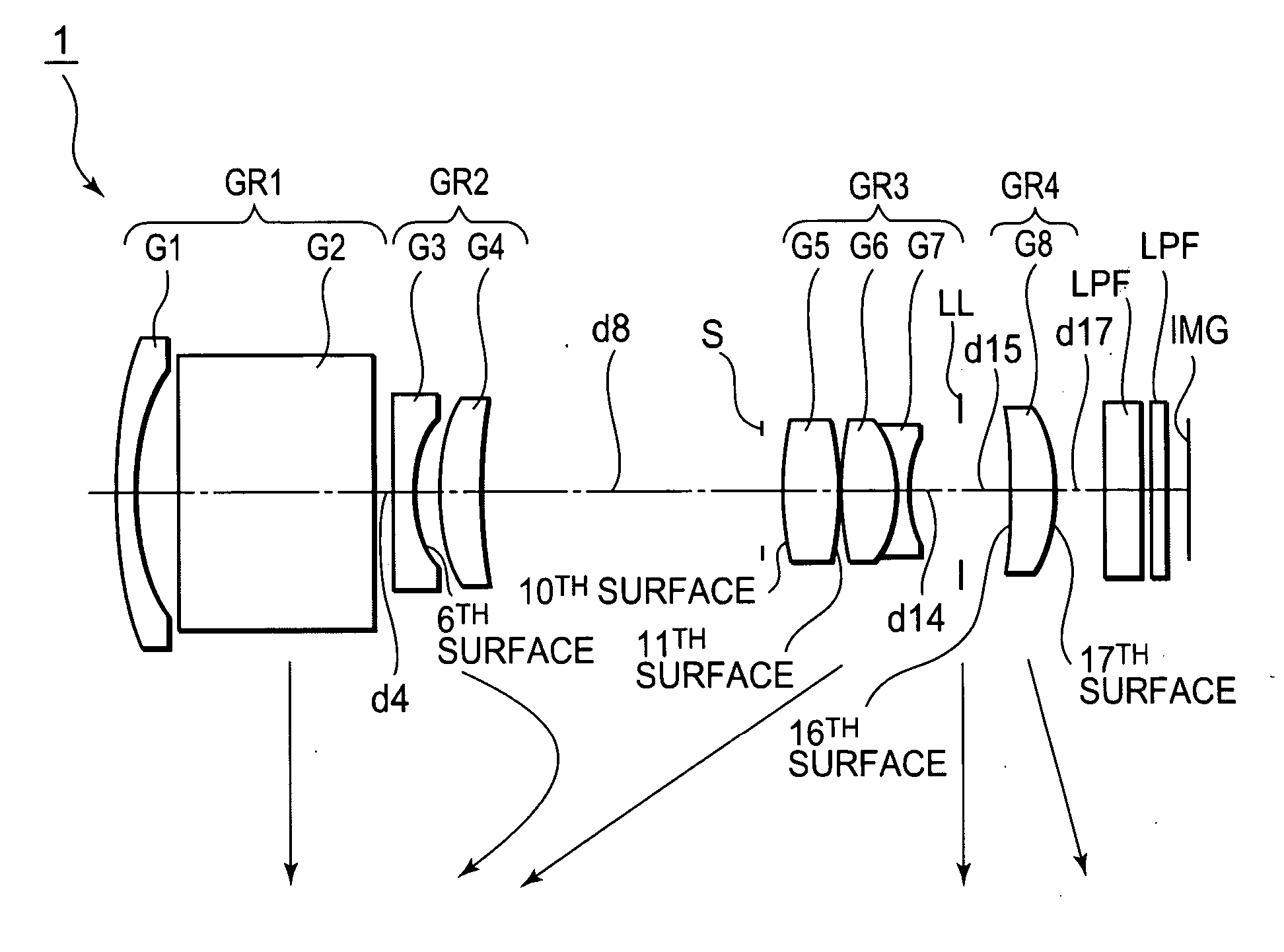
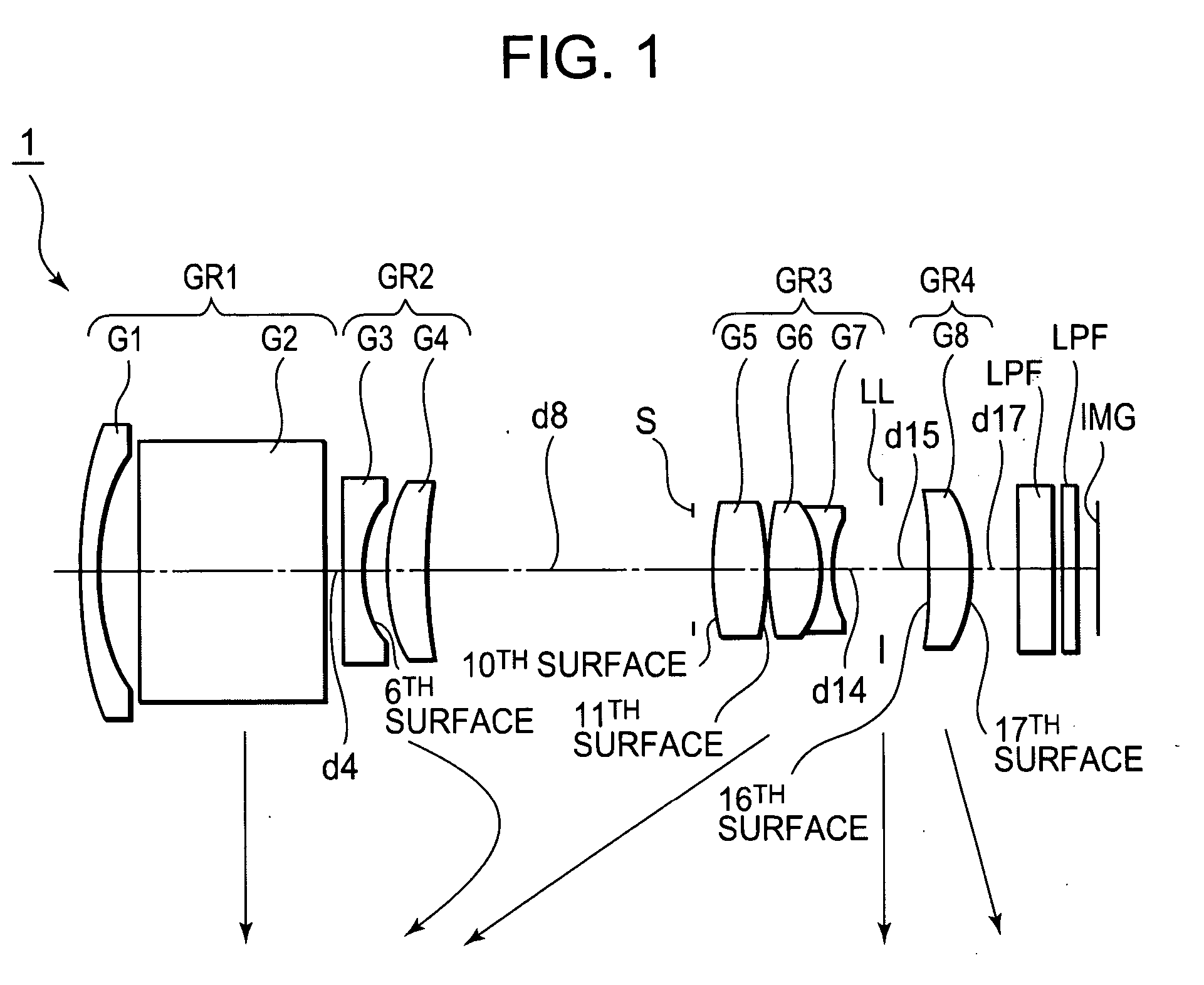
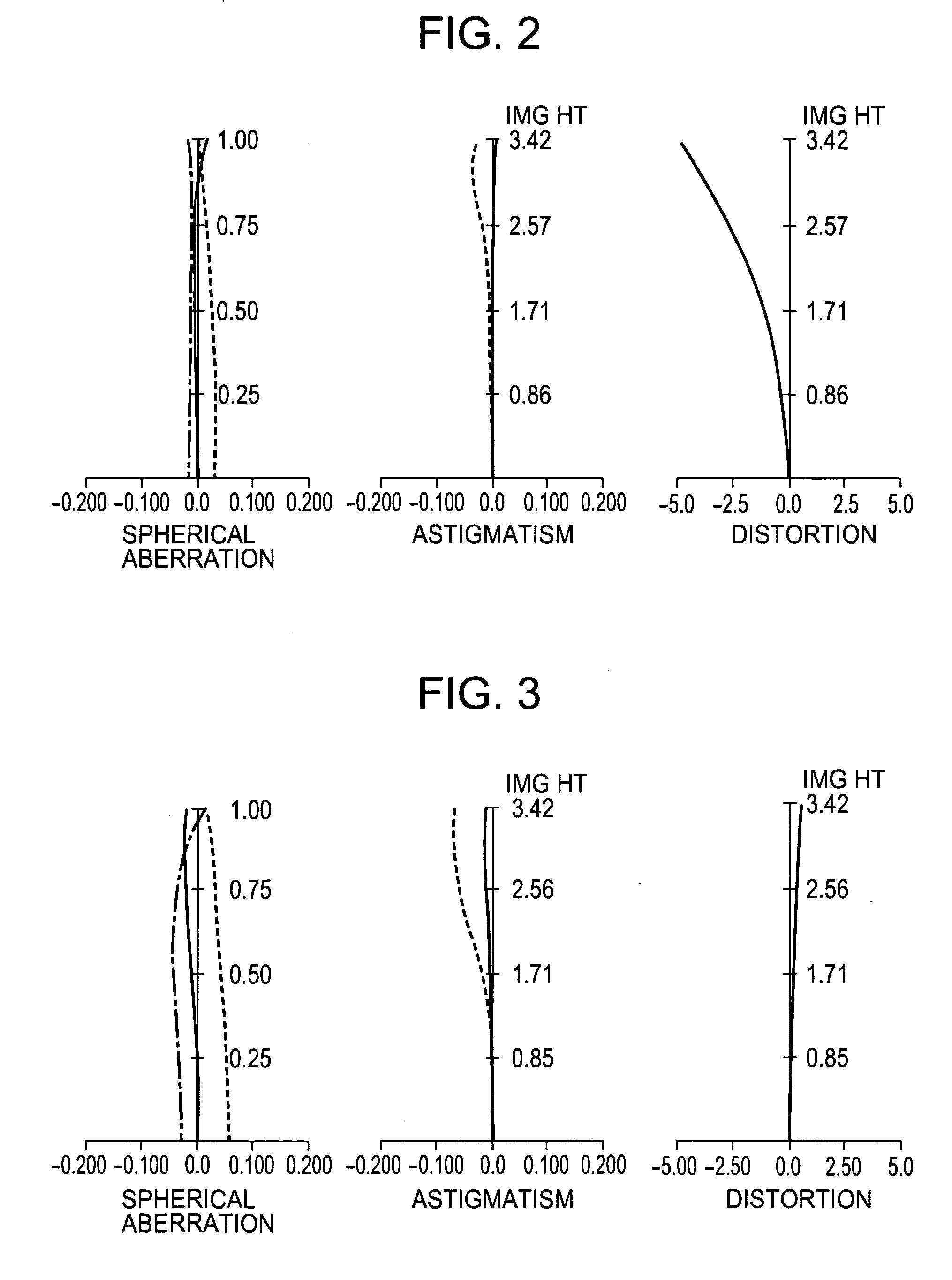
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49results about How to "Correcting blurring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Systems and methods for de-blurring motion blurred images
ActiveUS20060119710A1Correcting blurringTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer graphics (images)Deblurring
Systems and methods for providing a substantially de-blurred image of a scene from a motion blurred image of the scene are disclosed. An exemplary system includes a primary detector for sensing the motion blurred image and generating primary image information representing the blurred image, a secondary detector for sensing two or more secondary images of the scene and for generating secondary image information representing the two or more secondary images, and a processor for determining motion information from the secondary image information, estimating a point spread function for the motion blurred image from the motion information, and applying the estimated point spread function to the primary image information to generate information representing the substantially de-blurred image.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Motion blur correction
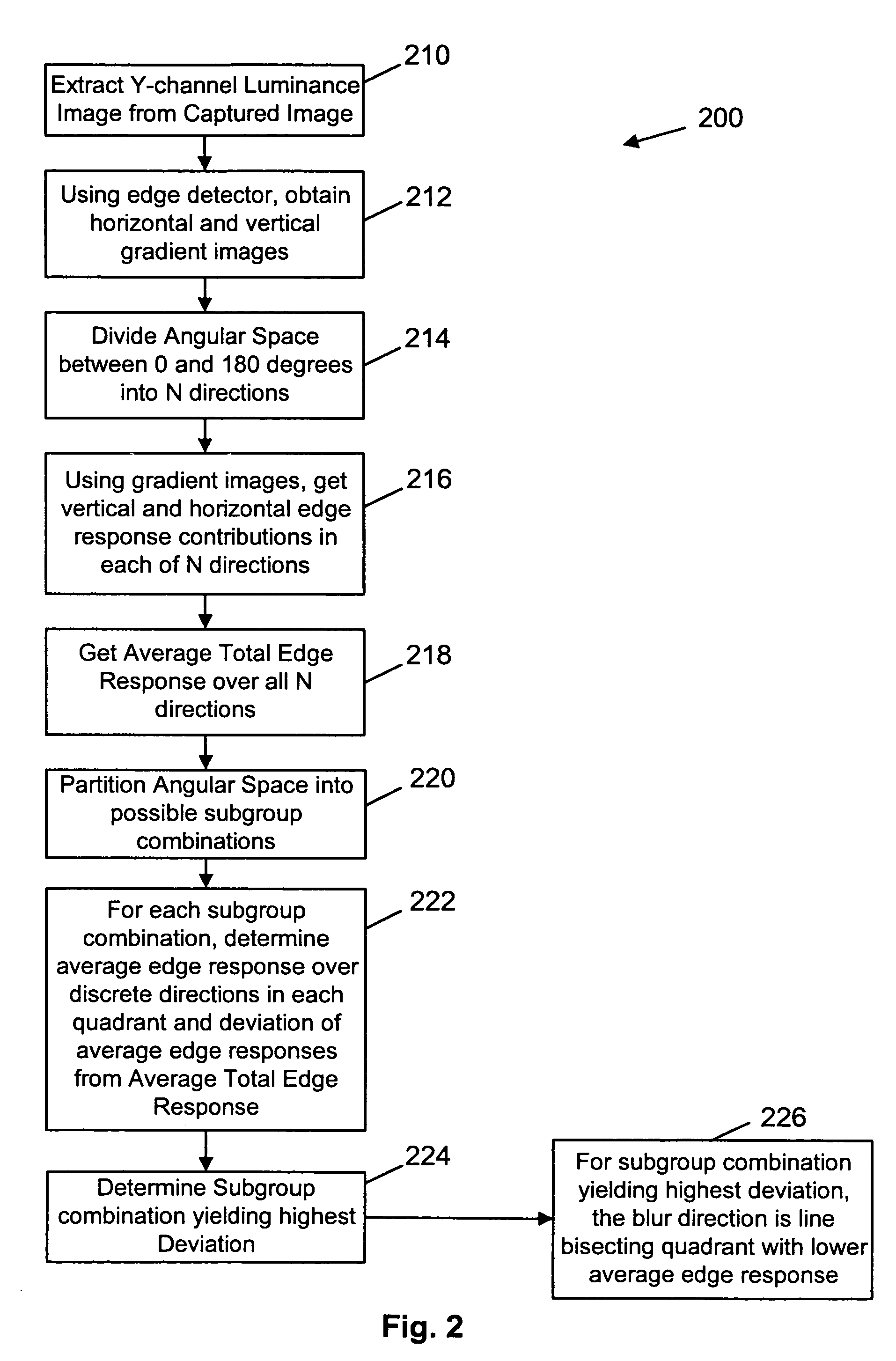
InactiveUS20050231603A1Correcting blurringReduce the possibilityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage basedMotion blur
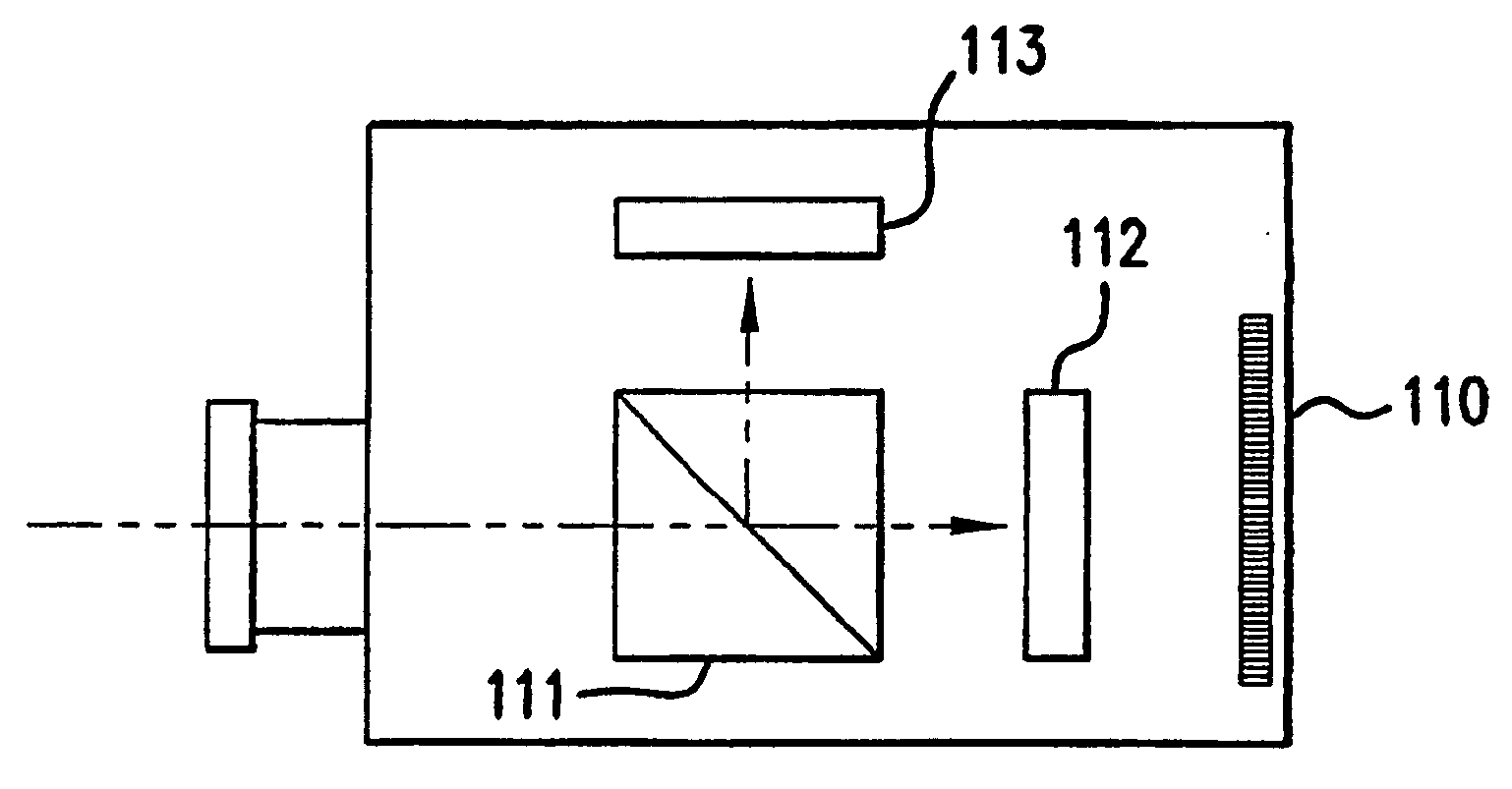
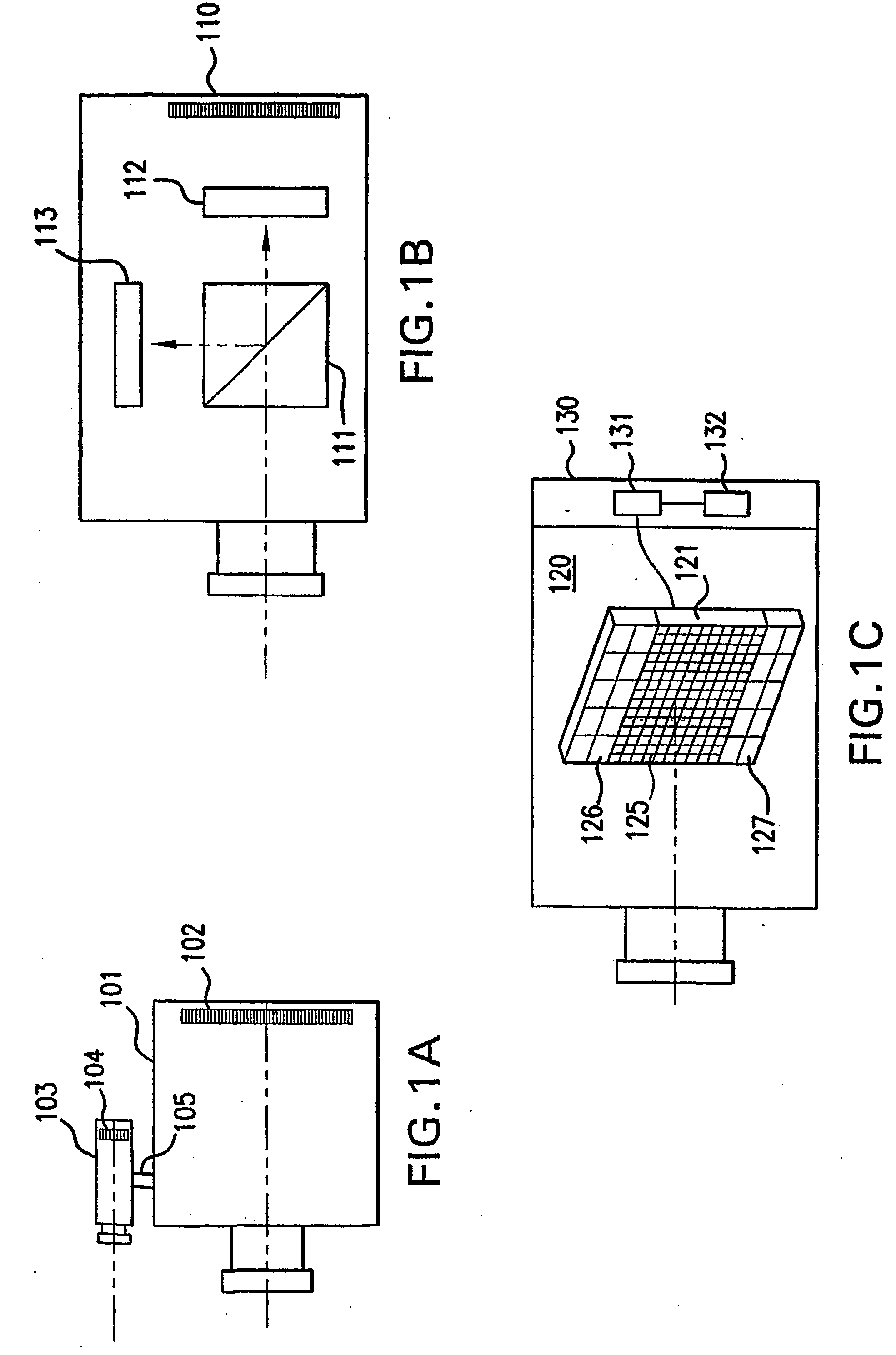
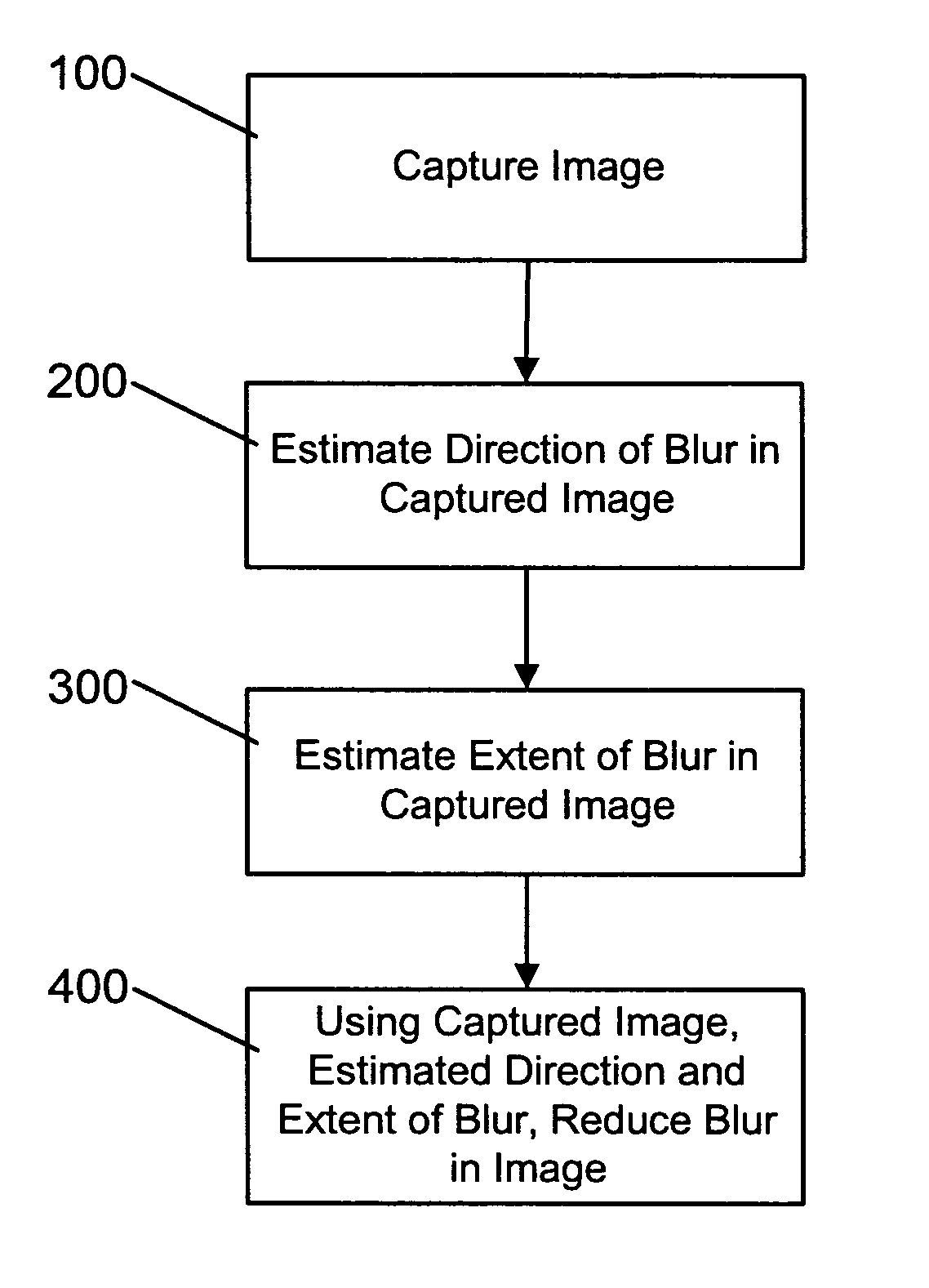
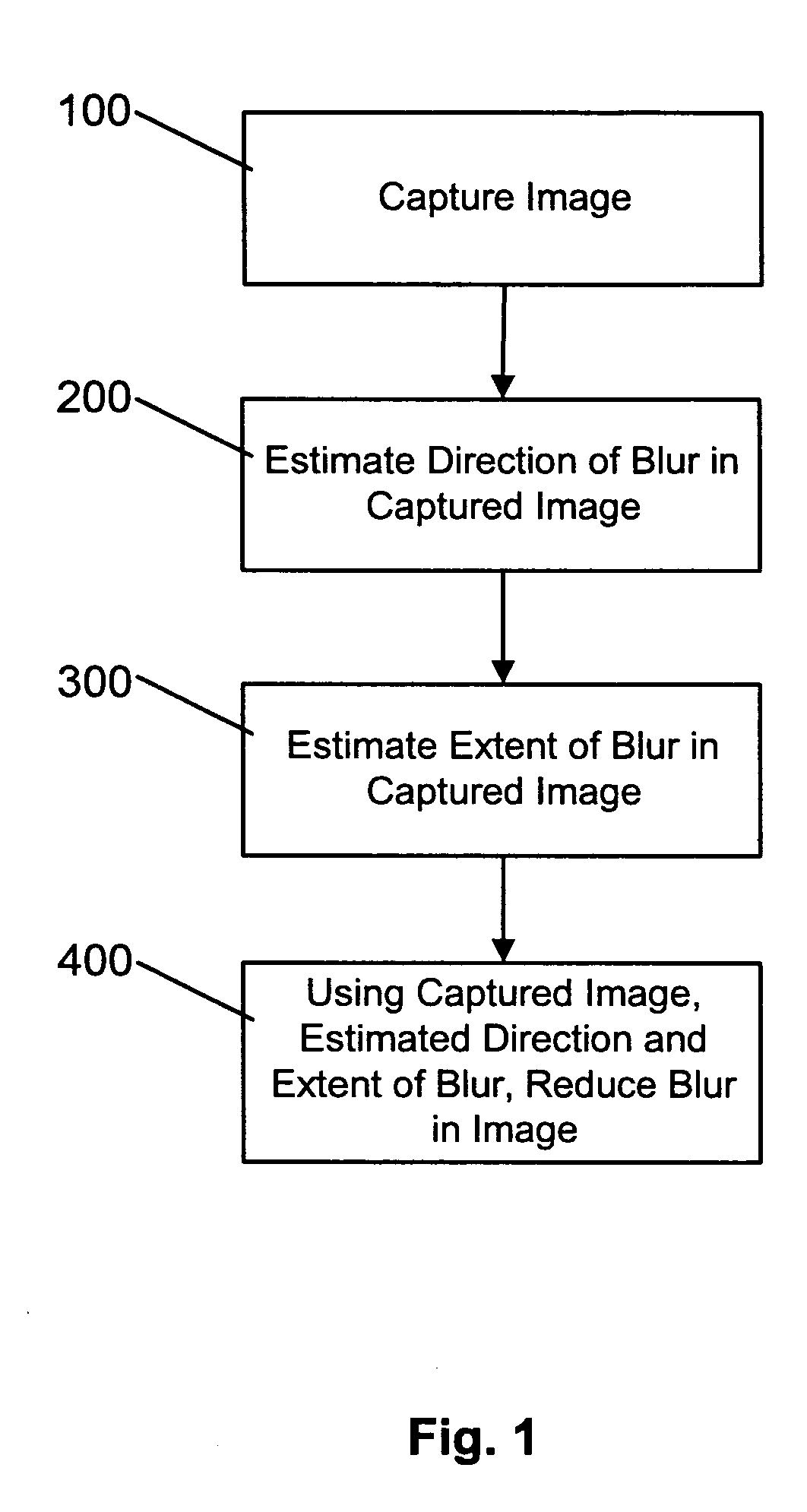
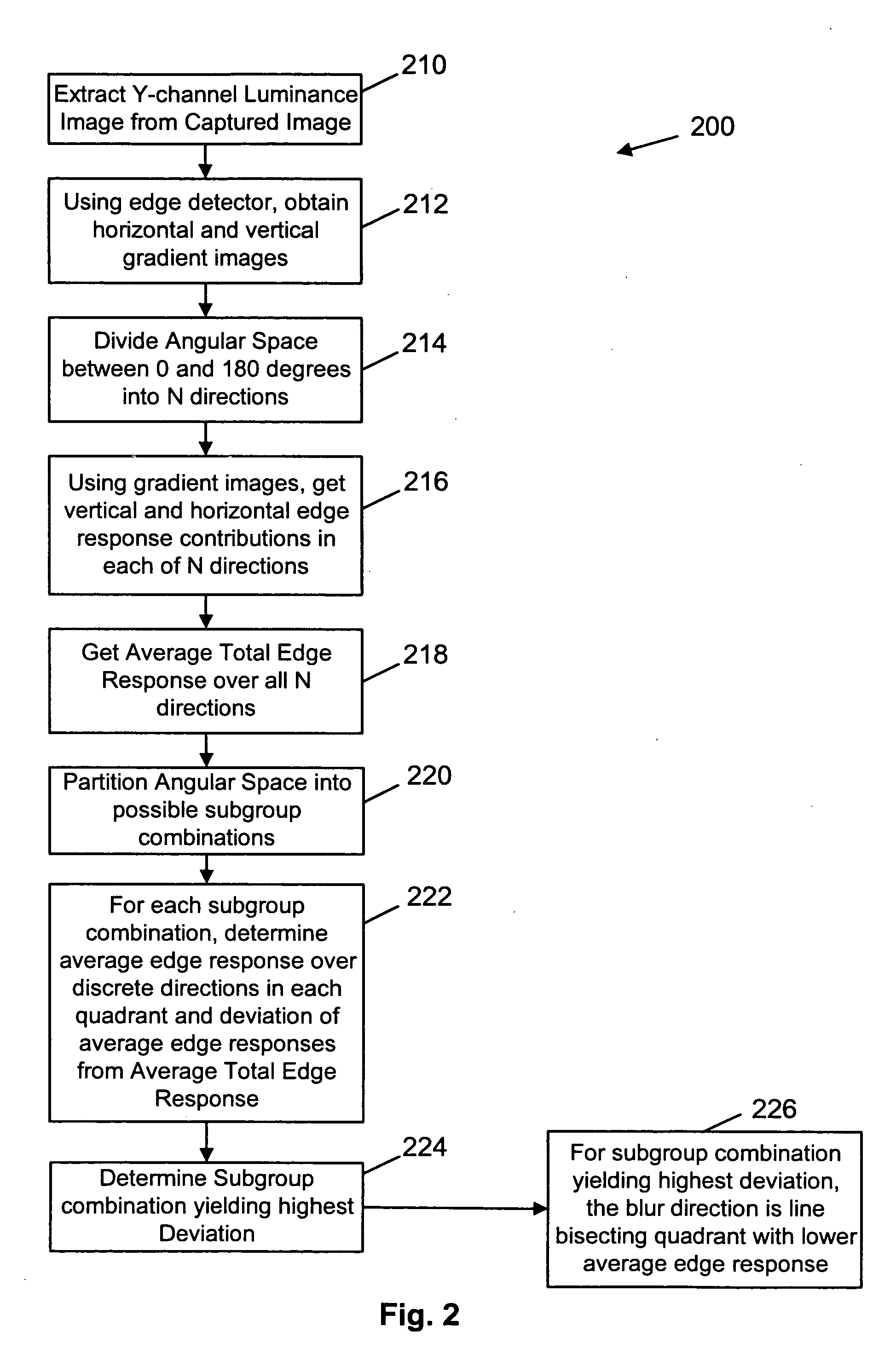
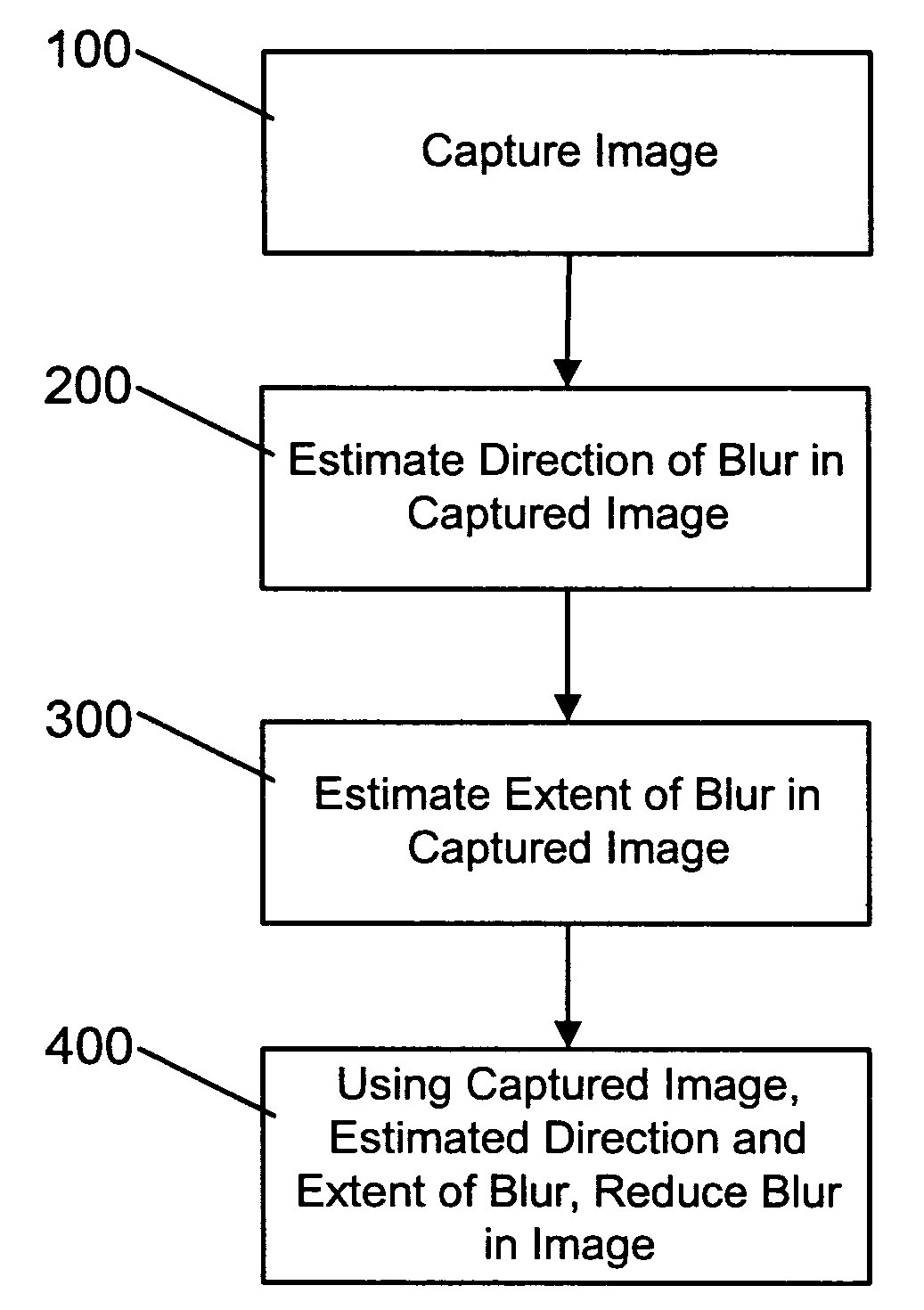
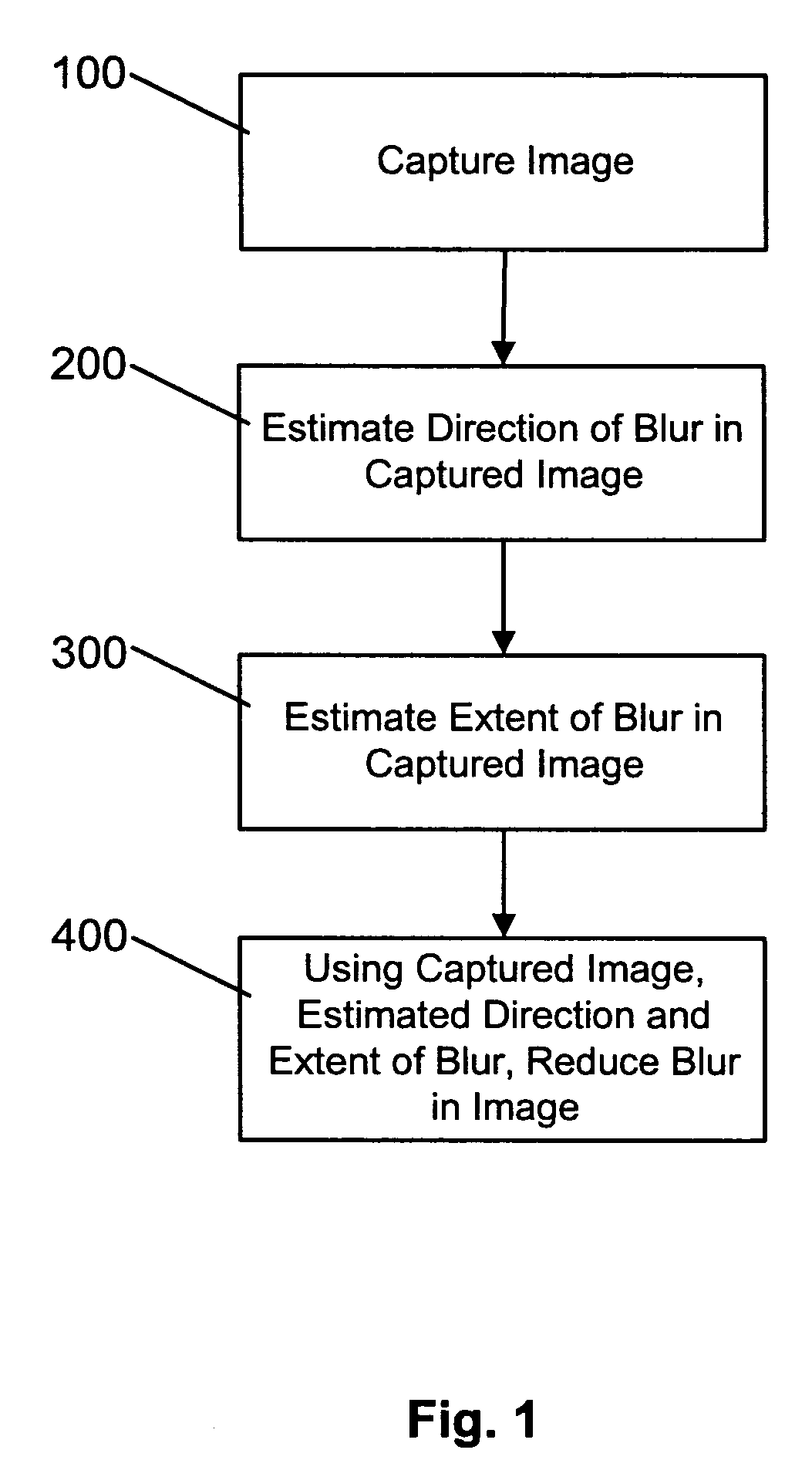
A method and apparatus of correcting blur in a motion blurred image includes estimating the direction of blur in the motion blurred image based on edge response of the motion blurred image over a set of discrete directions and over subgroups of the discrete directions. The extent of blur in the motion blurred image is also estimated. An initial guess image based on the motion blurred image is generated and the guess image is blurred as a function of the estimated blur direction and blur extent. The blurred guess image is compared with the motion blurred image to generate an error image. The error image is blurred and weighted and then combined with the initial guess image thereby to update the guess image and correct for blur.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Motion blur correction
InactiveUS7561186B2Correcting blurringReduce the possibilityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage basedMotion blur
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
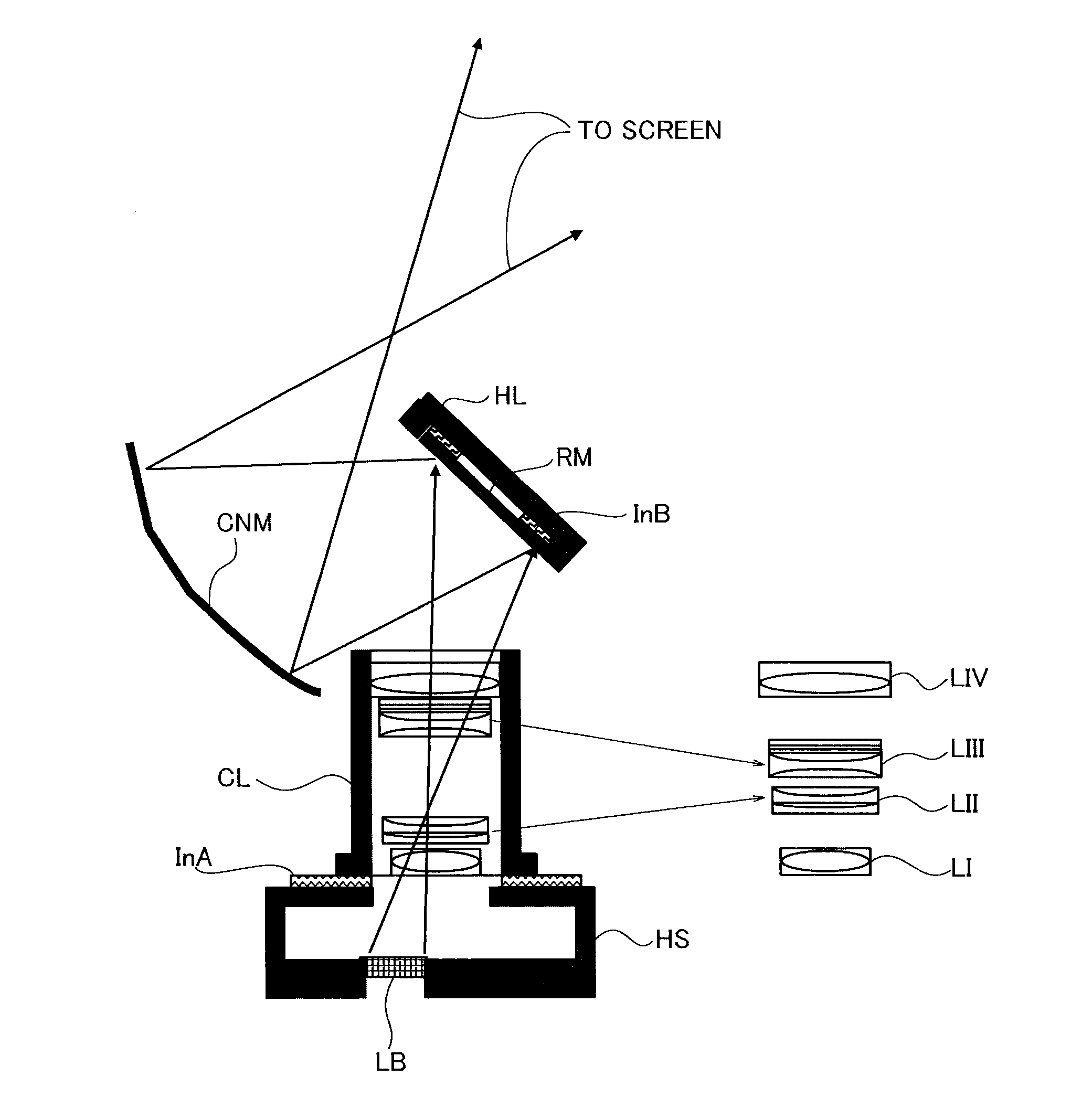
Image display device
ActiveUS20130114053A1Correcting blurringProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementPhysicsLighting system
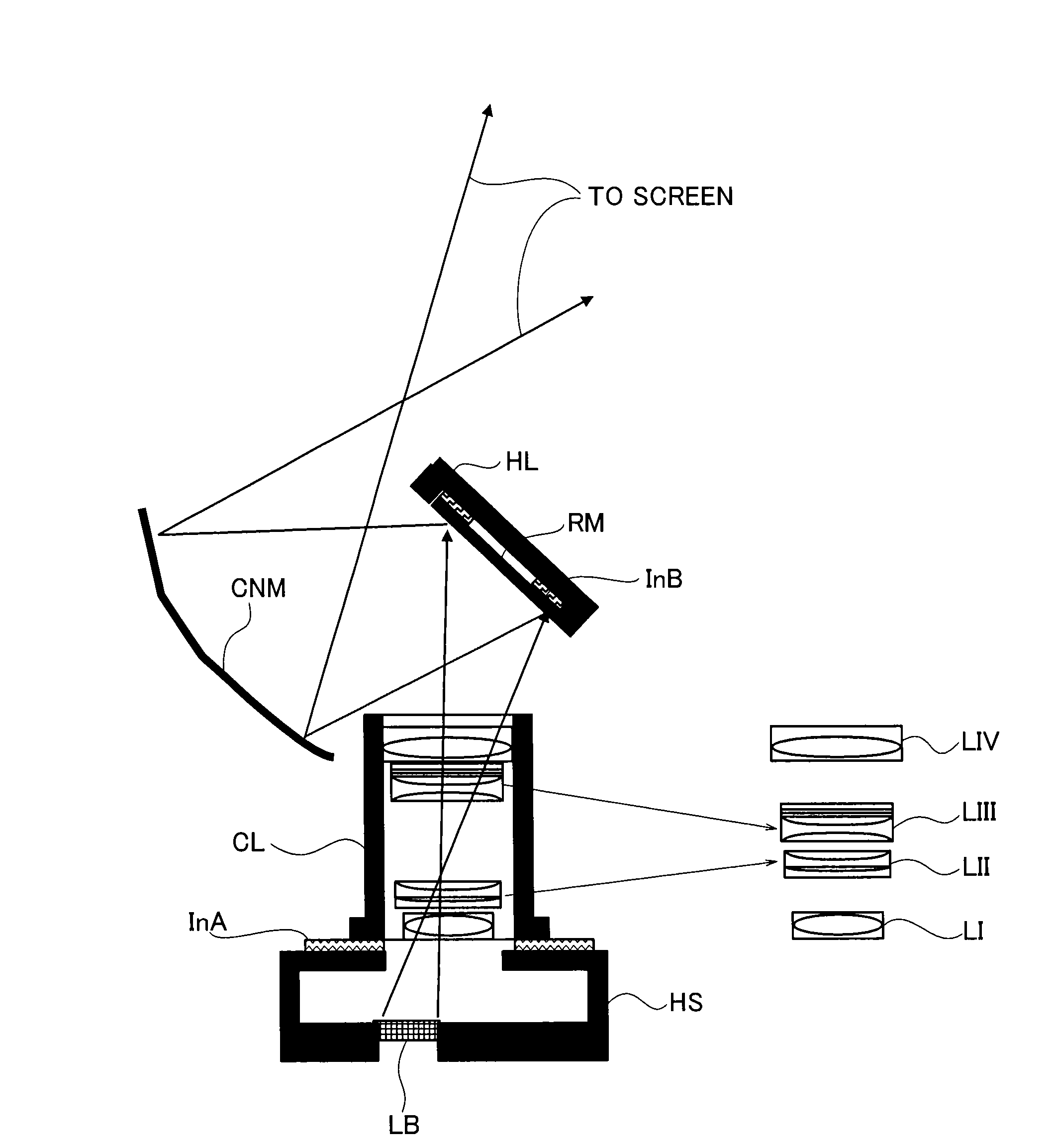
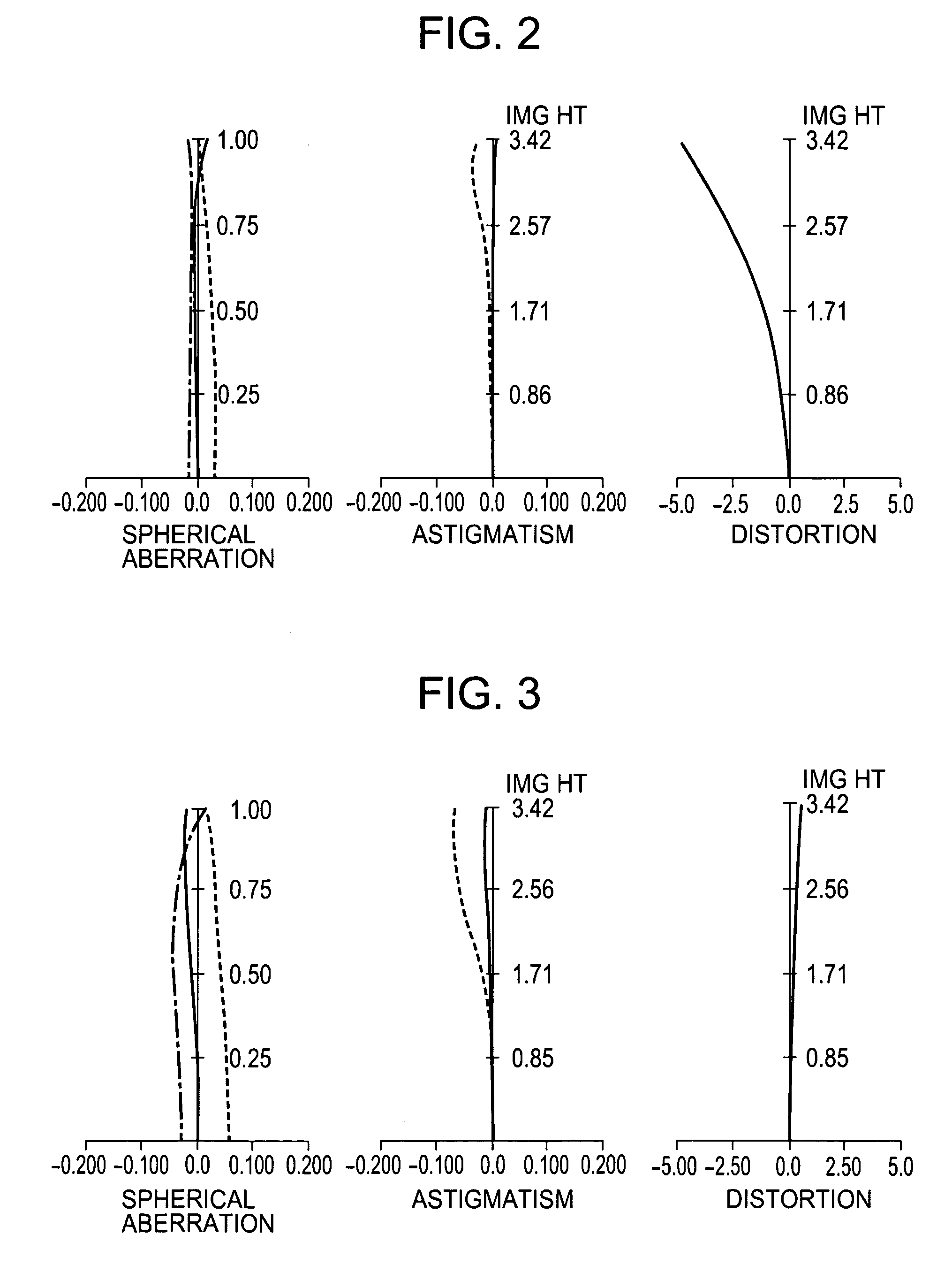
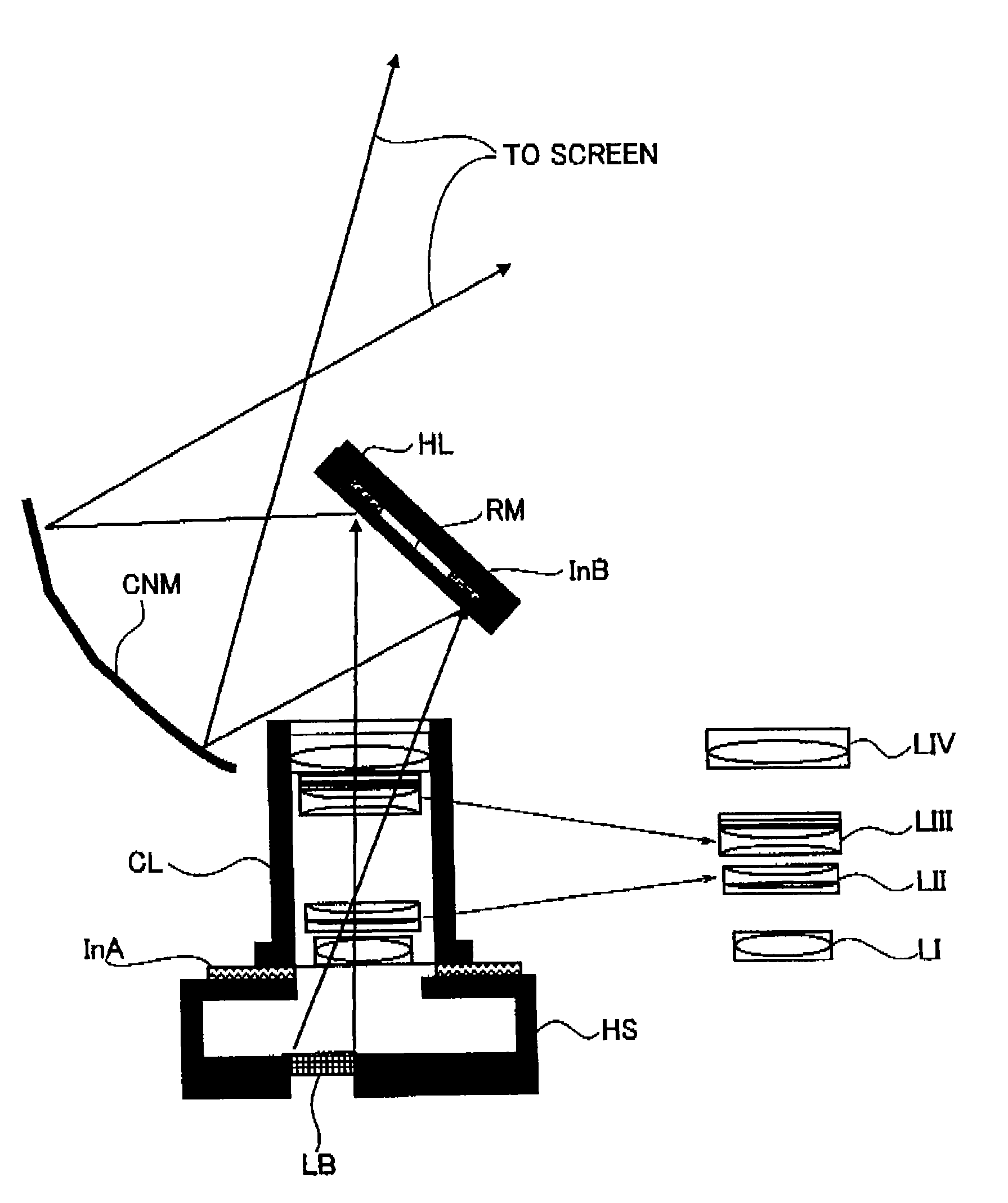
An image display device includes an image display element, a light source, an illumination system, a projector system comprising a refractive optical system including a plurality of lens groups, and a mirror train including a curved mirror, a first focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups of the refractive optical system by different amounts along a normal line of the image display element, and a second focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups along the normal line of the image display element by different amounts from those of the first focus structure.
Owner:RICOH KK
Prediction coefficient operation device and method, image data operation device and method, program, and recording medium
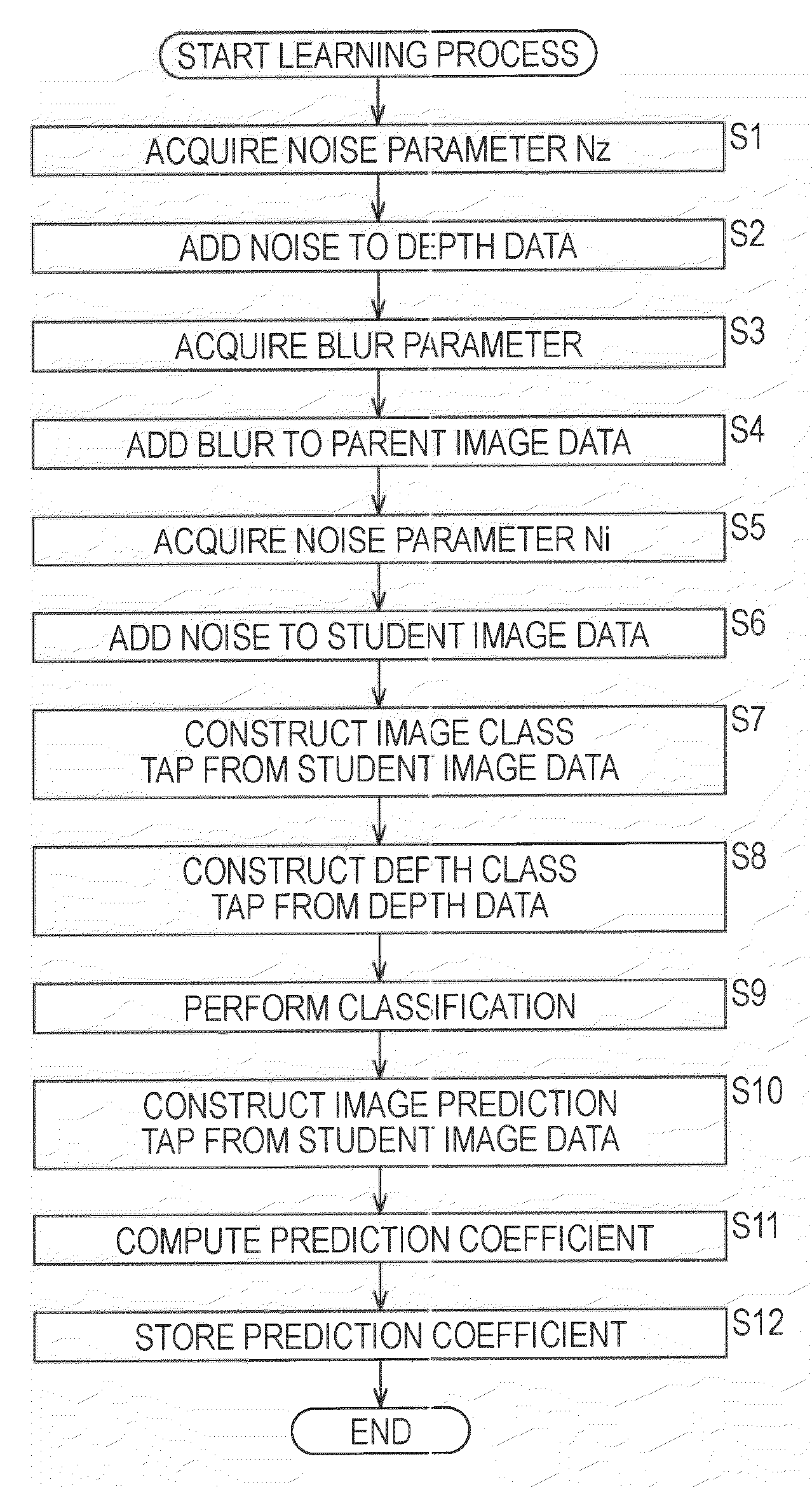
InactiveUS20100061642A1Correcting blurringAccurate imagingImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
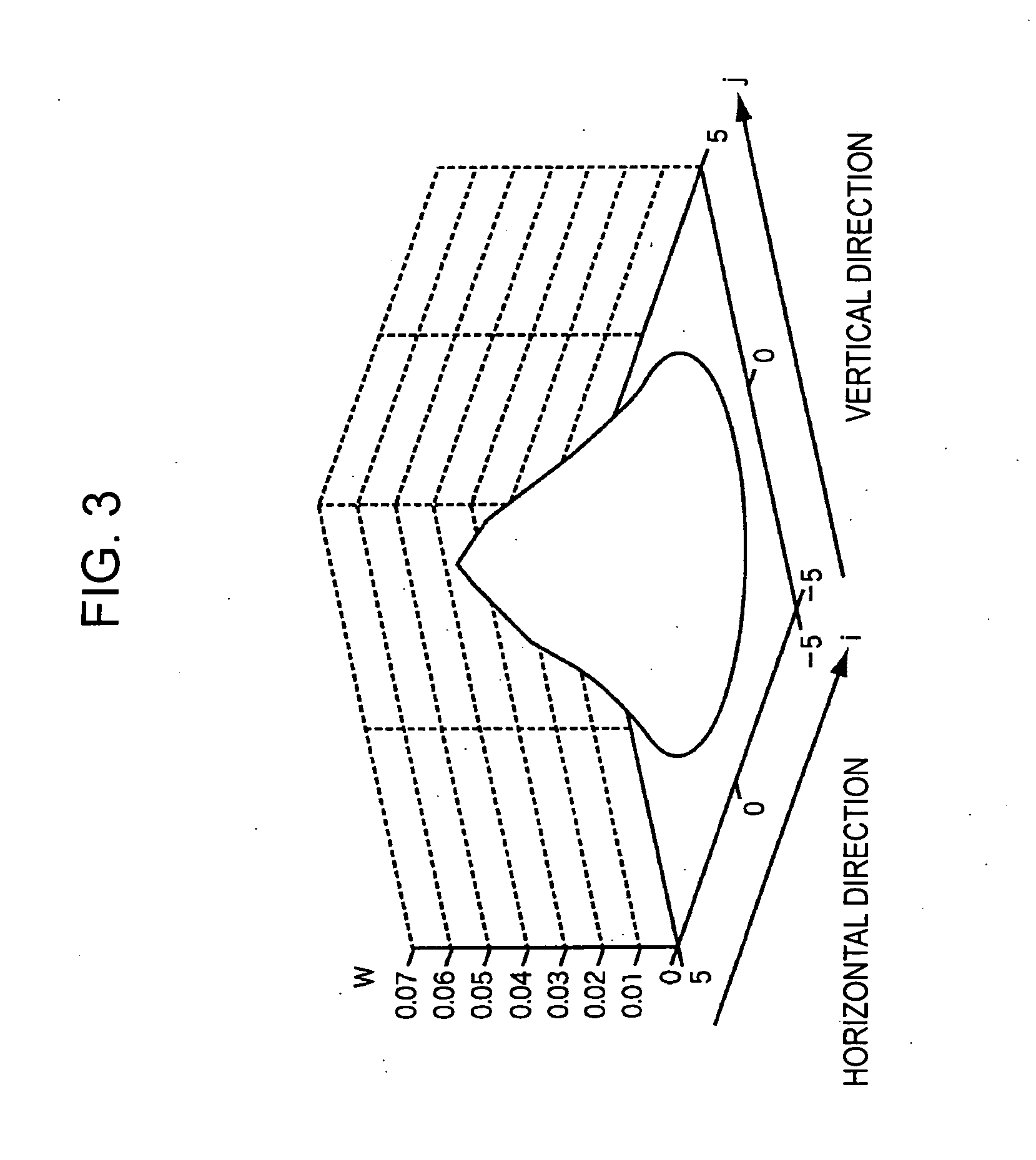
The present invention relates to a prediction coefficient computing device and method, an image data computing device and method, a program, and a recording medium which make it possible to accurately correct blurring of an image. A blur adding unit 11 adds blur to parent image data on the basis of blur data of a blur model to generate student image data. A tap constructing unit 17 constructs an image prediction tap from the student image data. A prediction coefficient computing unit 18 computes a prediction coefficient for generating image data corresponding to the parent image data, from image data corresponding to the student image data, on the basis of the parent image data and the image prediction tap. The present invention can be applied to an image processing device.
Owner:SONY CORP
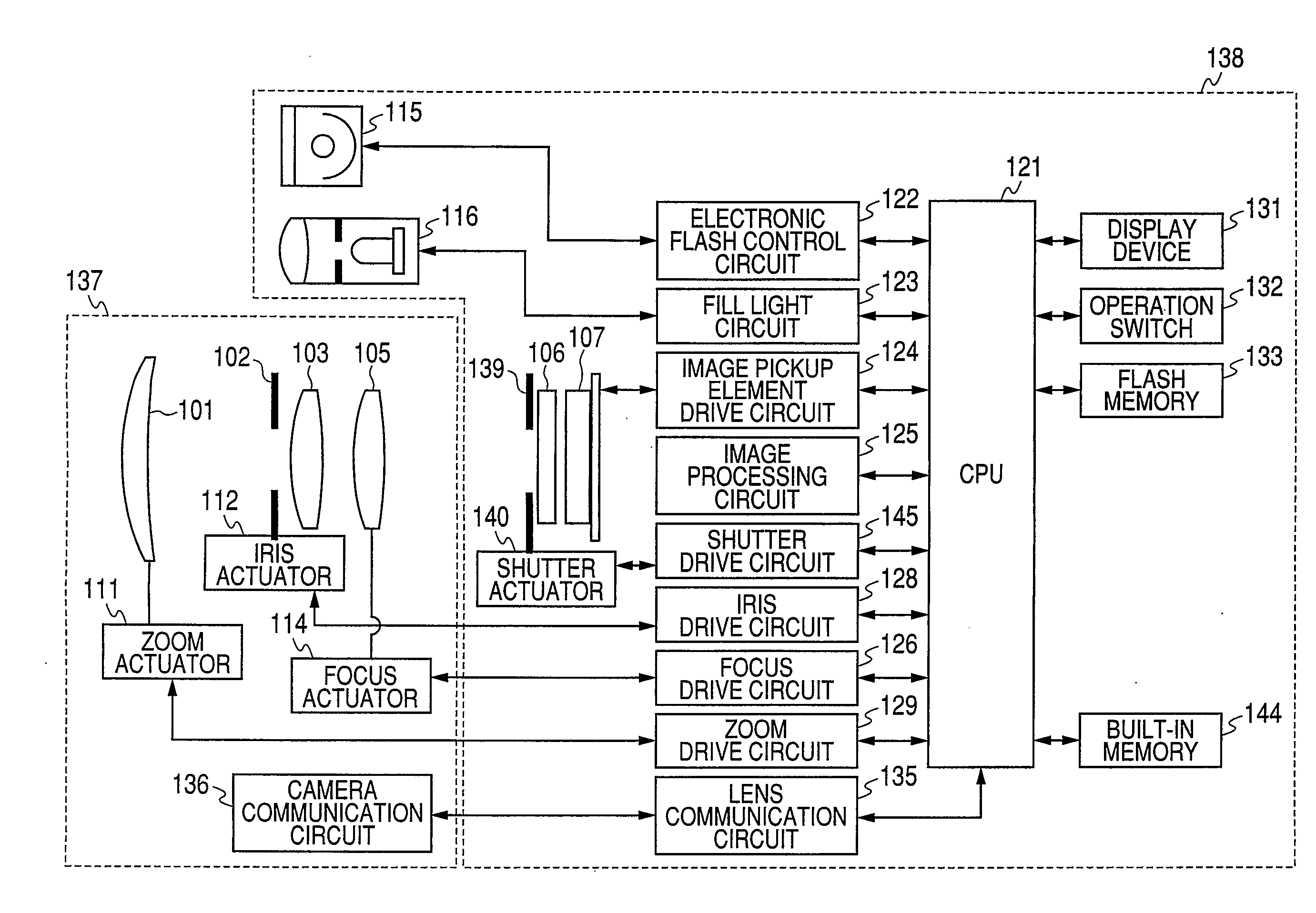
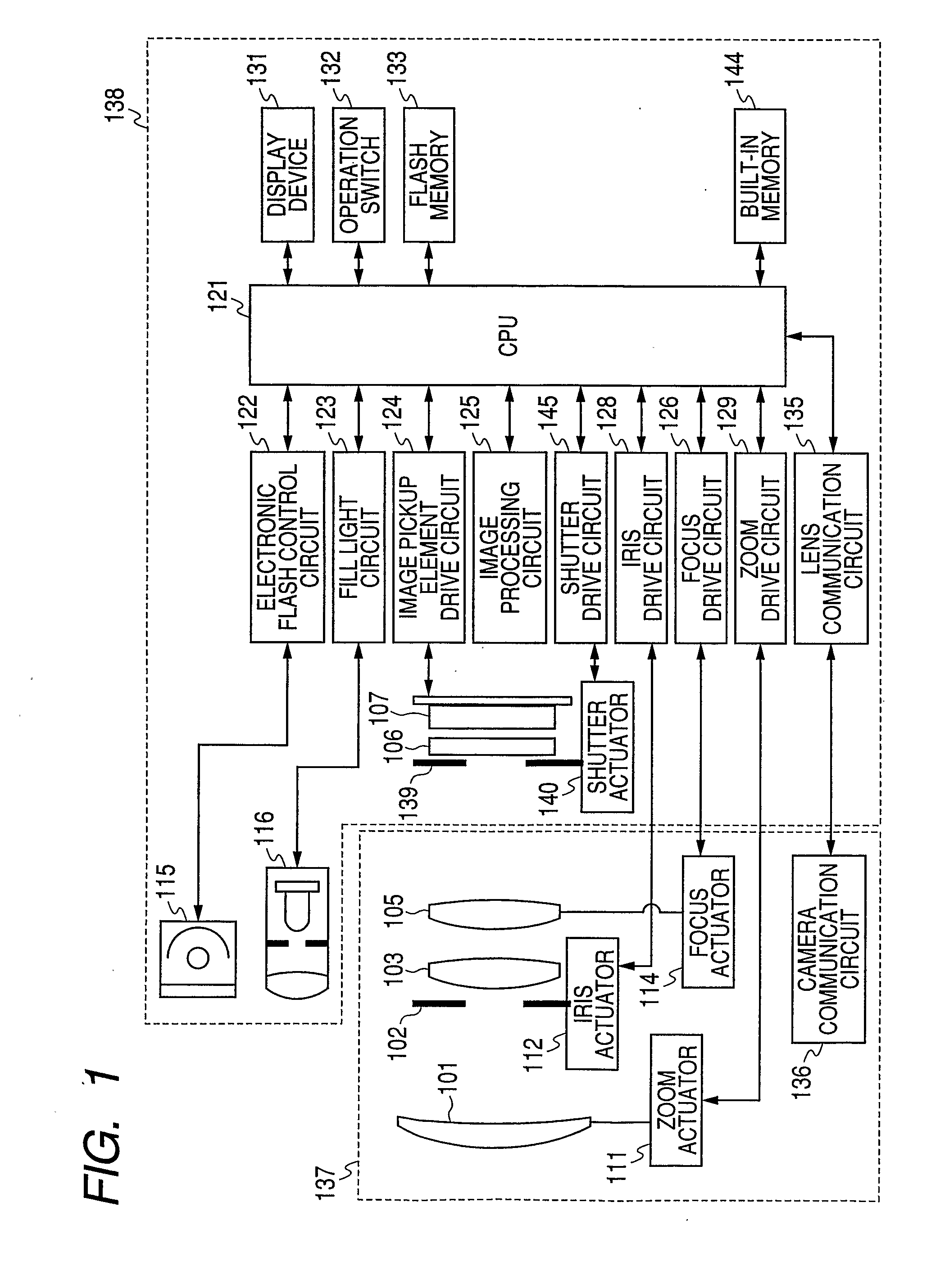
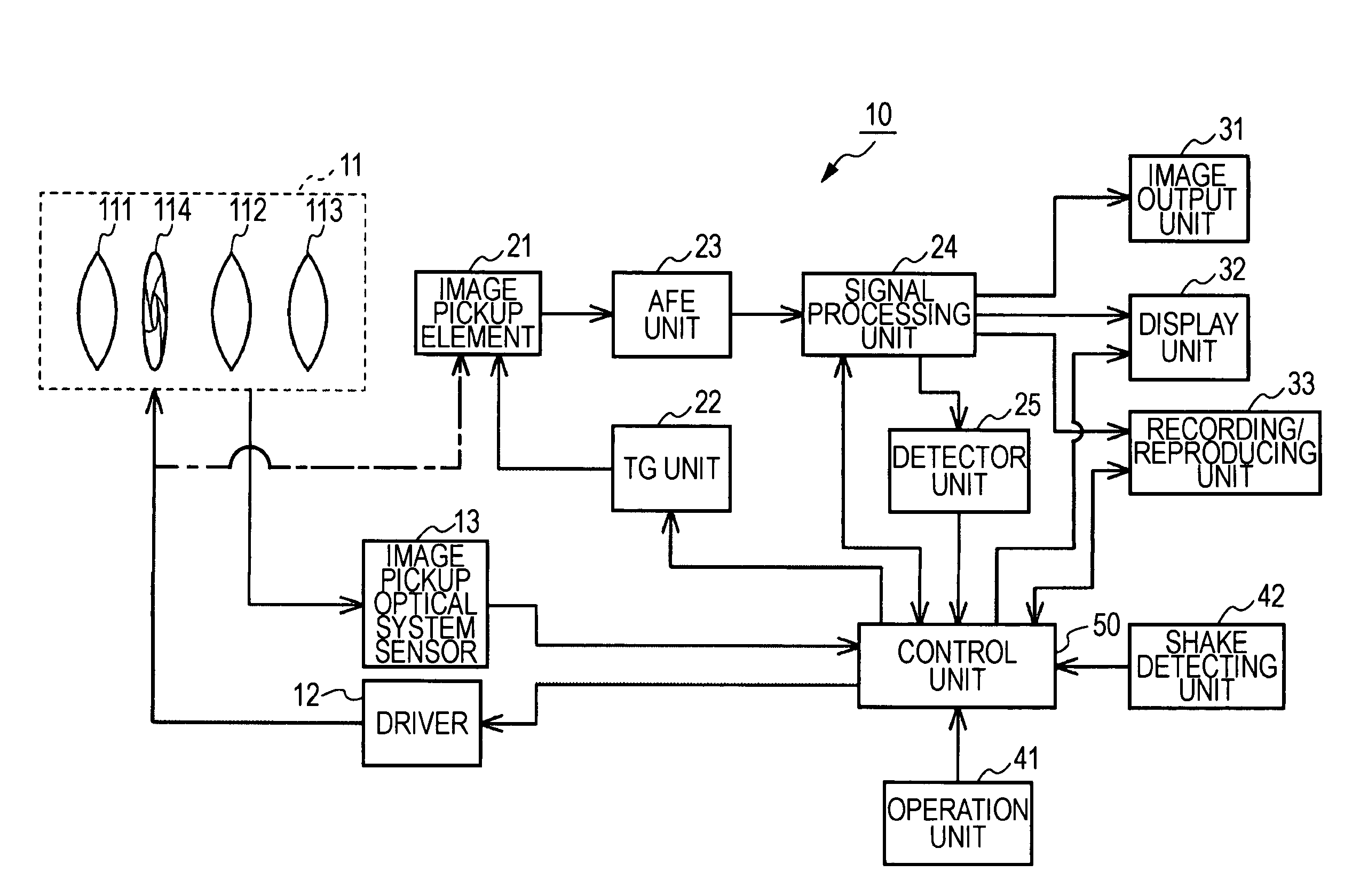
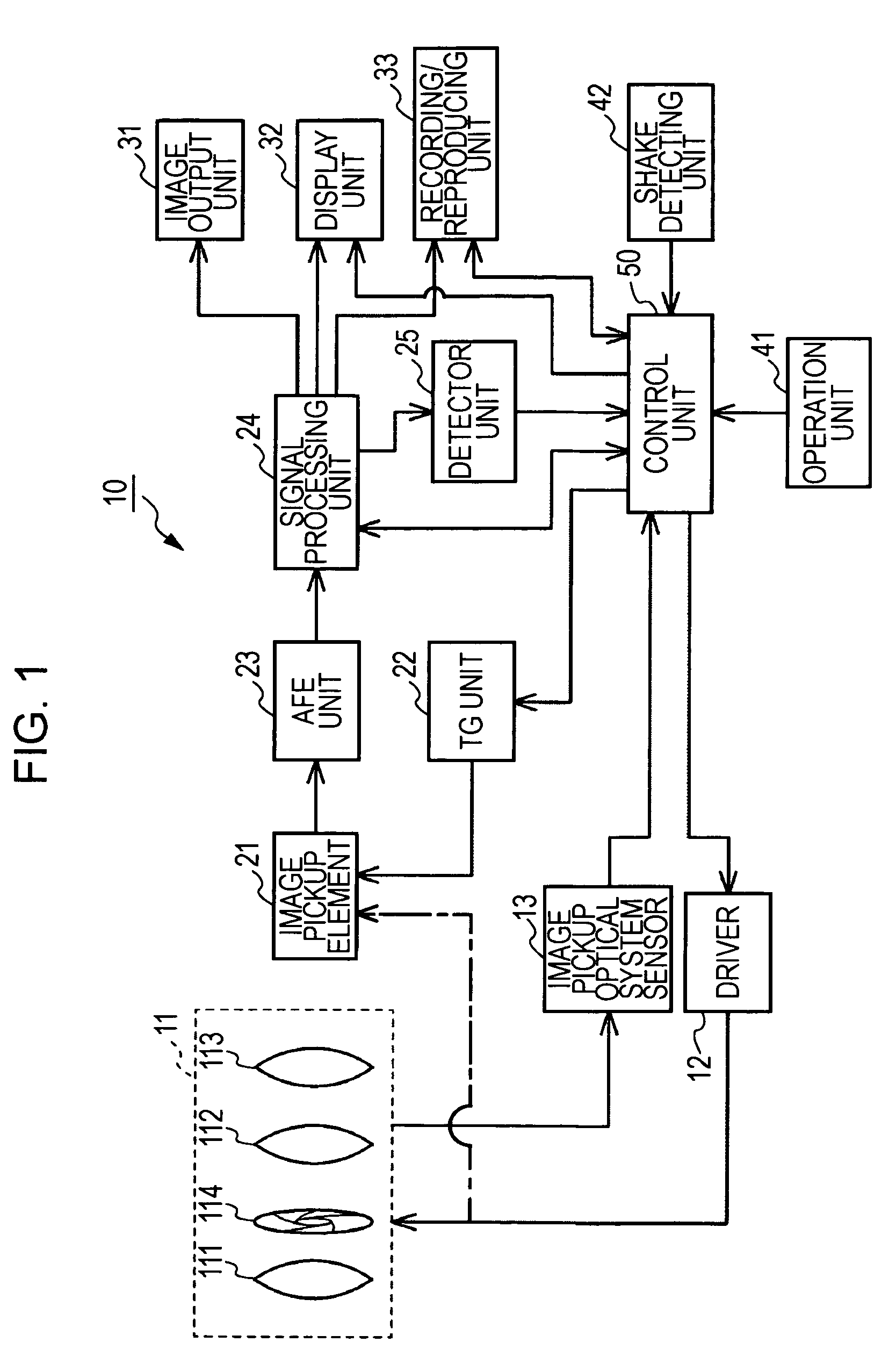
Image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20120007997A1Easy to confirmEasily grasp blur correctable rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Photoelectric conversion
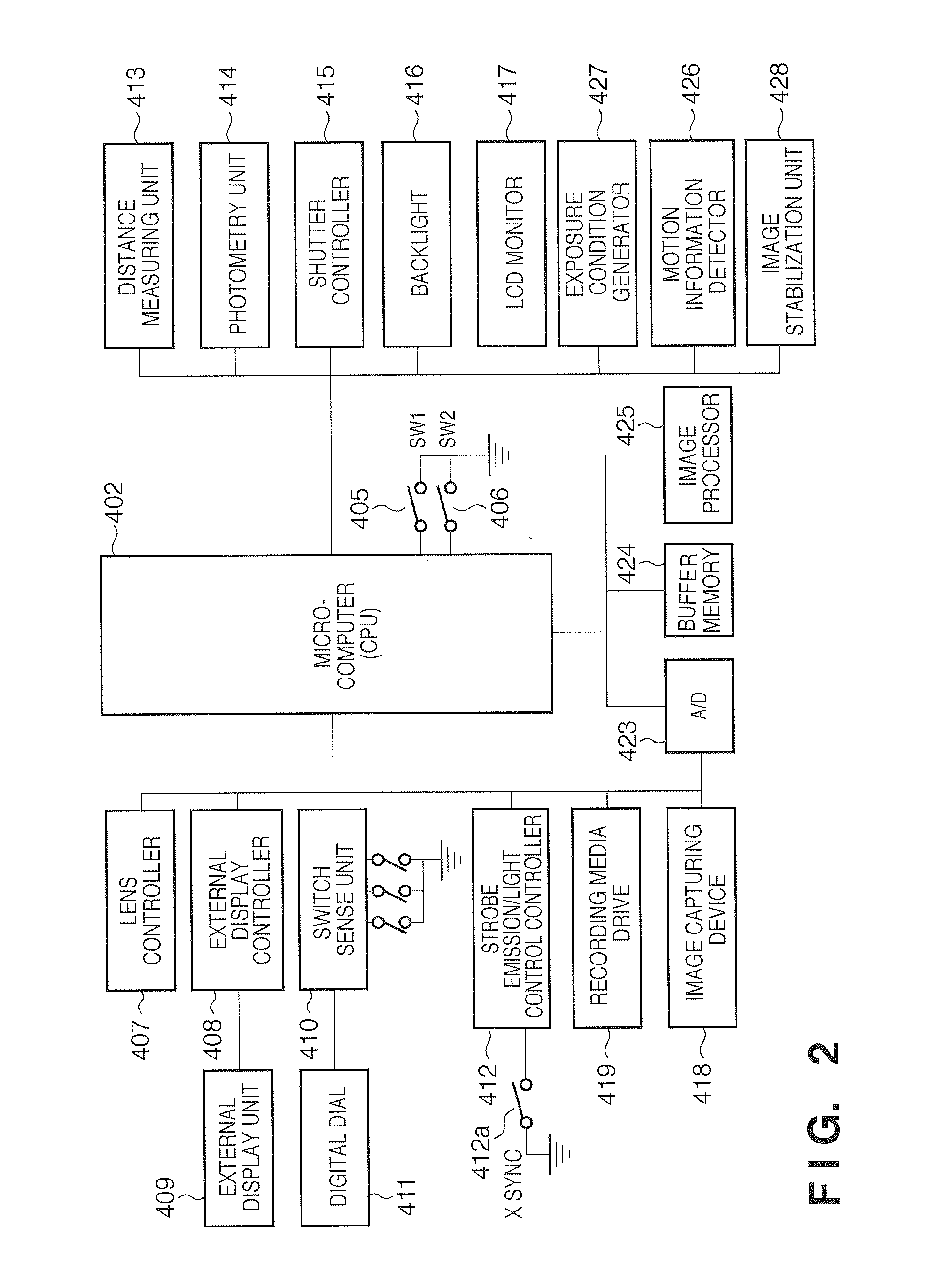
The invention provides an image pickup apparatus with a blur correcting unit which has a display function of causing a photographer to easily confirm a photographed image. The image pickup apparatus includes photographing lens which forms an object image, a photoelectric conversion unit which is disposed on a predicted image plane of the photographing lens, a display unit which displays a photographed image obtained by the photoelectric conversion unit, an image display control unit which displays the photographed image by the display unit after the photographed image is obtained by the photoelectric conversion unit, a distance information acquiring unit which obtains distance information in the photographed image, and a blur correcting unit which performs blur correction on the photographed image based on the distance information obtained by the distance information acquiring unit. The image display control unit displays the photographed image where plural distances in the photographed image are focused.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing unit, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS20120086829A1Correcting blurringImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing unit includes a memory unit, a comparative image generator to generate a comparative image from a non-reference image, an image divider to divide a reference image, a non-reference image, and a comparative image into image blocks of a predetermined size, a motion data calculator to calculate motion data between the reference image and comparative image, an average calculator to calculate an average of pixel output values for each image block of the reference image and the comparative image, a threshold determiner to determine a threshold for synthesis determination according to the average of pixel output values of an image block of the reference image, a synthesis determiner to determine whether or not the image blocks of the reference image and of the non-reference image are suitable for synthesis, and a ratio determiner to determine a synthesis ratio of the image blocks determined as suitable for synthesis.
Owner:RICOH KK
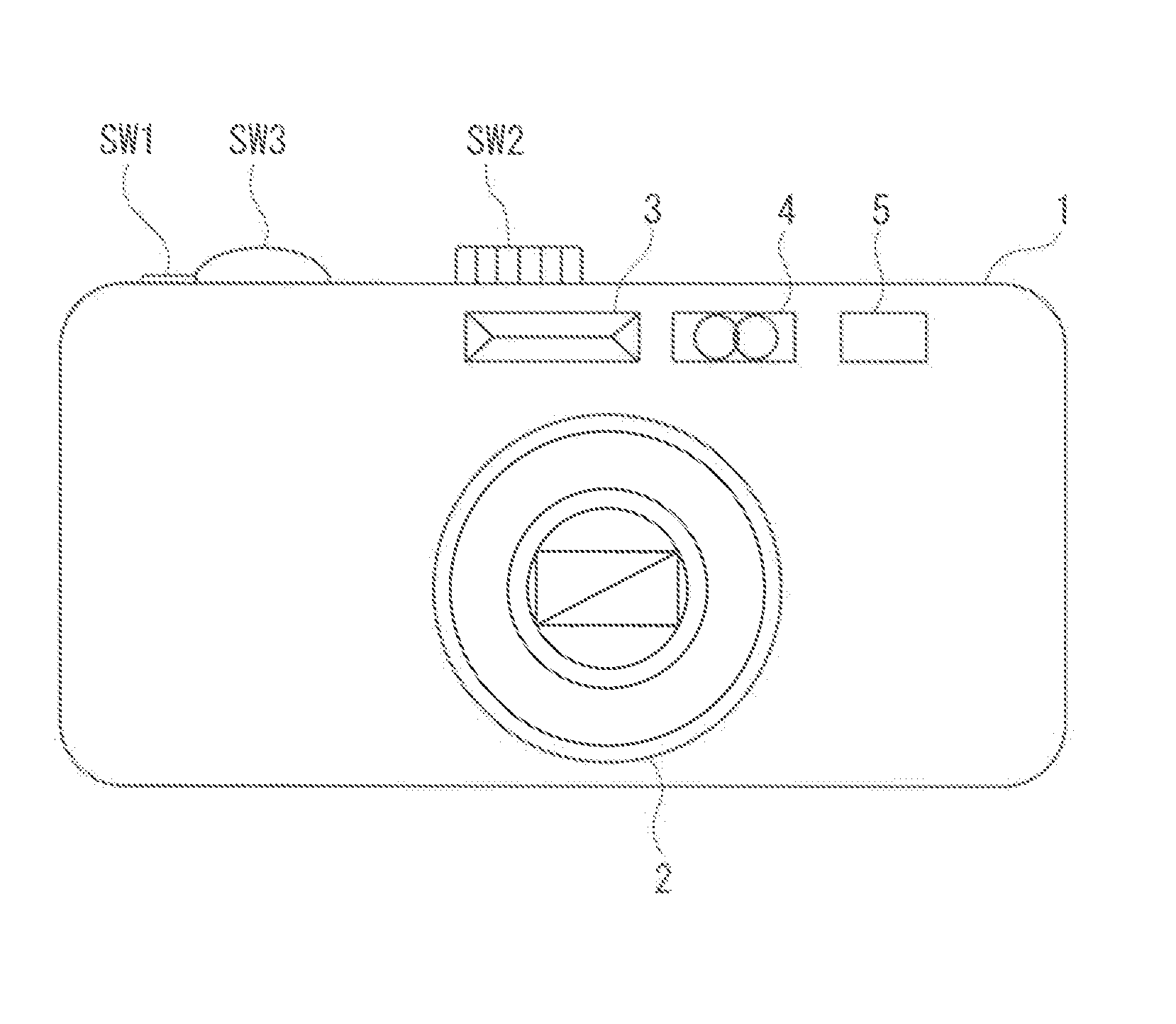
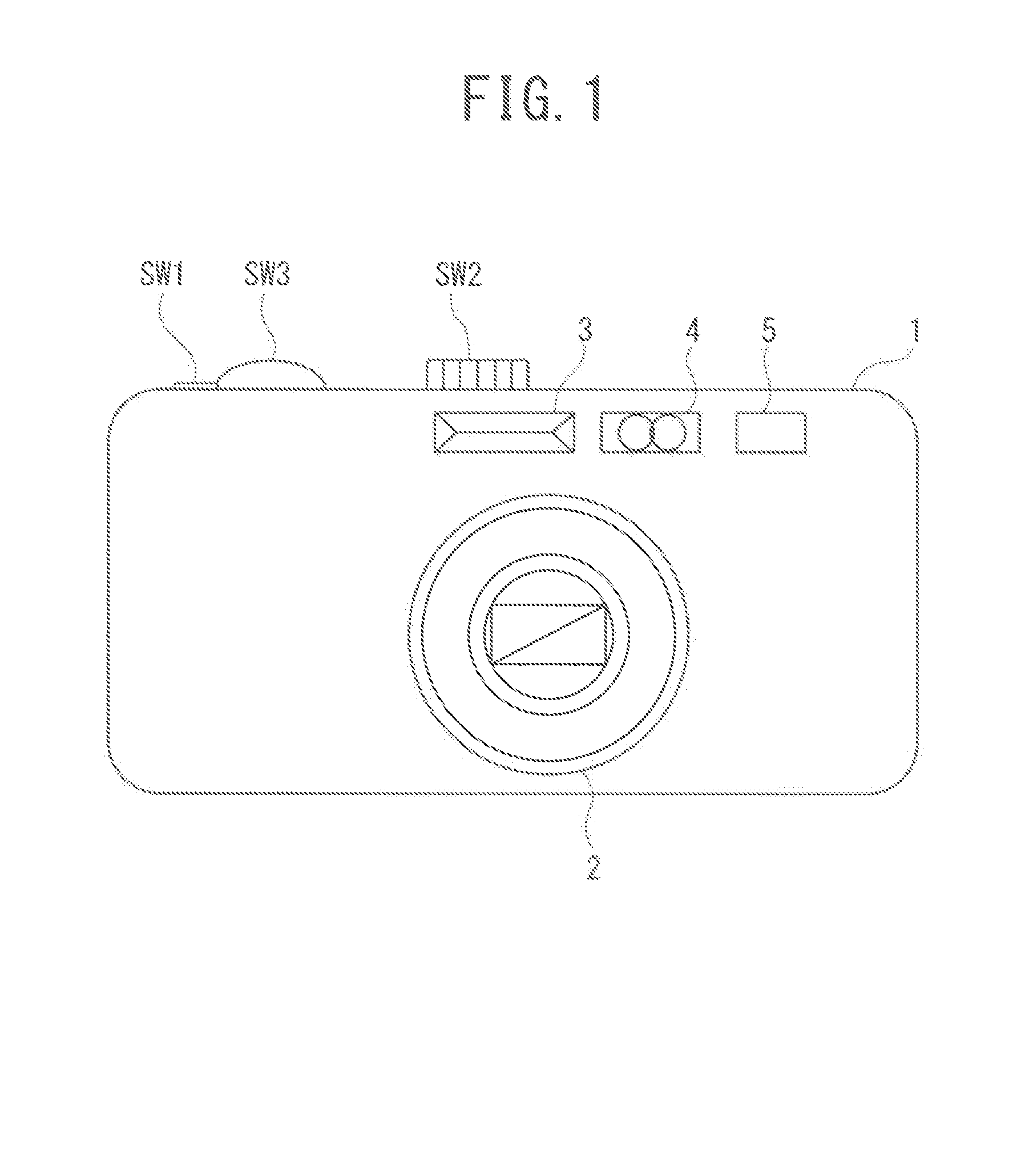
Clock generating device, vibration type gyro sensor, navigation device, imaging device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7258009B2Suppressing the device from being largeSubject to movementTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationTime informationGyroscope
A vibration gyro sensor is provided which is capable of generating time information and detecting an angular velocity. A driving signal for driving a tuning fork piezoelectric vibrating reed is generated based on an excitation signal generated by an oscillation circuit. An angular velocity signal is obtained based on a detection signal generated by a detection electrode of the tuning fork piezoelectric vibration reed. The excitation signal generated by the oscillation circuit is input to a divider such that a timer clock signal is generated.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
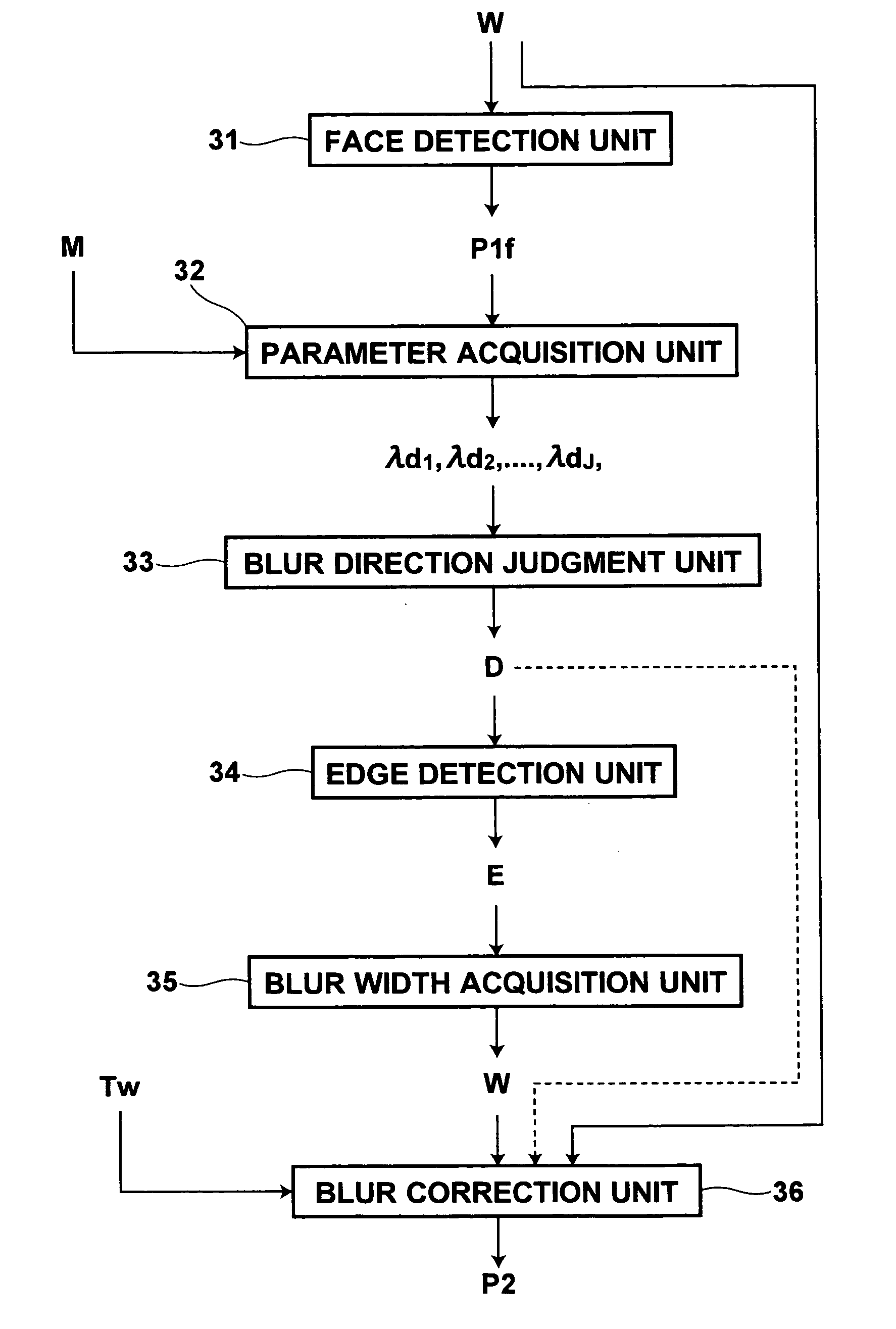
Method and apparatus for judging direction of blur and computer-readable recording medium storing a program therefor
ActiveUS20070071346A1Simple configurationImprove processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisMathematical modelAngular rate sensor
Without use of special hardware such as an angular rate sensor, a direction of blur can be judged with high accuracy. A parameter acquisition unit obtains weighting parameters for principal components representing directions of blur in a predetermined structure in an image by fitting to the structure a mathematical model generated by a method of AAM using a plurality of sample images representing the structure in different conditions of blur. A blur direction judgment unit judges the direction of blur based on the weighting parameters, and a blur width acquisition unit finds a width of blur based on an edge component found by an edge detection unit in the direction perpendicular to the direction of blur. A blur correction unit corrects the blur in the image based on the direction and the width of blur.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Magnification optical system
A magnification optical system forms an enlarged image of an object. It includes a refractive optical system including a plurality of lens groups; and a mirror train including a curved mirror, arranged in this order from an object side, a first focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups of the refractive optical system by different amounts along a normal line of a conjugate surface on the object side, and a second focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups along the normal line of the conjugate surface on the object side by different amounts from those of the first focus structure.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
ActiveUS20110199514A1Suppress generationCorrecting blurringTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingNon targeted
An image processor inputs image data from an image capturing device, and acquires blur-correction coefficients corresponding to the state of an imaging optical system which forms an image represented by light coming from an object on the image capturing device. Then, the image processor generates a target component and non-target components of blur correction from the image data, applies blur correction to the target component based on the blur-correction coefficients, and generates image data by synthesizing the target component after the blur correction and the non-target components.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus and image processing method
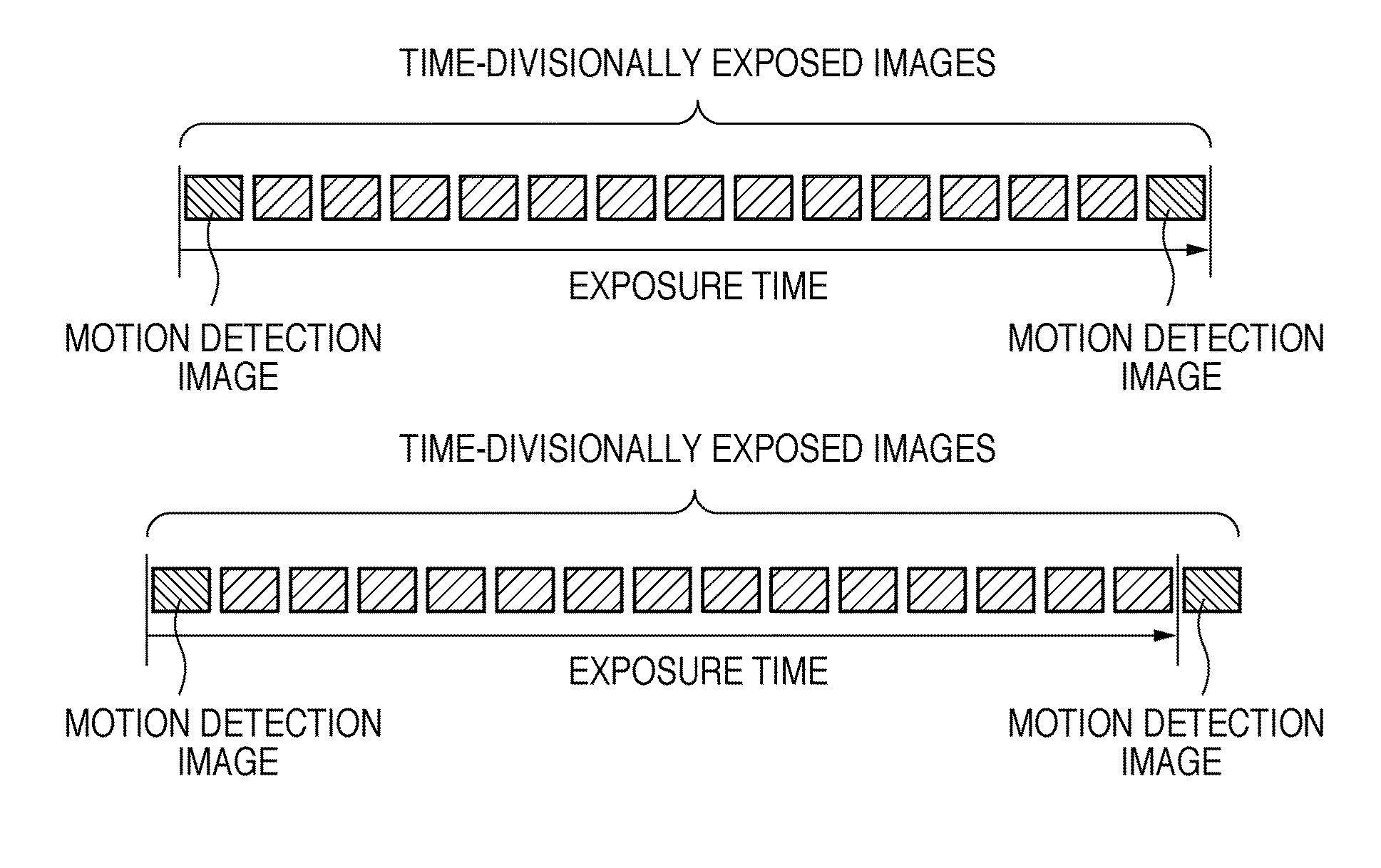
InactiveUS20100295954A1Effective correctionCorrecting blurringImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingData detection
A plurality of image capturing data time-divisionally exposed by a capturing unit are input, and are divided into synthesis images or motion detection images. A motion amount of the capturing unit at the time of time-division exposure is detected from the image capturing data of the motion detection images, and synthesized image capturing data is generated by synthesizing the synthesis images. Then, a vibration of the synthesized image capturing data is corrected based on a divide pattern indicating divisions, and the motion amount.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing device and method, recording medium, and program
InactiveUS20050281477A1Correction of blurring easily without placing a great burden on the userAccurate imagingImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
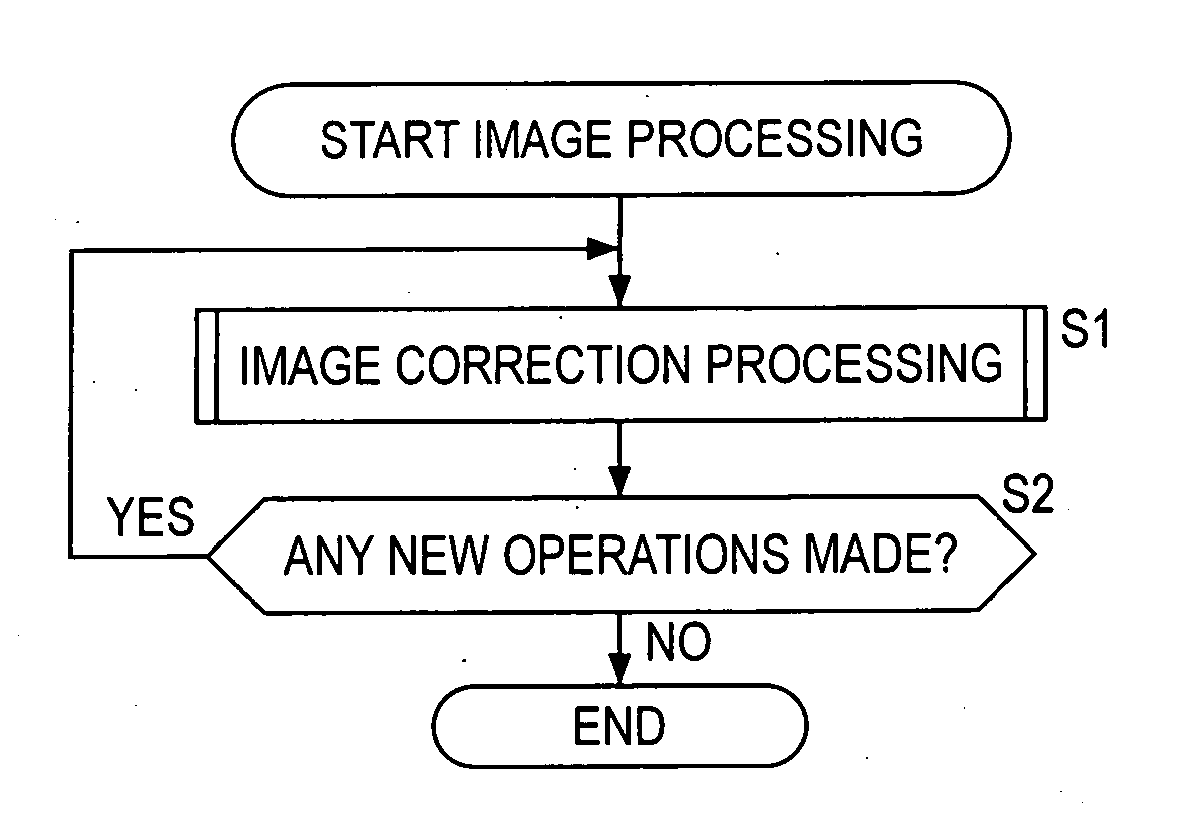
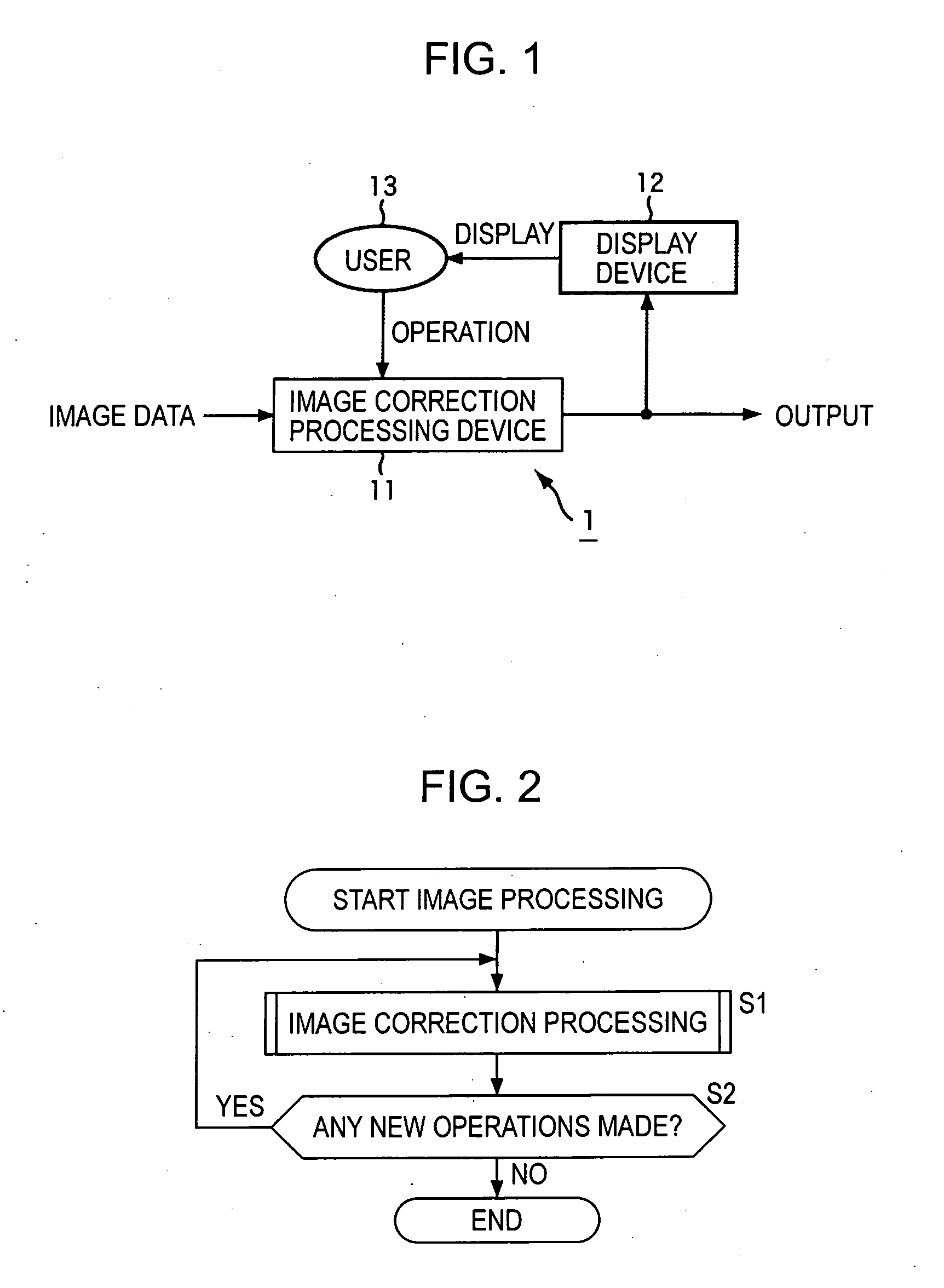
A user interface unit sets a parameter based on operations of a user, and outputs to a parameter correction unit. The parameter correction unit extracts the feature quantity of pixels in an observation region that corresponds to the value of the parameter, and based on the maximal value of that feature quantity, corrects the parameter specified by the user as the correction parameter. A blurring correction unit corrects input image data based on the correction parameter, and generates image data of the image wherein the blurring has been corrected. The present invention can be applied, for example, to a digital camera.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnification optical system
Owner:RICOH KK
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
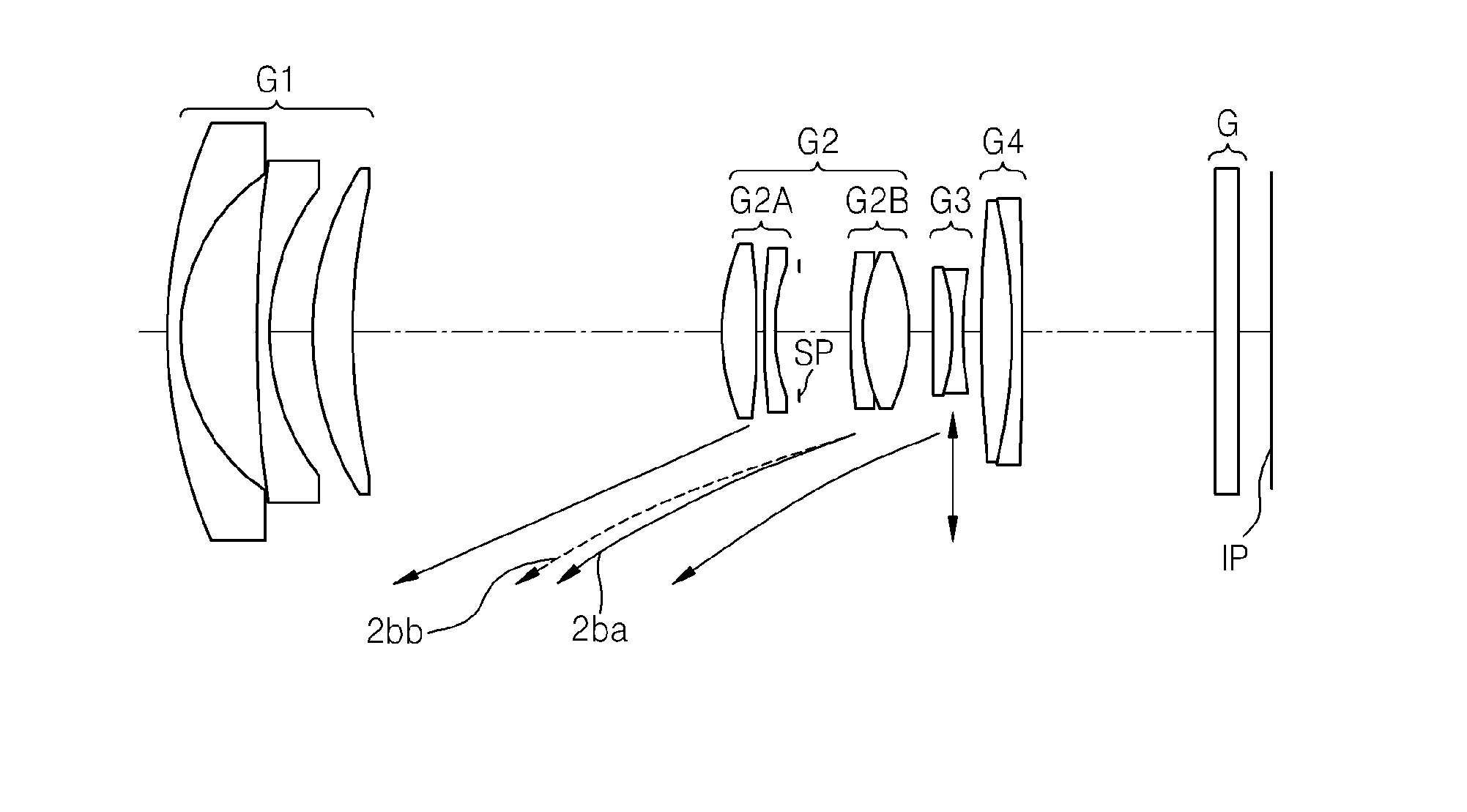
A zoom lens having at least a first lens group including a reflection member for bending an optical axis fixedly during zooming and having a negative refractive power, a second lens group having a negative refractive power, and a third lens group arranged in the order from an object side is provided. In the zoom lens, an image can be shifted into a direction perpendicular to the optical axis by moving either of the second and the third lens groups (“shift lens group”) in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis, and a following conditional expression (1) is satisfied,0.5<(1−βα)×βb<3.0, (1)where:βα: a magnification of the shift lens group in a maximum telephoto state, andβb: a magnification of a lens group arranged on an image surface side of the shift lens group in the maximum telephoto state.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnification optical system
A magnification optical system forms an enlarged image of an object. It includes a refractive optical system including a plurality of lens groups; and a mirror train including a curved mirror, arranged in this order from an object side, a first focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups of the refractive optical system by different amounts along a normal line of a conjugate surface on the object side, and a second focus structure configured to move the respective lens groups along the normal line of the conjugate surface on the object side by different amounts from those of the first focus structure.
Owner:RICOH KK
Image-taking apparatus
ActiveUS20070047935A1Counteracting forceSuppress noiseTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsLens ControllerTransmitted power
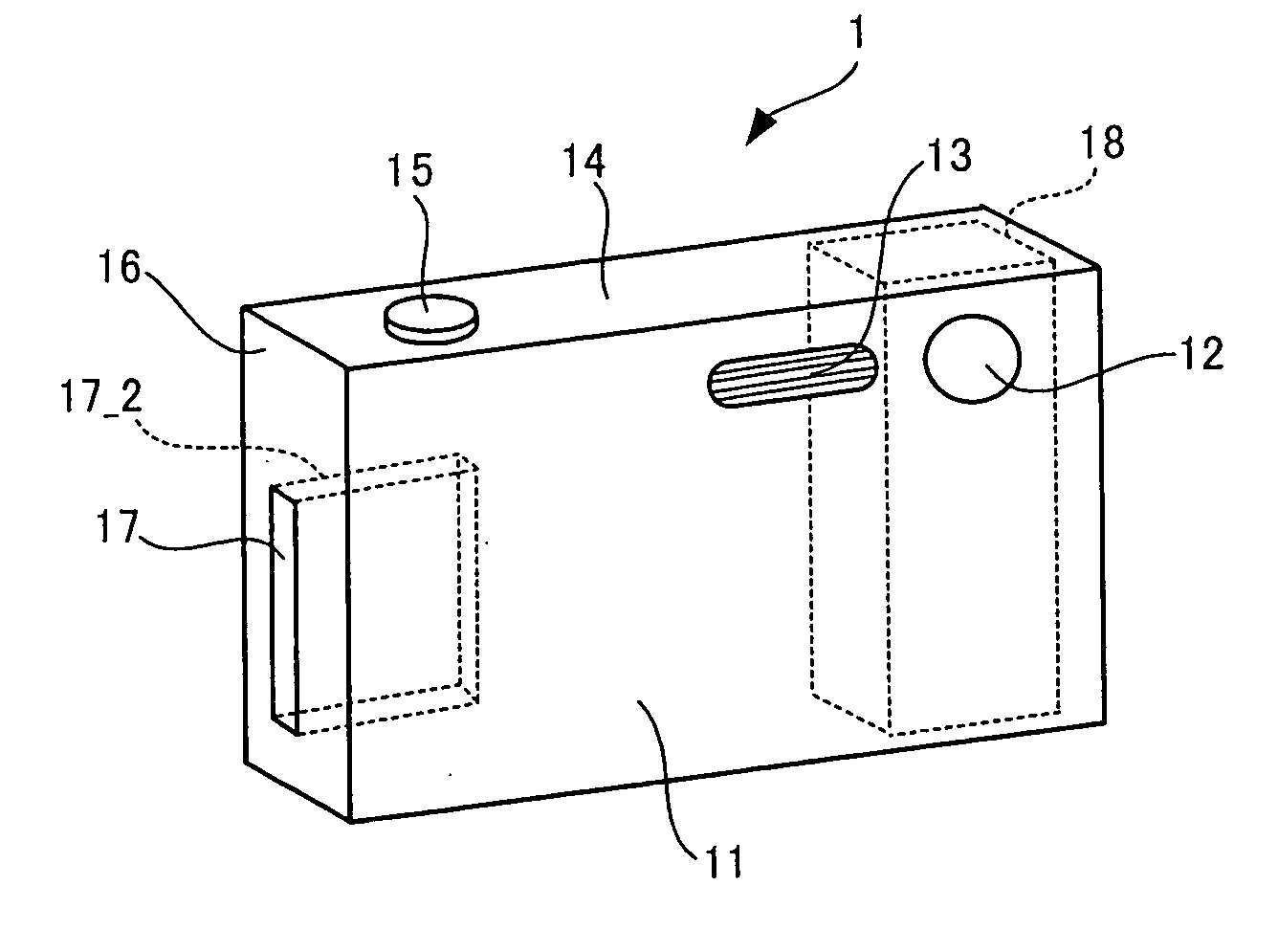
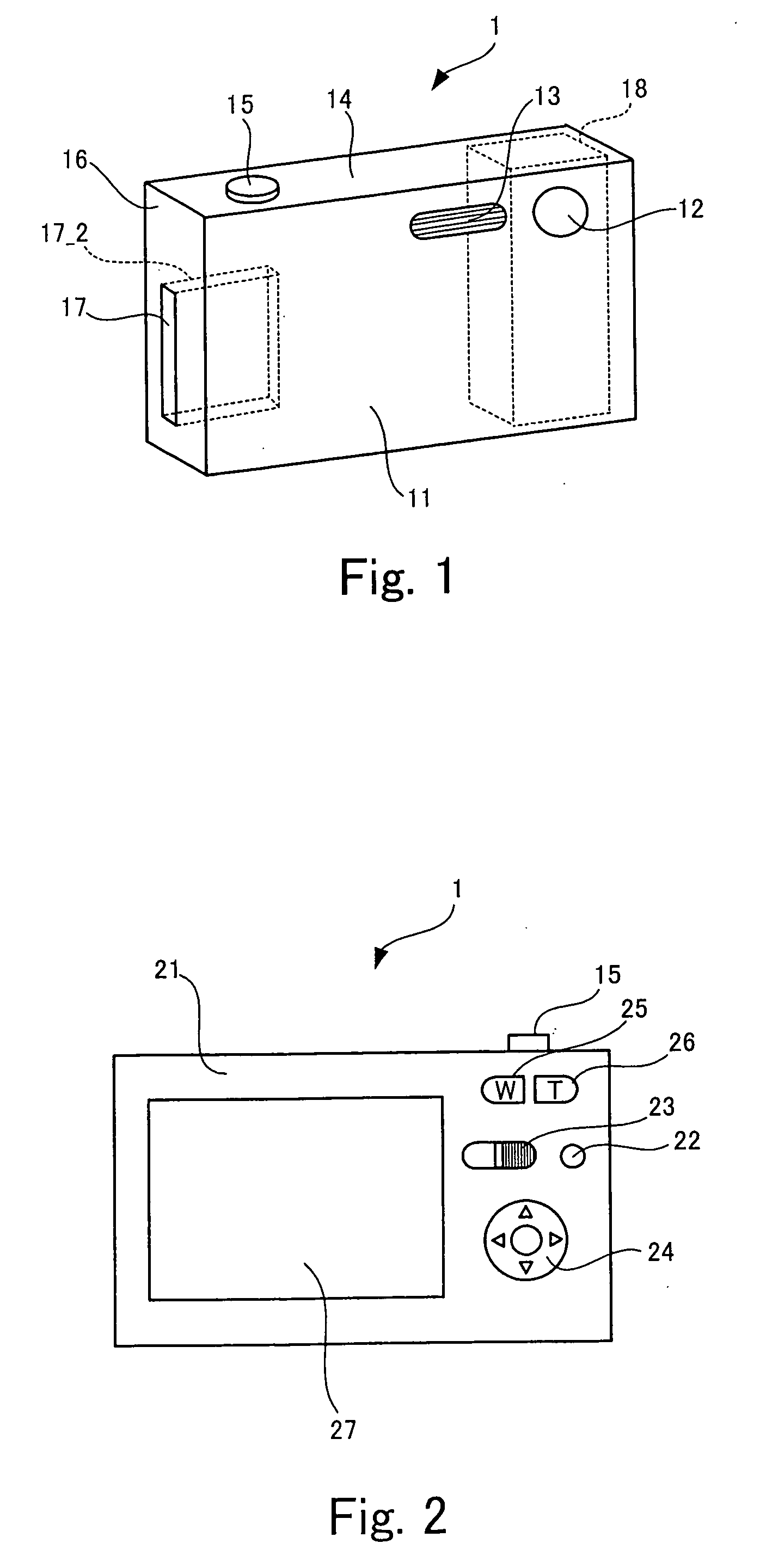
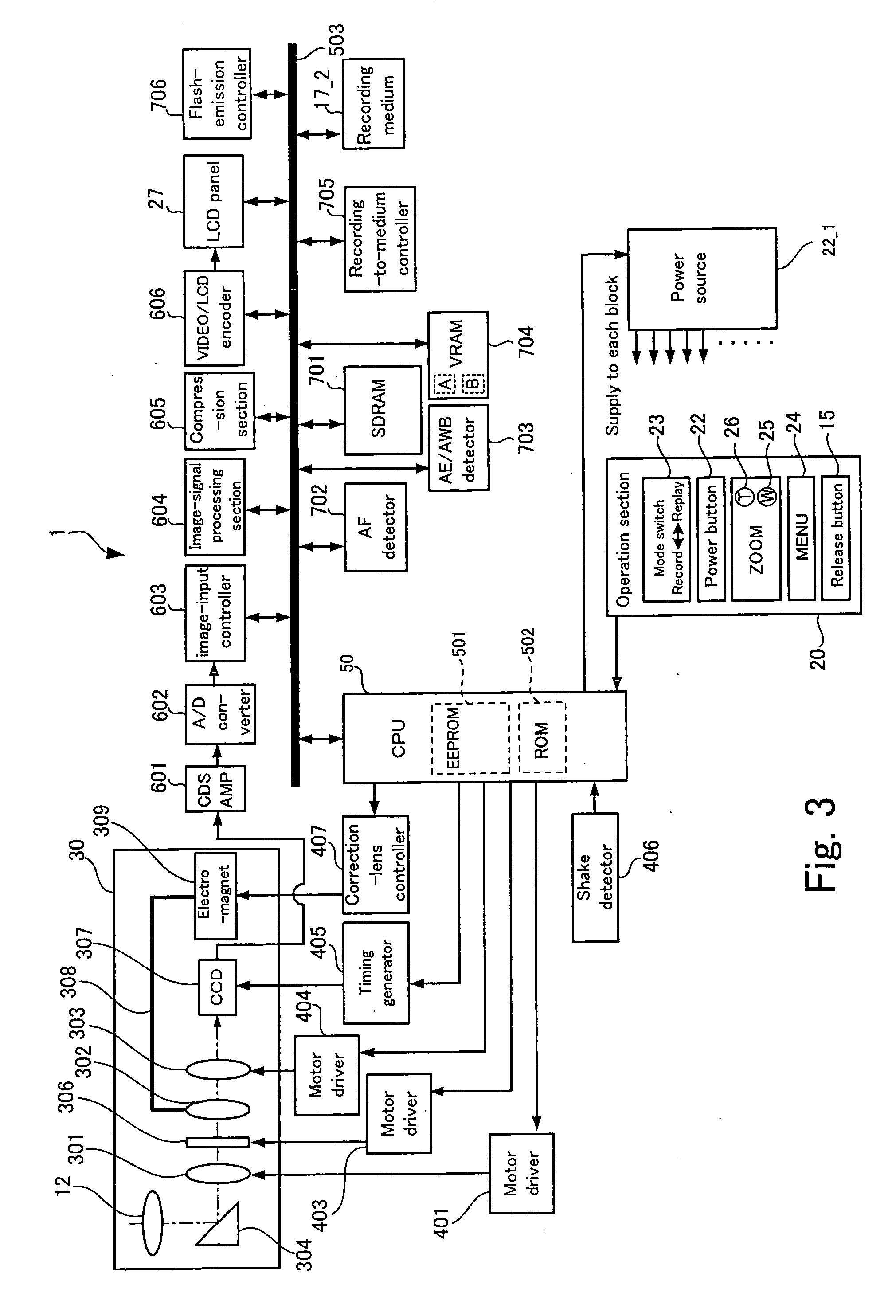
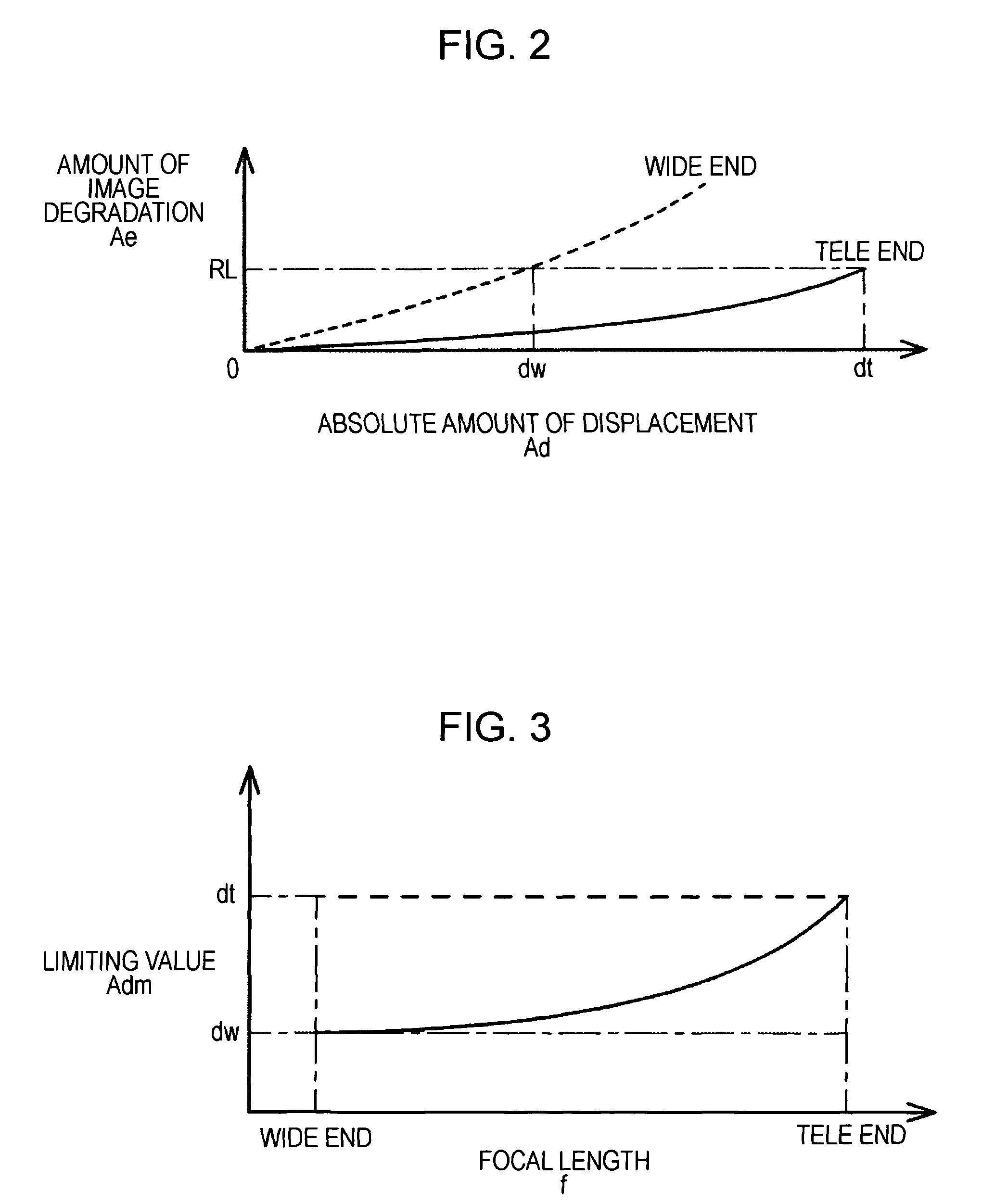
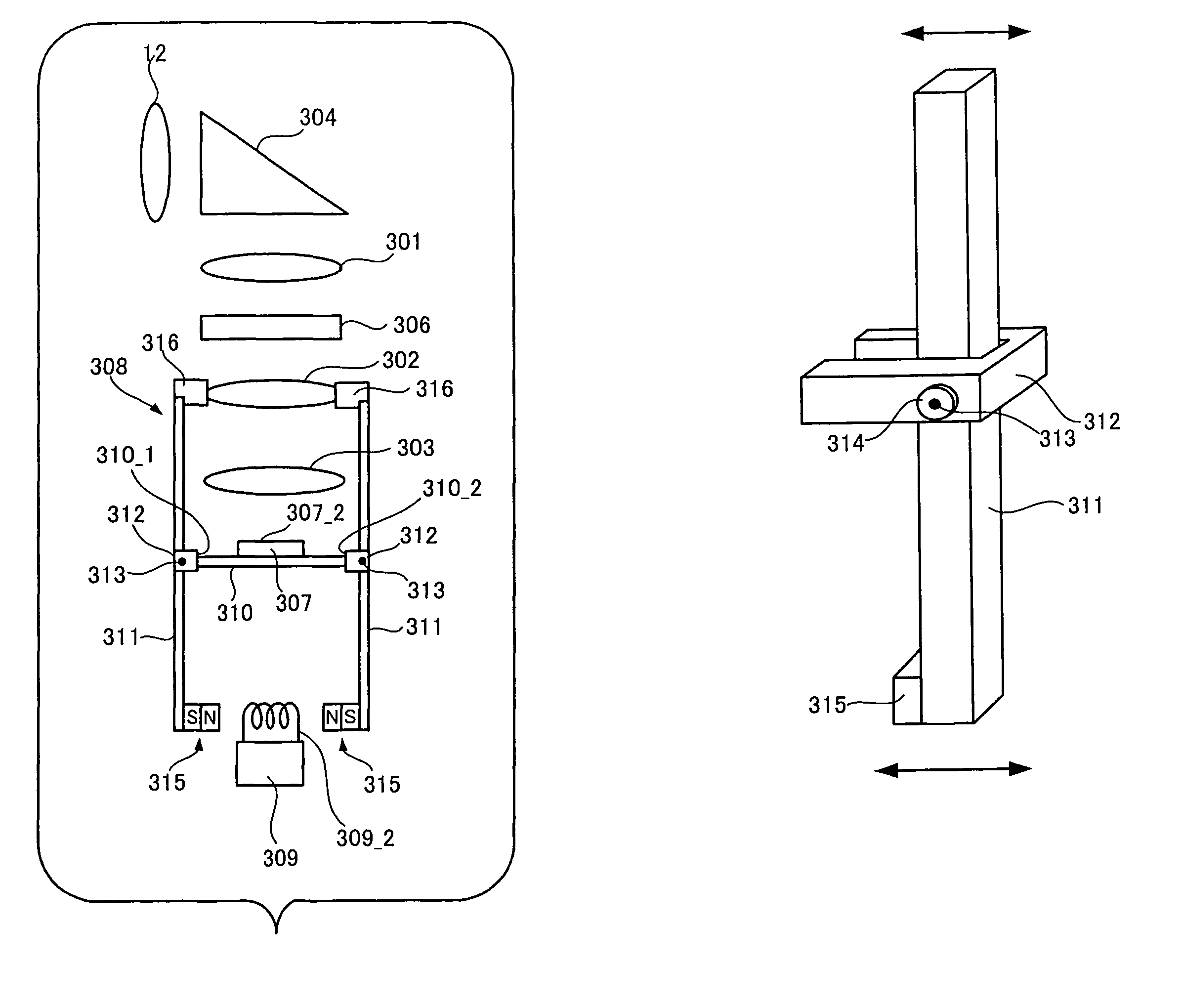
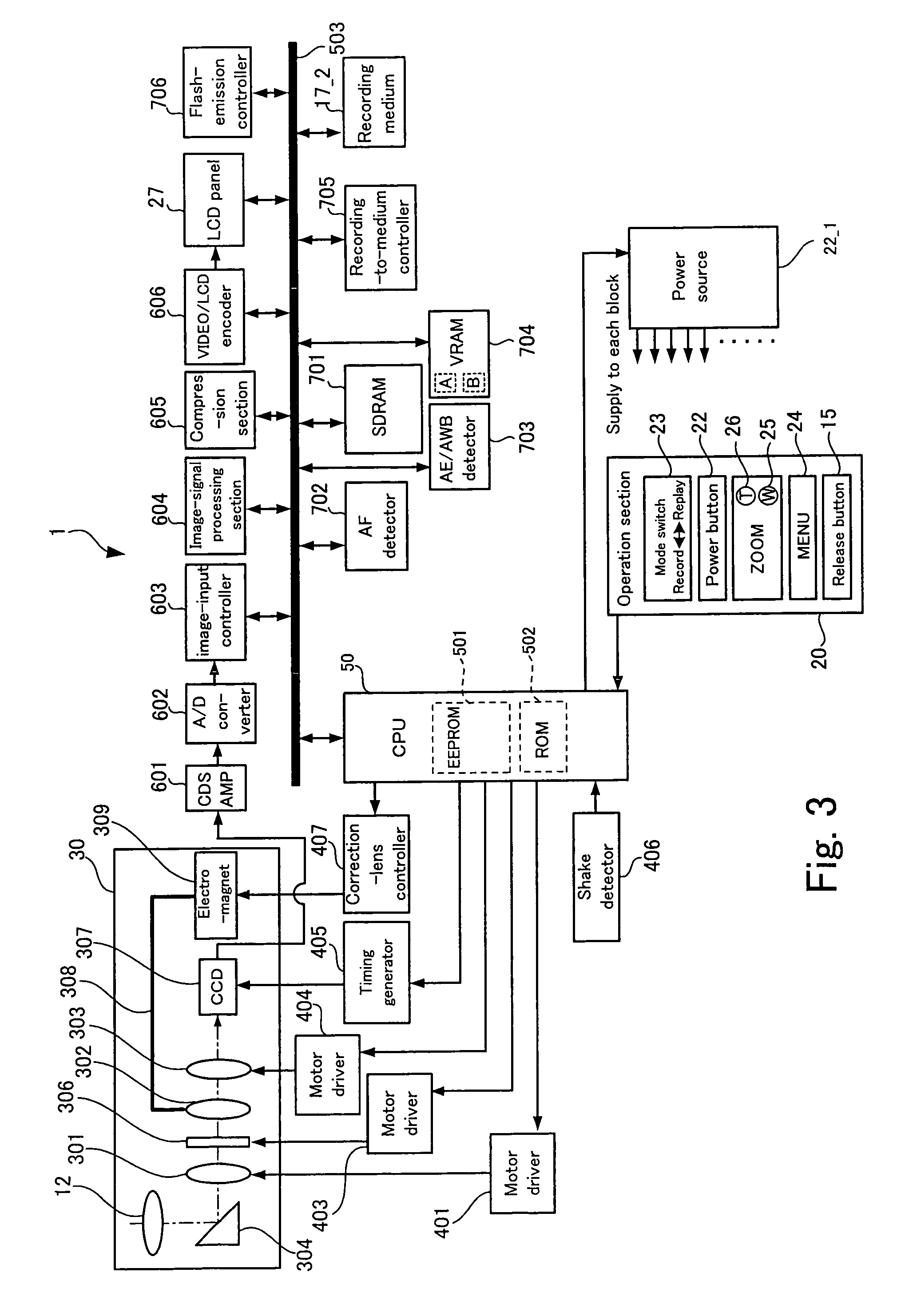
An image-taking apparatus includes: a CCD having an imaging surface; and an image-taking optical system having an objective lens. The apparatus further includes: a shake detector that detects a shake of the image-taking apparatus; and a correction lens disposed between the objective lens and the CCD and moving in parallel with the imaging surface to correct a blur in an image formed on the imaging surface caused by the shake of the image-taking apparatus. The apparatus further includes: an electromagnet disposed behind the CCD and driving the correction lens; a power transmission system that moves the correction lens by transmitting power from the electromagnet to the correction lens; and a correction-lens controller that causes, based on a detection result from the shake detector, the electromagnet to drive the correction lens such that an image whose blur due to the shake is corrected is formed on the imaging surface.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Zoom lens and electronic device including the same
ActiveUS20140152887A1Correcting blurringTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisZoom lens
A zoom lens includes, sequentially from an object side, a first lens group having negative refractive power, a second lens group having positive refractive power, a third lens group having negative refractive power; and a fourth lens group having positive refractive power. When zoom is varied from a wide-angle end to a telephoto end, positions of the first lens group and the fourth lens group are fixed on an optical axis. The second lens group includes, sequentially from the object side, a second A lens group having positive refractive power and a second B lens group having positive refractive power, and the second B lens group is moved in the optical axis direction to perform a focusing function from an object disposed in a close range to an object disposed at infinity. The third lens group is shifted in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis to correct image blur.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program
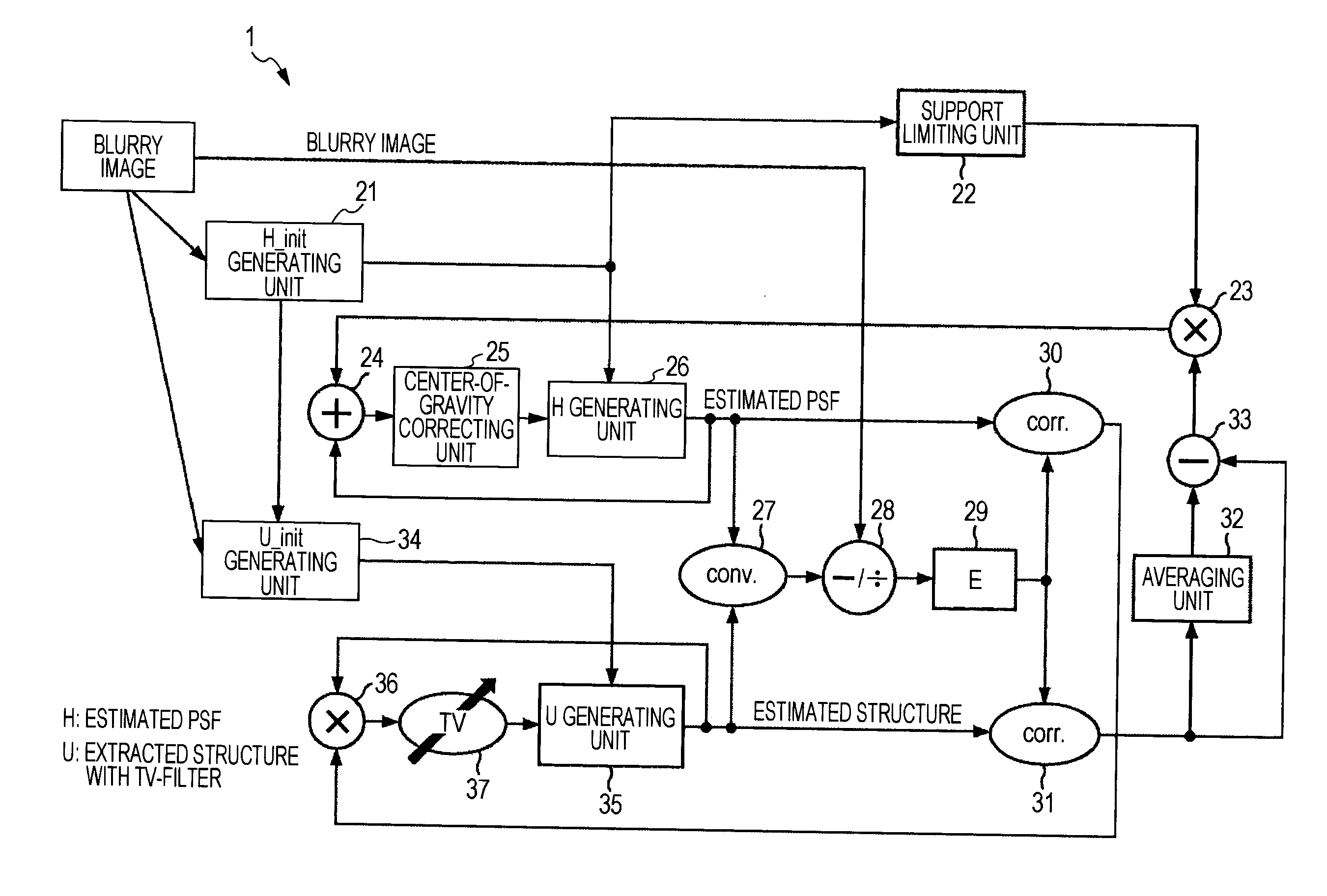
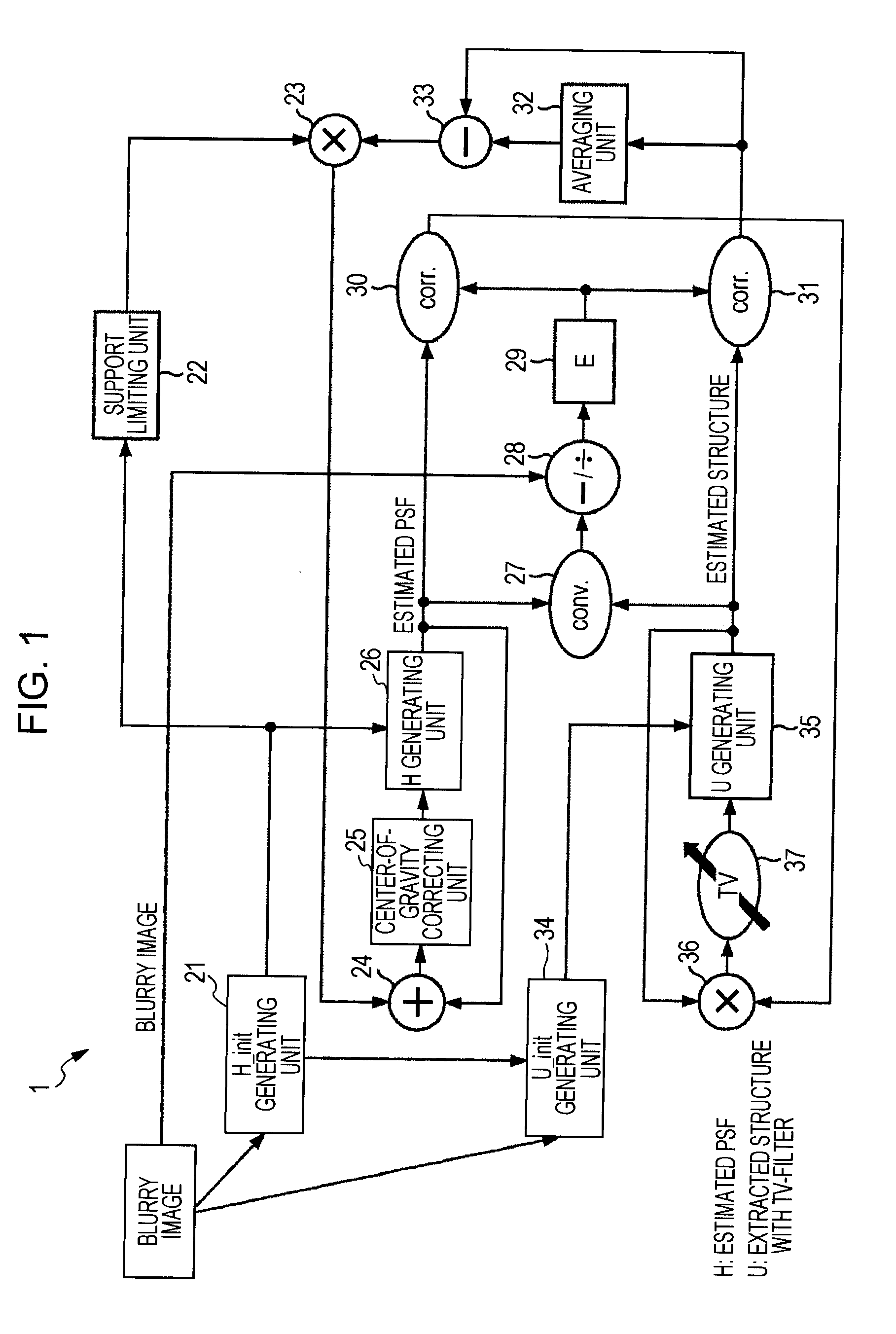
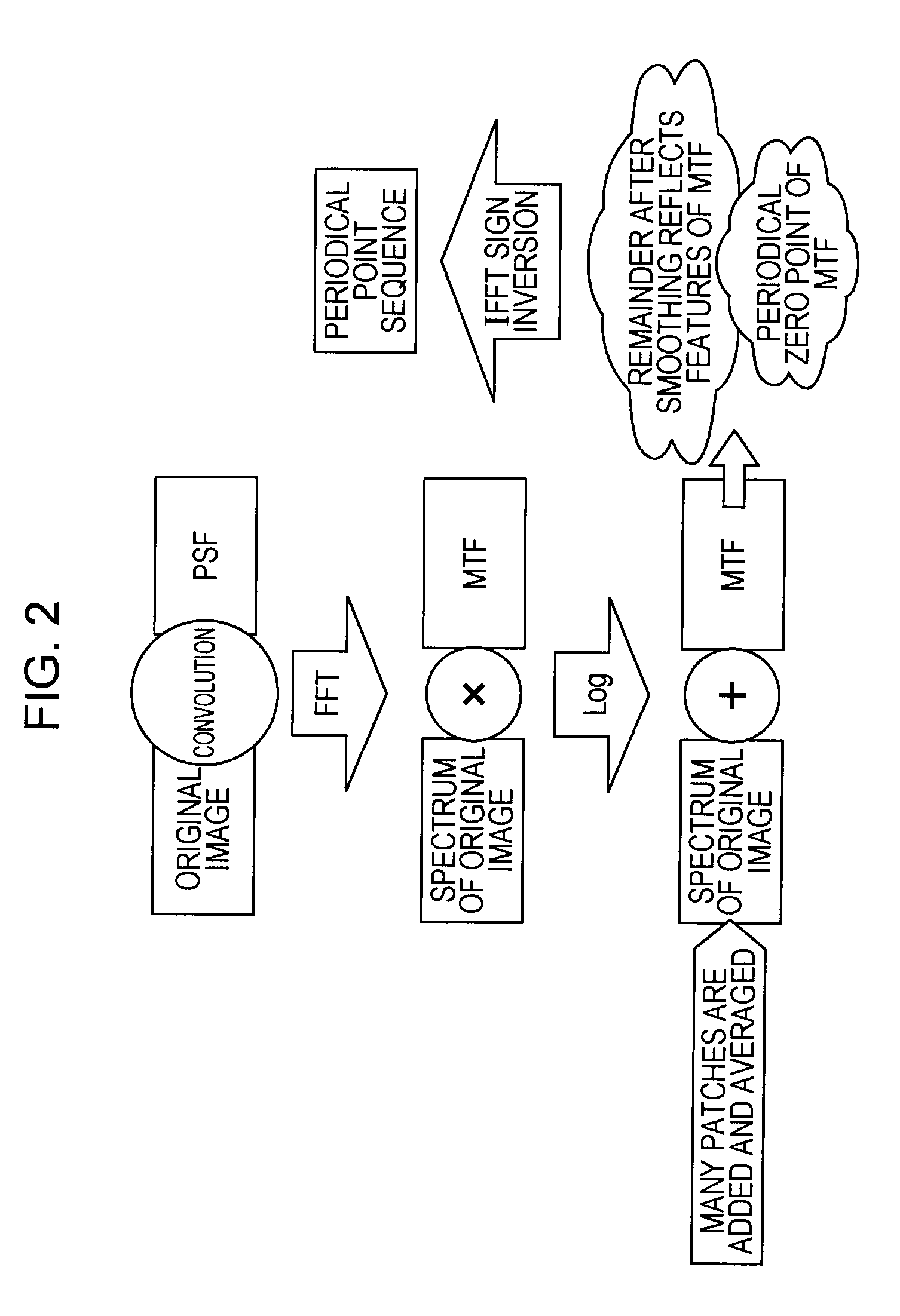
InactiveUS20110150353A1Avoid decrease in qualityCorrect image blurImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImage basedGenerating unit
An information processing apparatus includes a first generating unit, a second generating unit, and an updating unit. The first generating unit generates a point spread function representing the degree of blurring generated in the input image. The second generating unit generates a plurality of corrected block images obtained by correcting blurring of structure components of plural input block images based on the point spread function. The updating unit executes one or more times an updating process to update the corrected block images, followed by making structure components of the updated corrected block images into new corrected block images.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information Processing Apparatus, Information Processing Method, and Program
InactiveUS20100054590A1Focal length can be correctedCorrecting blurringImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation processingPoint spread function
An information processing apparatus includes: a first generating unit which generates, based on feature points detected on a cepstrum from an input image, a point-spread function that represents the degree of blurring generated in the input image; a second generating unit which generates a structure that represents an image obtained by reducing the input image with a size based on the point-spread function and enlarging this with the size, based on the point-spread function; and an updating unit which executes an updating process to update at least either the point-spread function or the structure such that the point-spread function and the structure approximate to a true value, with the updating unit repeatedly executing the updating process to set, of a structure component and a texture component making up the updated structure, the structure component as a new updated structure, and set the updated point-spread function as a new updated target.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image capture apparatus and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20140232886A1Correcting blurringTelevision system detailsColor television detailsReference RegionImage capture
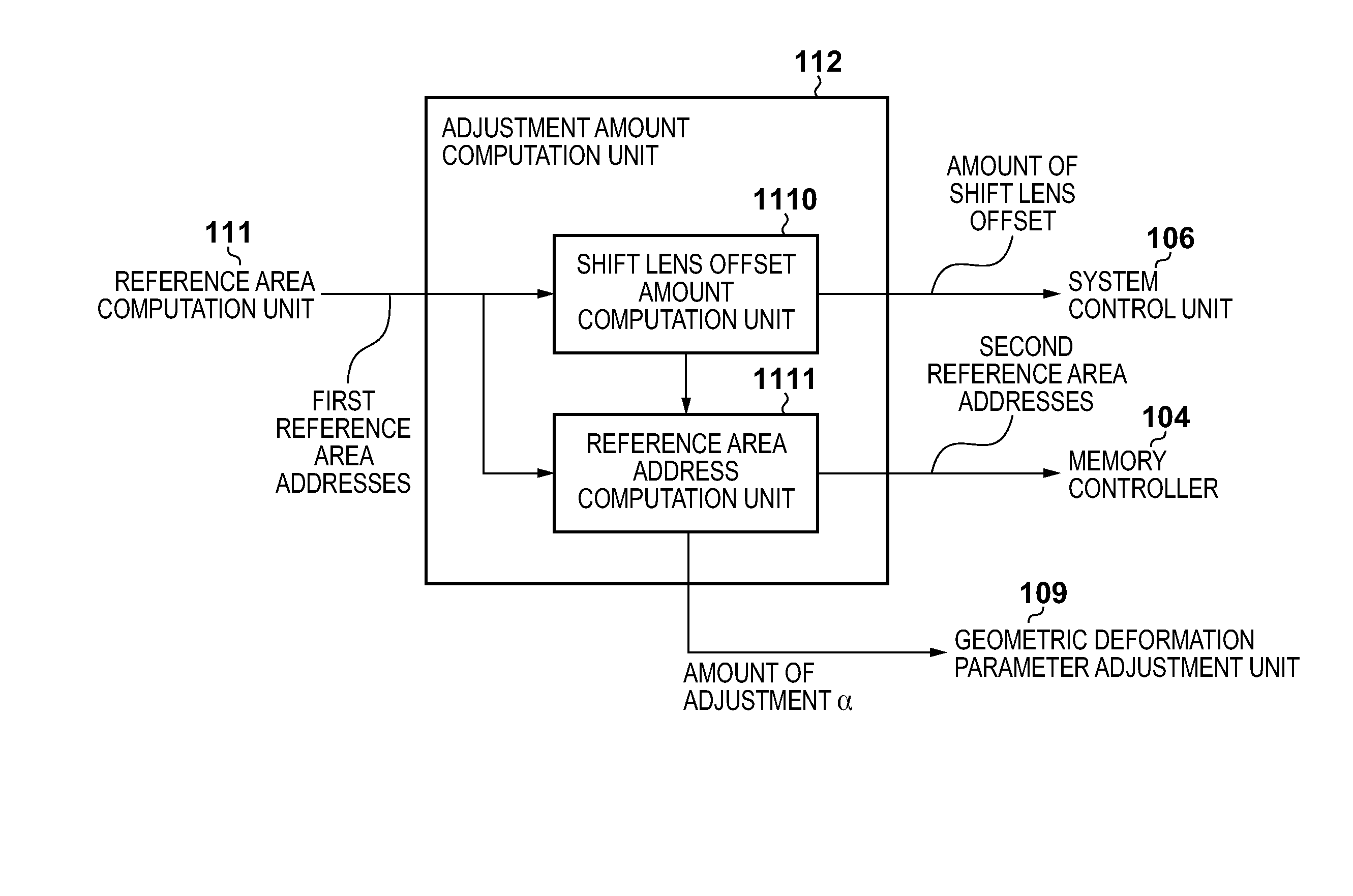
An offset corresponding to an amount of geometric deformation is added to an amount of drive of an optical member due to an optical image shake correction so that the center of a reference area necessary for geometric deformation processing comes closer to the center of an imaging area. Because of this, a possibility is increased that a reference area necessary for geometric deformation processing is fully contained in an imaging area, and blurring of an image due to a motion of an image capture apparatus is effectively corrected by combining an optical image shake correction and a geometric deformation process.
Owner:CANON KK
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, image processing program, and image capturing apparatus
InactiveUS8194996B2Correcting blurringImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingComputer science
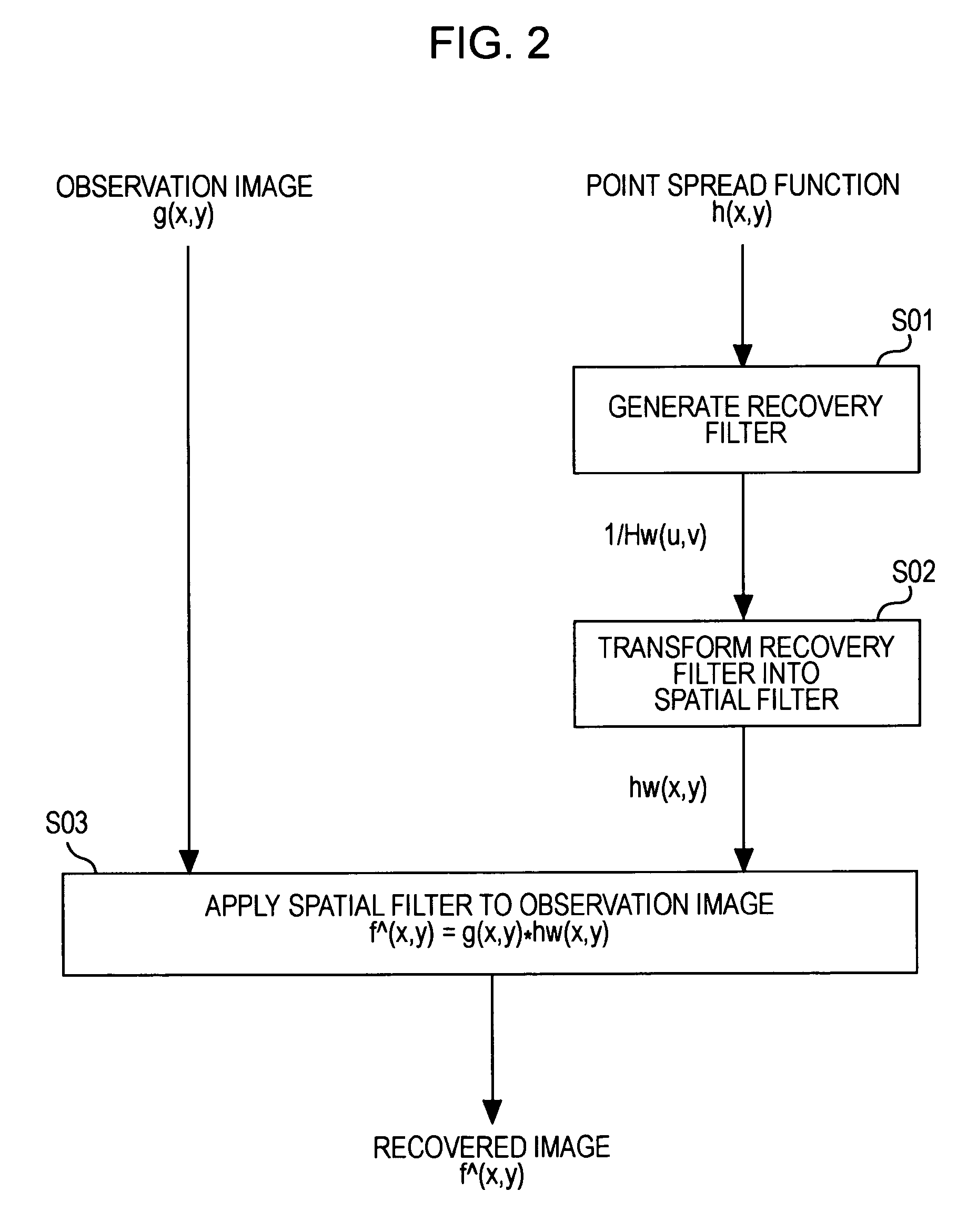
An image processing apparatus for correcting an input image for blur using a recovery filter in accordance with image blurriness includes a blurriness determining unit that receives a target image to be corrected, applies to the target image a recovery filter including a degree-of-blur parameter corresponding to blurriness while changing a value of the degree-of-blur parameter, evaluates a degree of recovery of each of corrected target images which have been corrected with recovery filters having different degree-of-blur parameter values, and determines blurriness of the target image based on the degree-of-blur parameter value of the highly evaluated recovery filter; and a blur correction unit that sets a recovery filter for the target image based on the degree-of-blur parameter in accordance with the determined blurriness of the target image and corrects the target image for blur using the recovery filter.
Owner:SONY CORP
Zoom lens and image pickup
InactiveUS7245442B2Great reductionAvoid performance degradationOptical elementsCamera lensOptical axis
A zoom lens is disclosed which is superior in reduction of the lens diameter and can suppress degradation in performance while a high zoom ratio is achieved. The zoom lens is formed as a zoom lens of a four-group configuration having positive, negative, positive and positive groups. The second and fourth lens groups move whereas the first and third lens groups are fixed. An aperture stop is disposed on the object side of the third lens group. The third lens group includes negative and positive sub groups with an air distance left therebetween. The positive sub group is shiftable perpendicularly to the optical axis to shift an image substantially perpendicularly. A conditional expression 1.4<|f3n| / f3<3 is satisfied where f3n is the focal distance of the negative sub group and f3 is the focal distance of the third lens group.
Owner:SONY CORP
Zoom lens system, imaging apparatus, and method for zooming the zoom lens system
InactiveUS20110194191A1Good optical performanceHigh zoom ratioOptical elementsOptoelectronicsImaging equipment
Owner:NIKON CORP
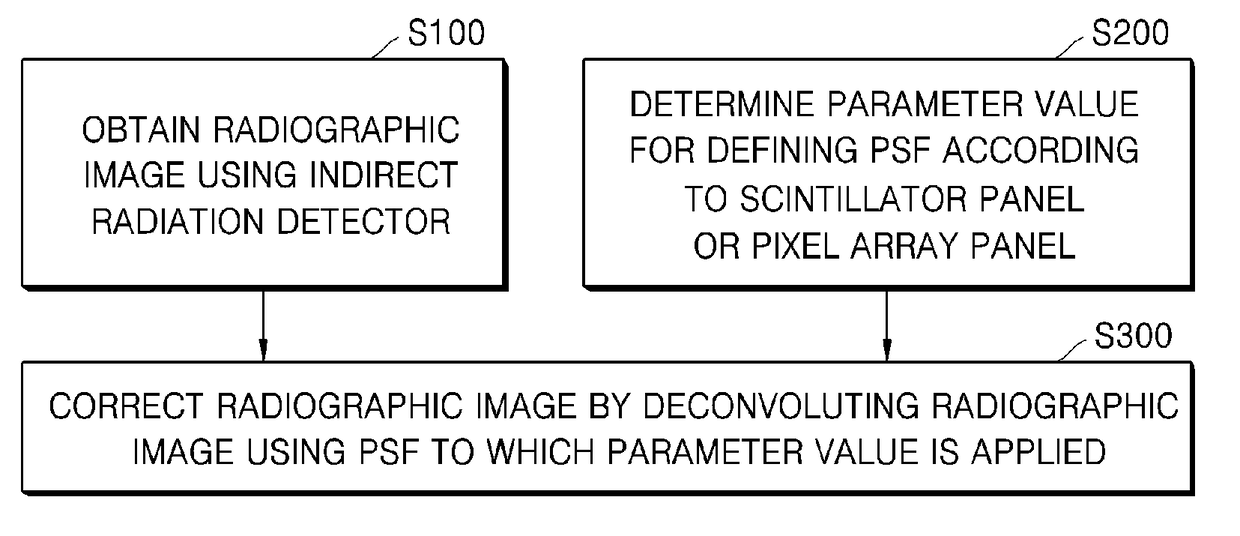
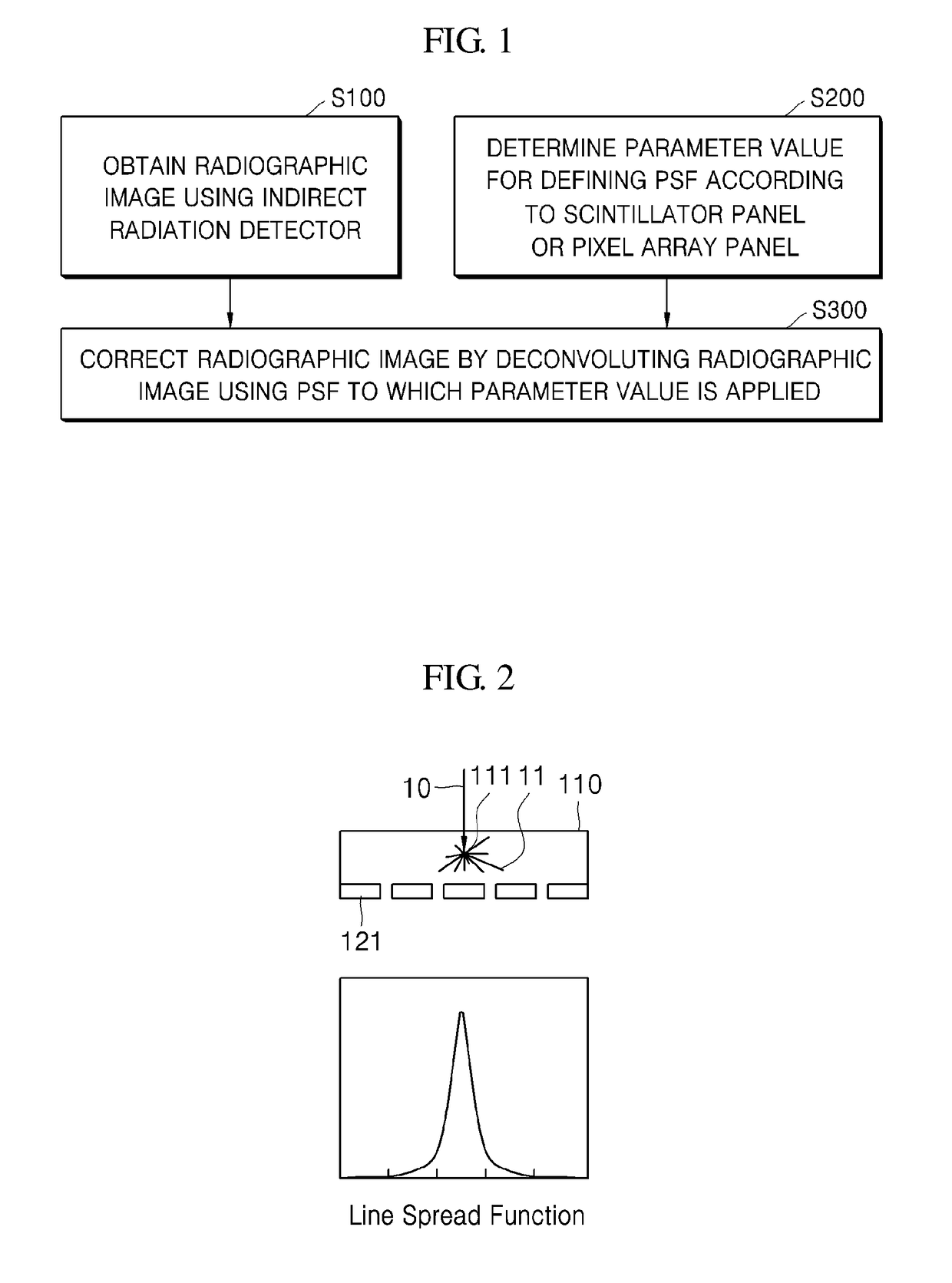
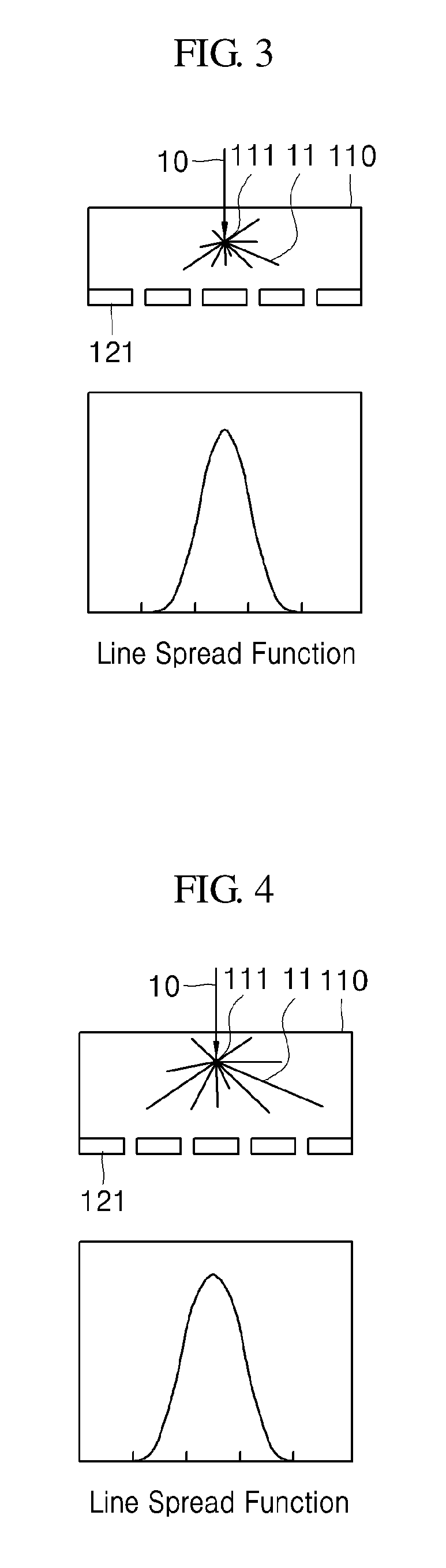
Method for processing radiographic image and radiography system
ActiveUS9916656B2Improve clarityImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spread functionScintillator
Owner:DRTECH
Blur correcting device, blur correcting method, and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS7962024B2Reduce degradationImprove the correction effectTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsOptical axisCorrection method
A blur correcting device includes a shake detecting unit configured to detect a shake and output a detection signal indicating a result of the detection; a drive unit configured to displace a relative positional relationship between a lens unit and an image pickup element relative to an optical axis such that a position of an optical image formed on an image pickup surface of the image pickup element is displaced on the image pickup surface; and a control unit configured to increase a displacement range when the amount of shake indicated by the detection signal is larger than a predetermined level, displace the relative positional relationship between the lens unit and the image pickup element within the increased displacement range in accordance with the detection signal, and thereby correct a blur of the optical image on the image pickup surface caused by the shake detected by the shake detecting unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image-taking apparatus
ActiveUS7764874B2Correcting blurringReduce thicknessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectric power transmissionLens Controller
An image-taking apparatus includes: a CCD having an imaging surface; and an image-taking optical system having an objective lens. The apparatus further includes: a shake detector that detects a shake of the image-taking apparatus; and a correction lens disposed between the objective lens and the CCD and moving in parallel with the imaging surface to correct a blur in an image formed on the imaging surface caused by the shake of the image-taking apparatus. The apparatus further includes: an electromagnet disposed behind the CCD and driving the correction lens; a power transmission system that moves the correction lens by transmitting power from the electromagnet to the correction lens; and a correction-lens controller that causes, based on a detection result from the shake detector, the electromagnet to drive the correction lens such that an image whose blur due to the shake is corrected is formed on the imaging surface.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Zoom lens and imaging apparatus
A zoom lens having at least a first lens group including a reflection member for bending an optical axis fixedly during zooming and having a negative refractive power, a second lens group having a negative refractive power, and a third lens group arranged in the order from an object side is provided. In the zoom lens, an image can be shifted into a direction perpendicular to the optical axis by moving either of the second and the third lens groups (“shift lens group”) in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis, and a following conditional expression (1) is satisfied, 0.5<(1−βα)×βb<3.0, (1) where: βα: a magnification of the shift lens group in a maximum telephoto state, and βb: a magnification of a lens group arranged on an image surface side of the shift lens group in the maximum telephoto state.
Owner:SONY CORP
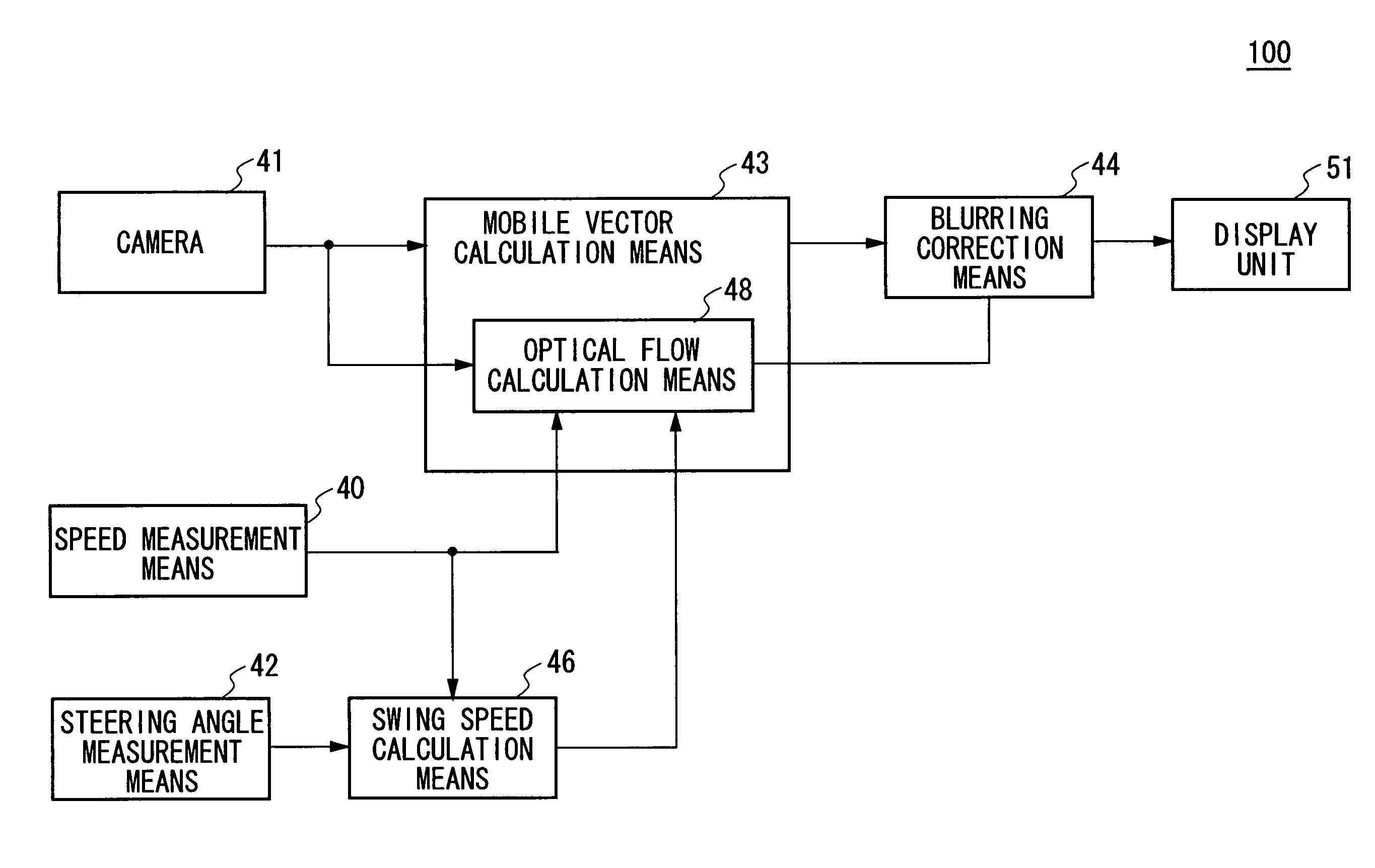
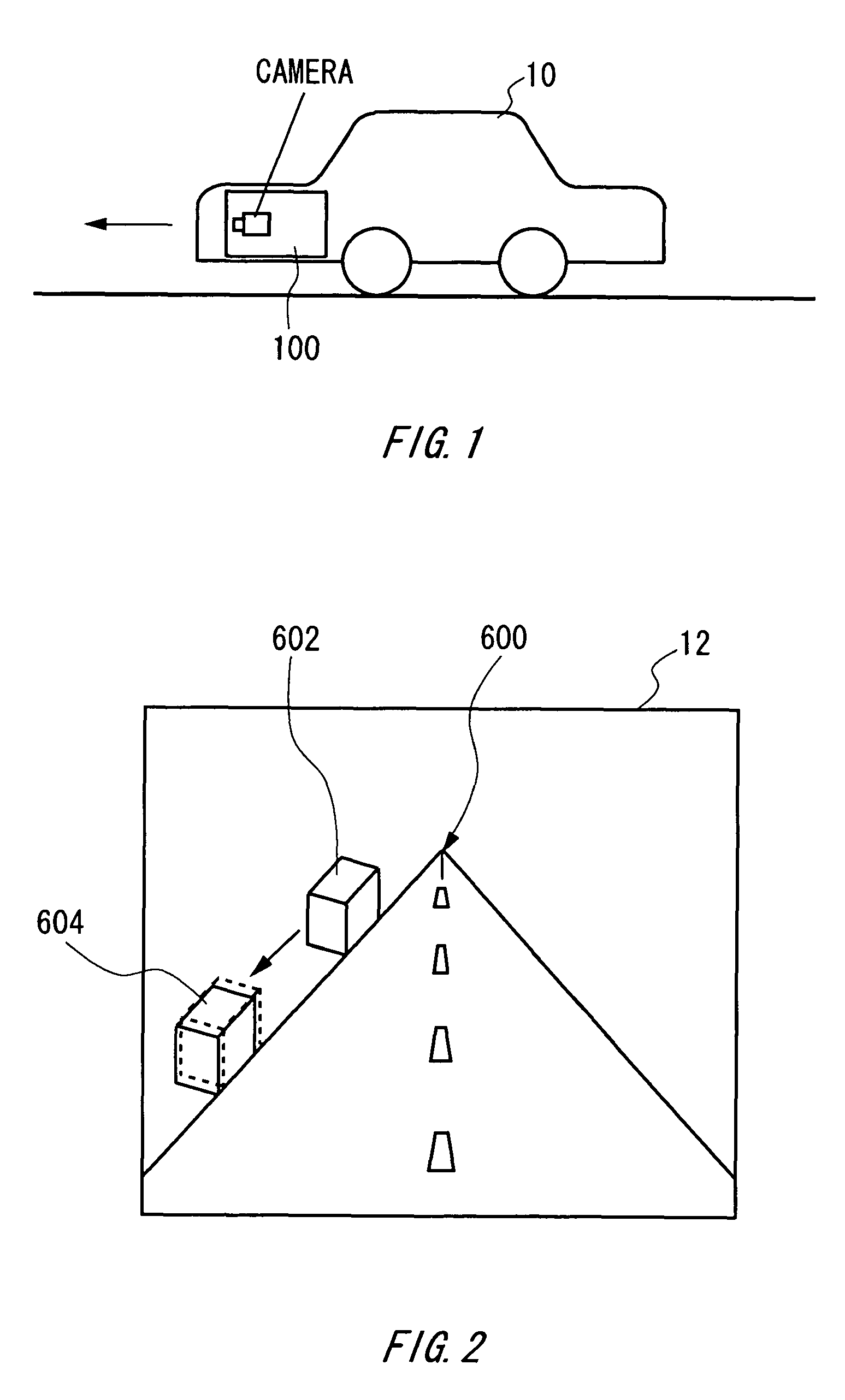
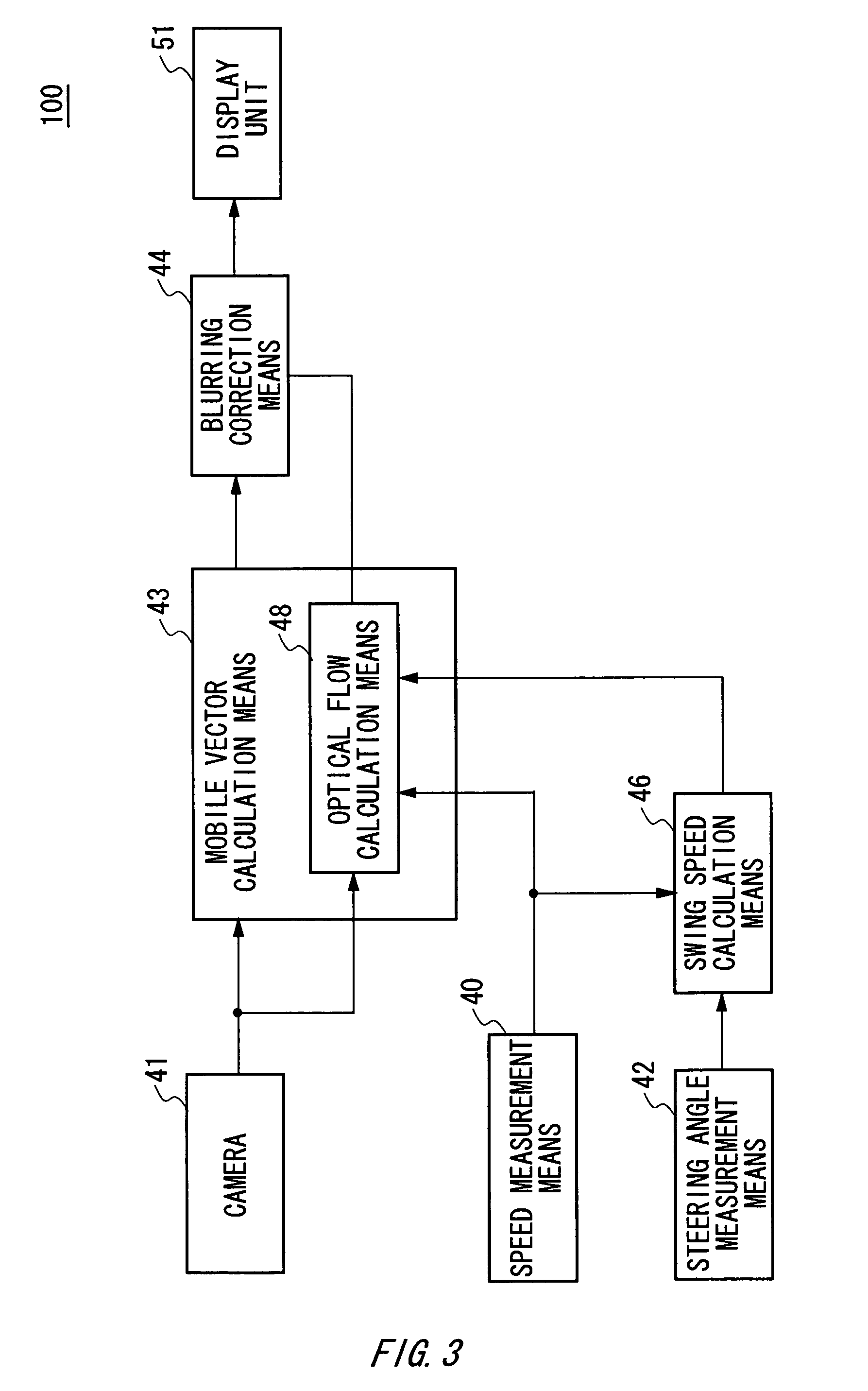
Image correction apparatus and image correction method for correcting image blur using a mobile vector
InactiveUS7982772B2Significant blurringReduce blurImage enhancementTelevision system detailsObject basedImage correction
An image correction apparatus which corrects blurring generated by the traveling of a vehicle in the captured image, including: a camera which captures an image of front of a vehicle continuously; mobile vector calculation means of calculating a mobile vector in an image of each object based on a position of an object in each image continuously captured by the camera; and blurring correction means of correcting blurring of the image captured by the camera using the mobile vector calculated by the mobile vector calculation means.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Information processing apparatus and method for correcting vibration
InactiveUS8760526B2Effective correctionCorrecting blurringTelevision system detailsImage enhancementInformation processingData detection
A plurality of image capturing data time-divisionally exposed by a capturing unit are input, and are divided into synthesis images or motion detection images. A motion amount of the capturing unit at the time of time-division exposure is detected from the image capturing data of the motion detection images, and synthesized image capturing data is generated by synthesizing the synthesis images. Then, a vibration of the synthesized image capturing data is corrected based on a divide pattern indicating divisions, and the motion amount.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com