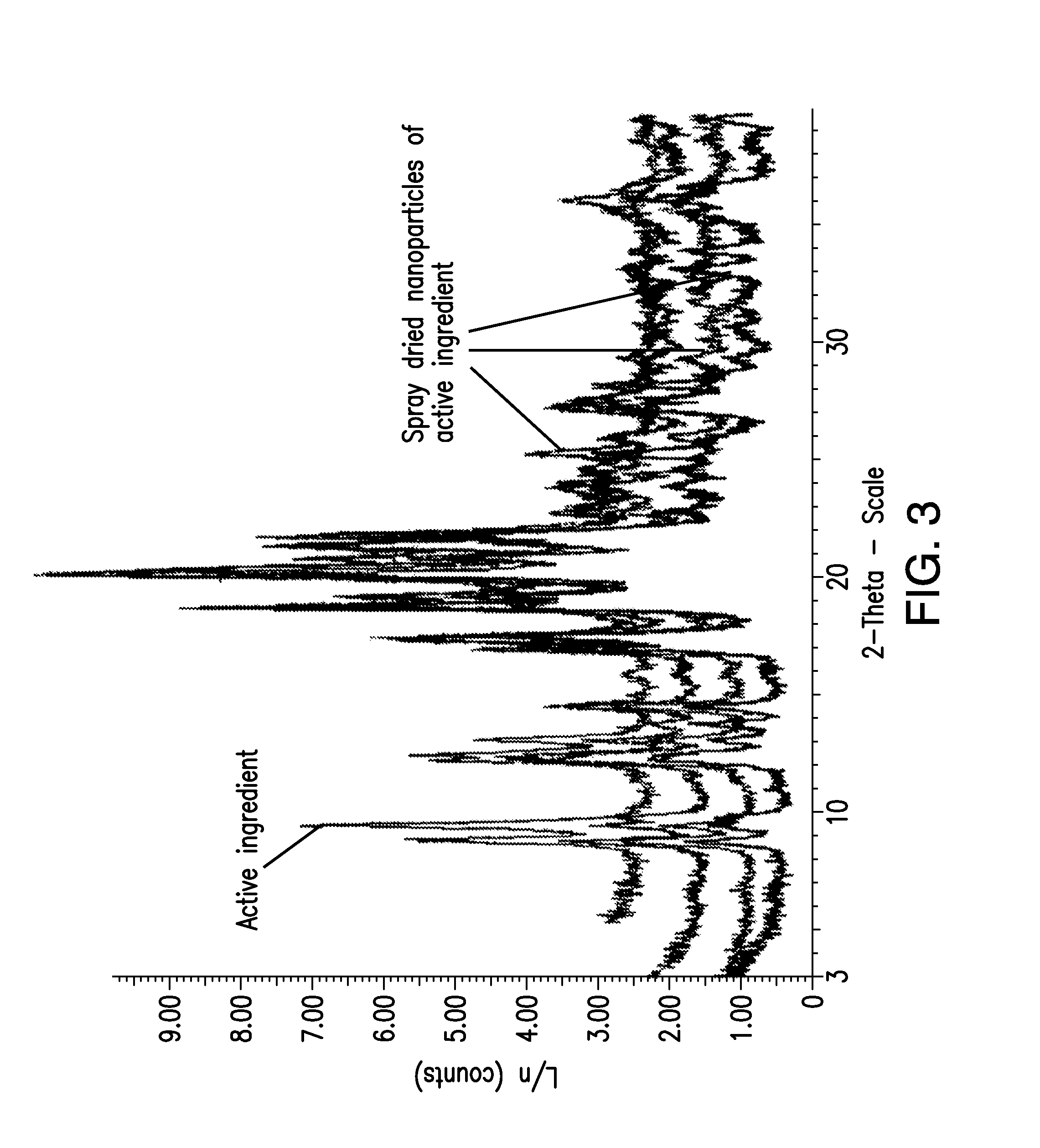
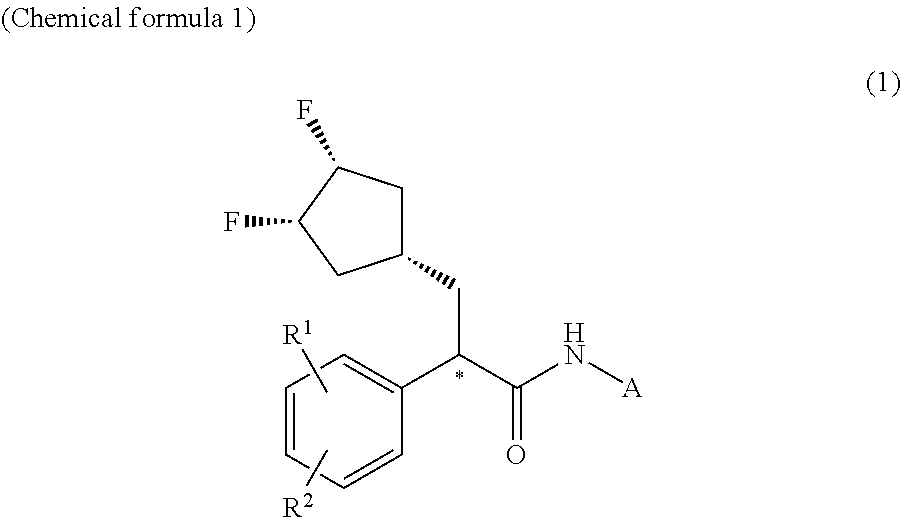
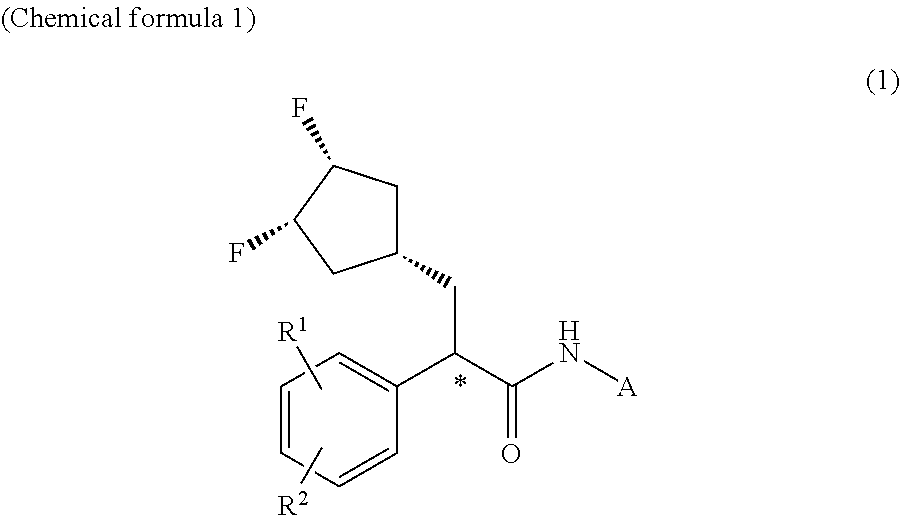
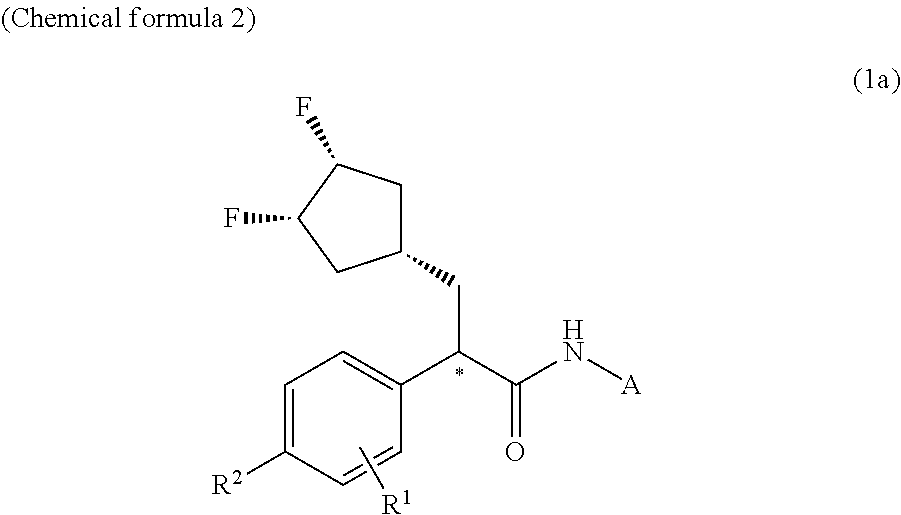
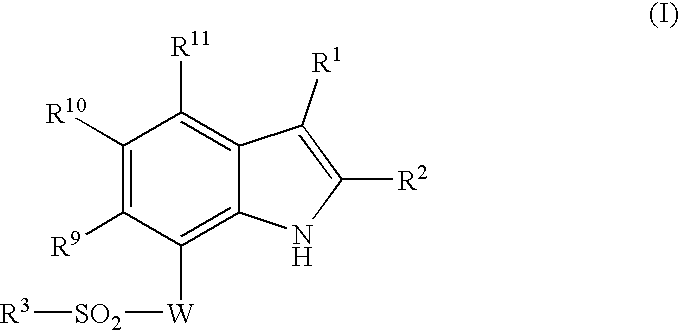
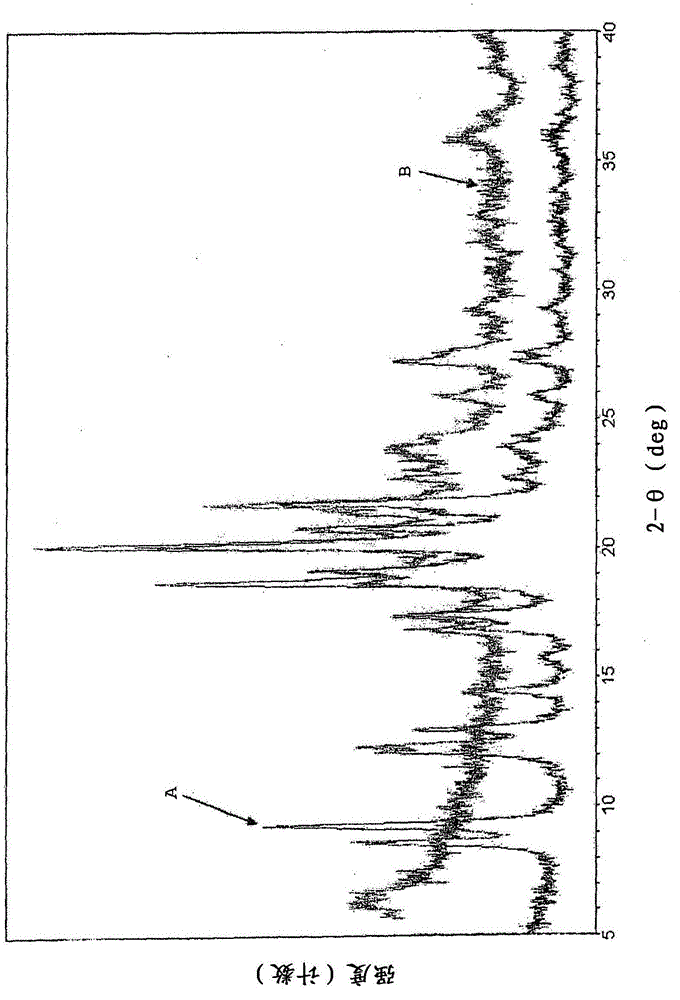
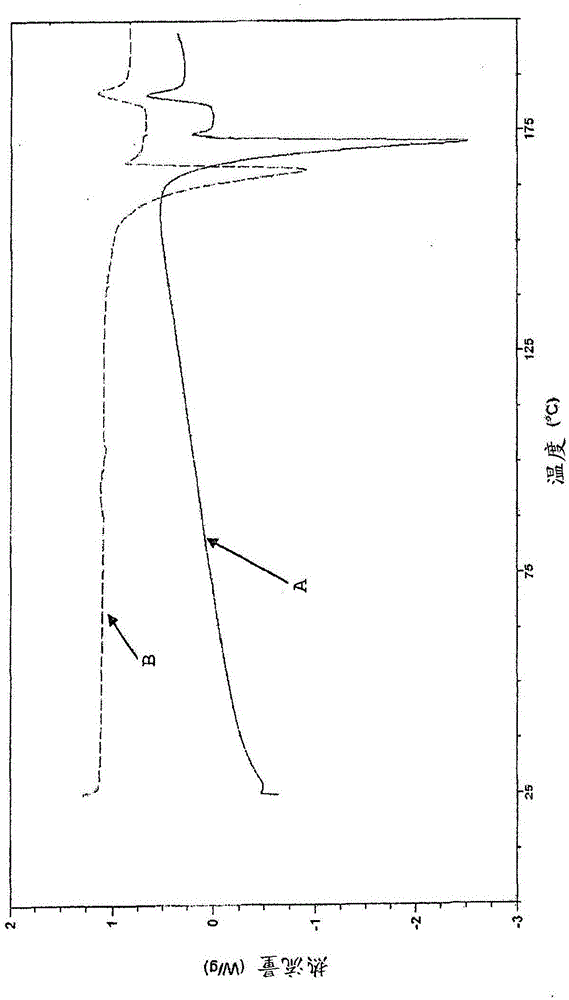
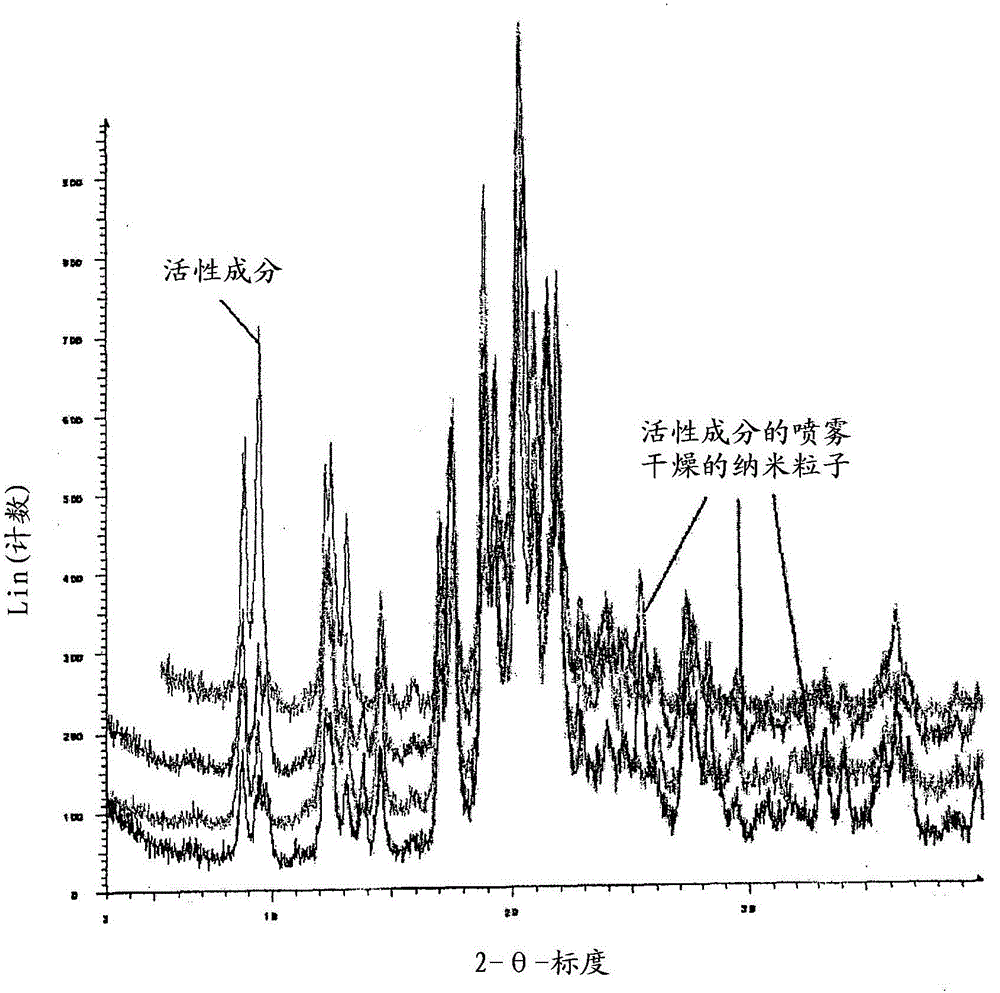
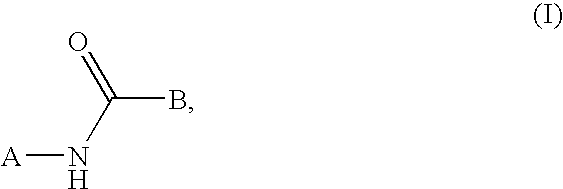Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
111 results about "Glucokinase activator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
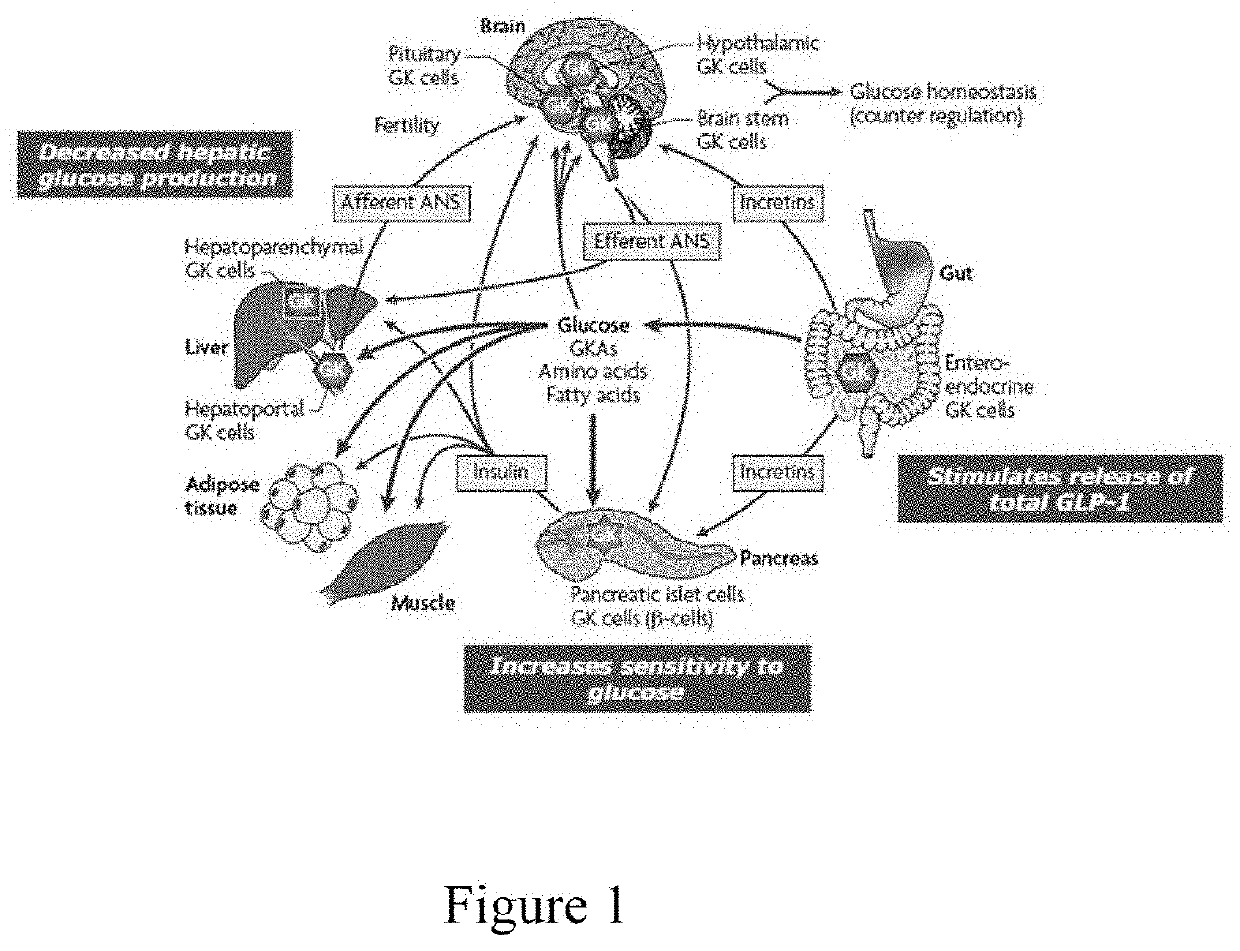
The intracellular enzyme glucokinase (GK) is a key component of the body’s glucose-sensing network. GK activity is regulated by changes in blood glucose in the physiological range. Considerable effort has therefore been made to activate GK pharmaceutically and led to the discovery of Glucokinase Activators (GKAs).
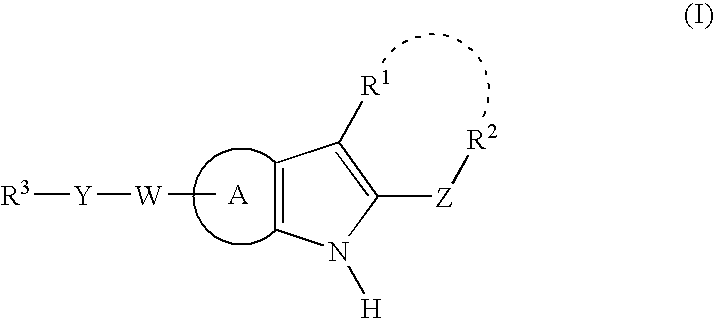
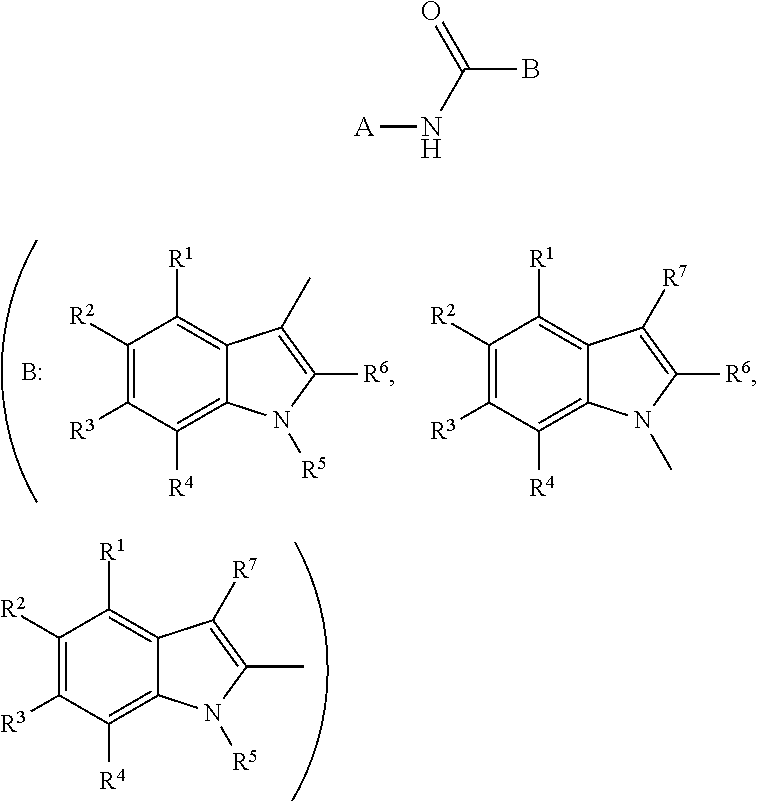
N-heteroaryl indole carboxamides and analogues thereof, for use as glucokinase activators in the treatment of diabetes
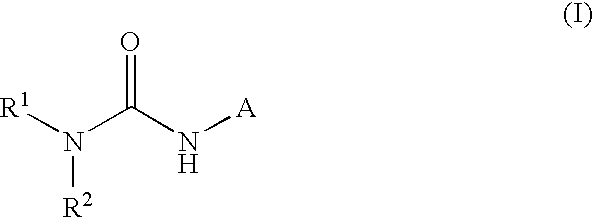
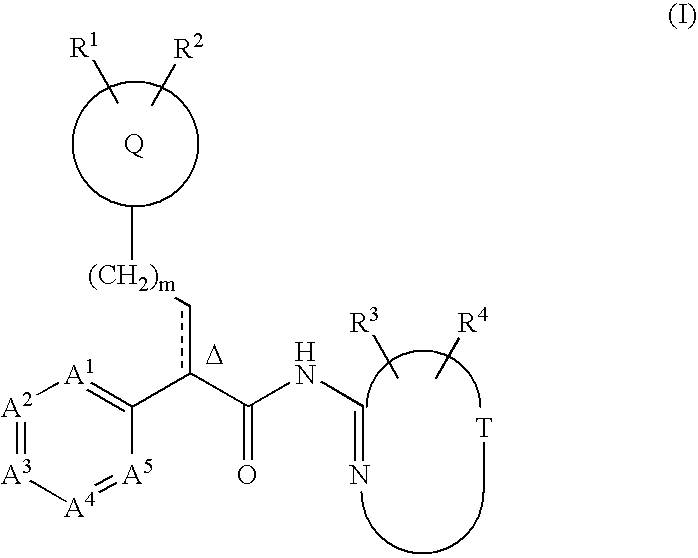
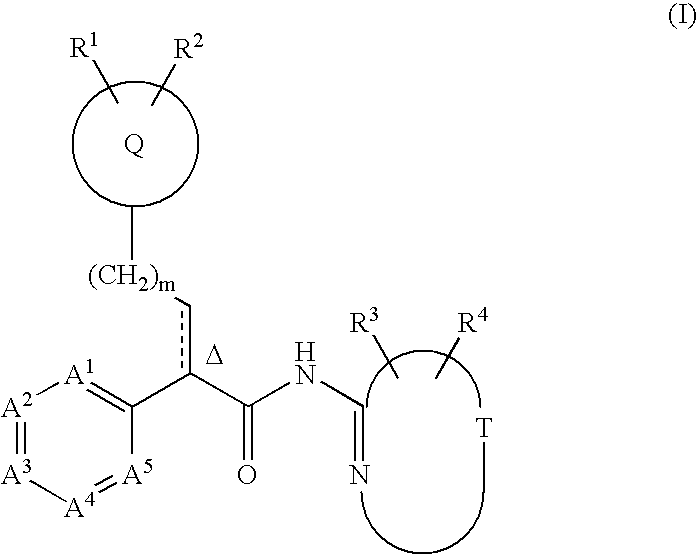
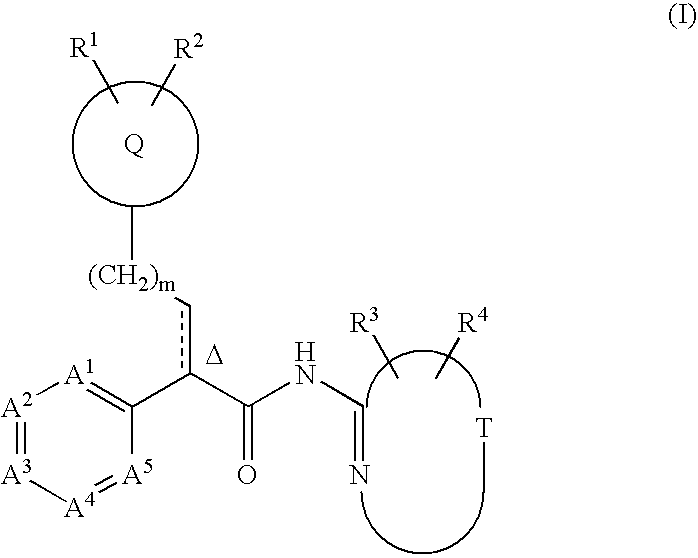
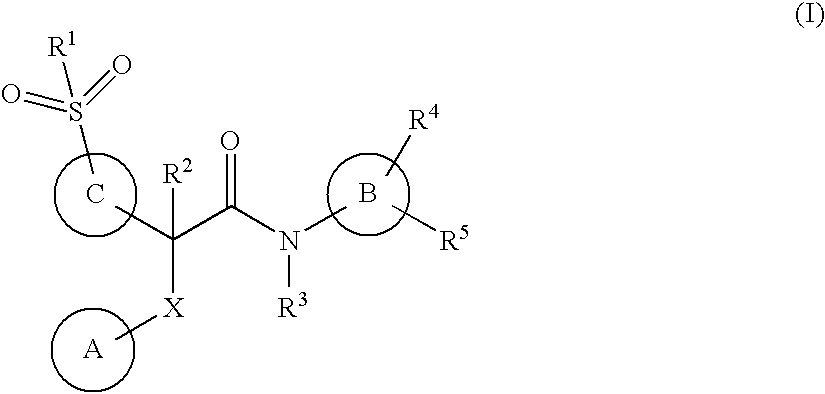
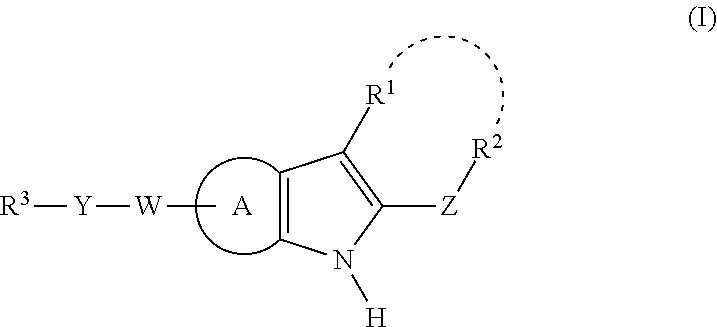
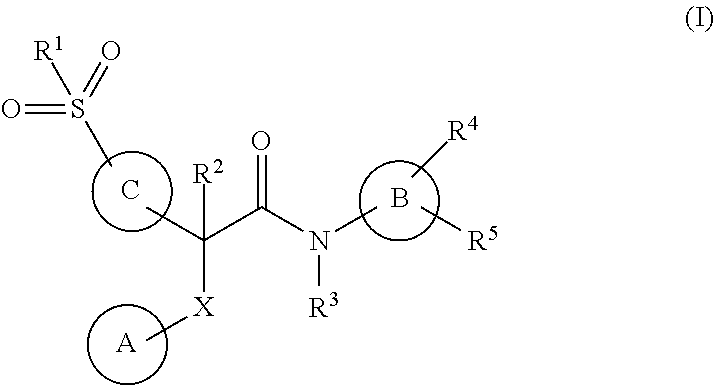
This invention relates to compounds that are activators of glucokinase and thus may be useful for the management, treatment, control, or adjunct treatment of diseases, where increasing glucokinase activity is beneficial. The compounds are of the general formula (I)wherein A and B are further defined in the application.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA INC
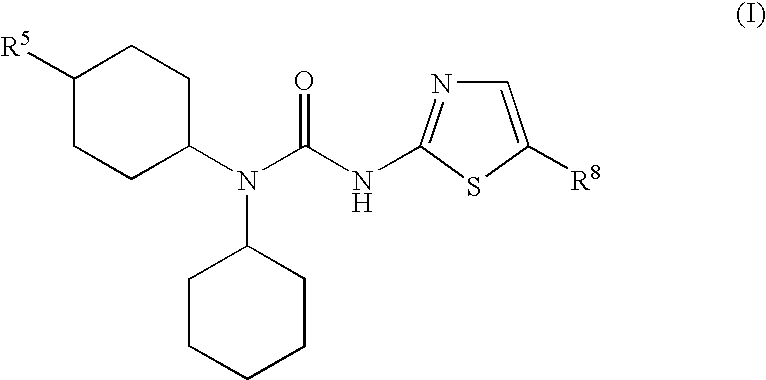
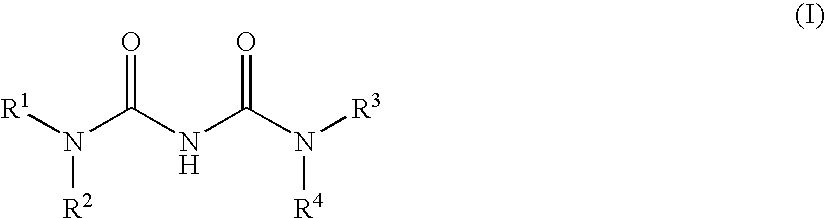
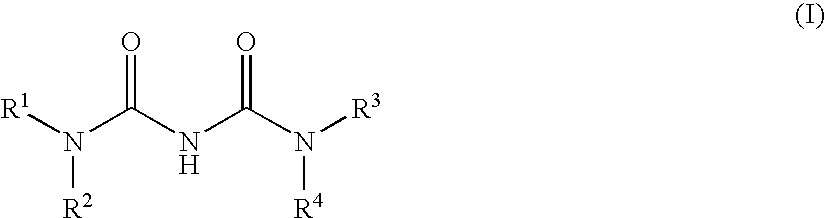
Heteroaryl-ureas and their use as glucokinase activators
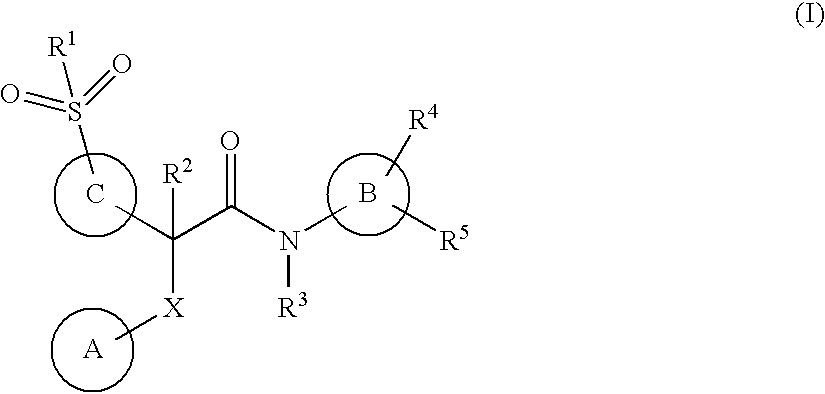
This invention relates to compounds of formula (I) which are activators of glucokinase and thus may be useful for the management, treatment, control, or adjunct treatment of diseases, where increasing glucokinase activity is beneficial.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Substituted Heteroaryls
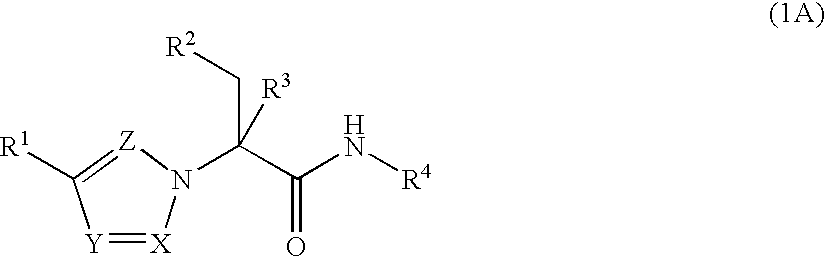
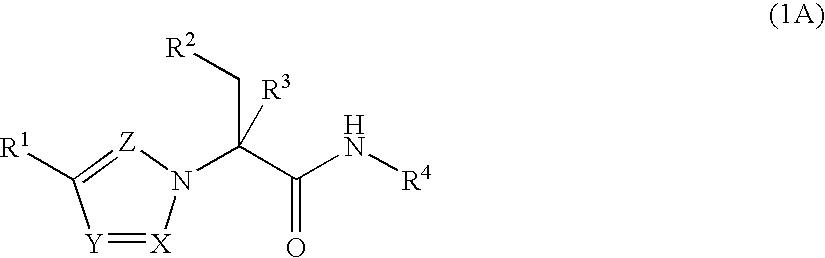
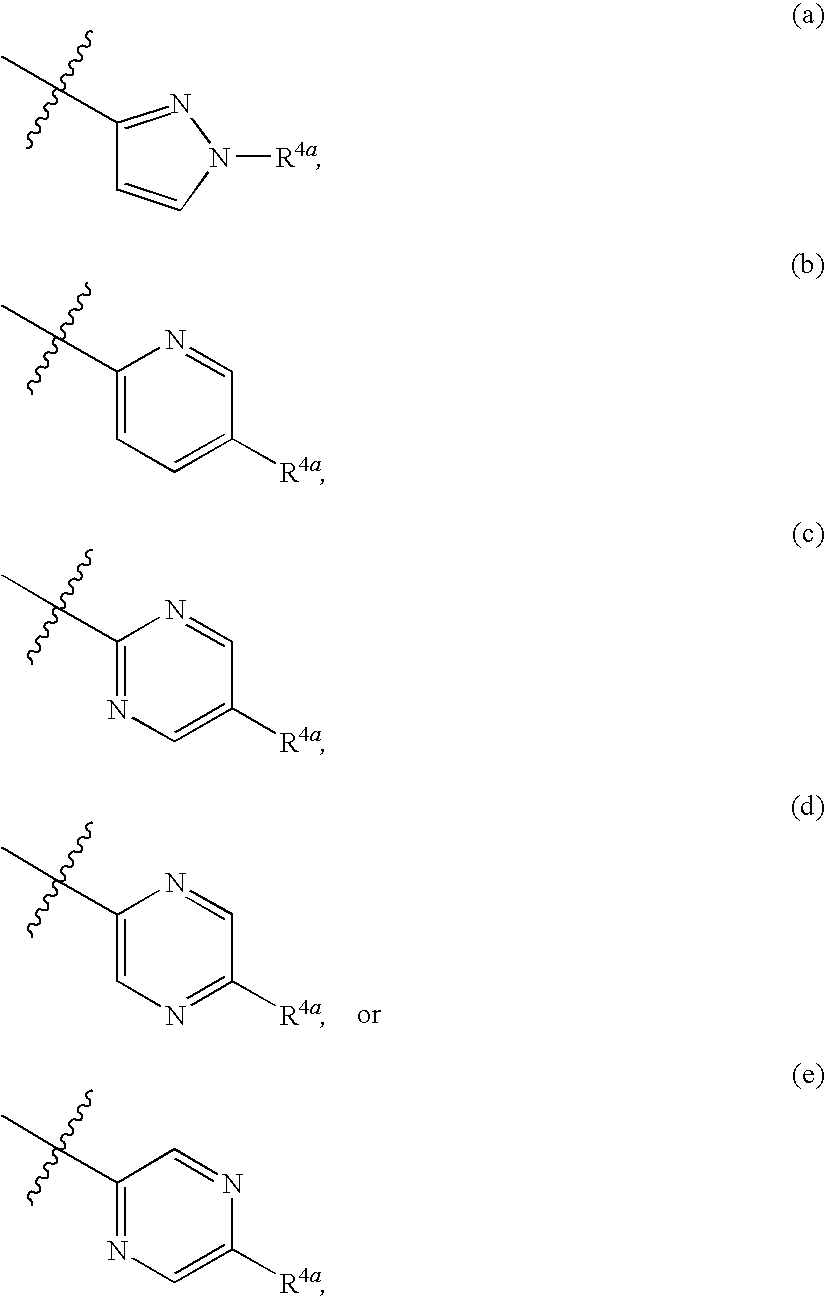
The present invention provides Formula (1A) compoundsthat act as glucokinase activators; pharmaceutical compositions thereof; and methods of treating diseases, disorders, or conditions mediated by glucokinase. X, Y, Z, R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as described herein.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Dicycloalkyl urea glucokinase activators
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Fused heterocyclic compound
InactiveUS20090247746A1Superior glucokinase activating actionEasy to useOrganic chemistryMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusObesity
The present invention provides a glucokinase activator containing a compound represented by the formula (I):wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification, or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof. According to the present invention, a glucokinase activator useful as a pharmaceutical agent such as agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes, obesity and the like, and the like can be provided.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Heteroaryl-Ureas and Their Use as Glucokinase Activators
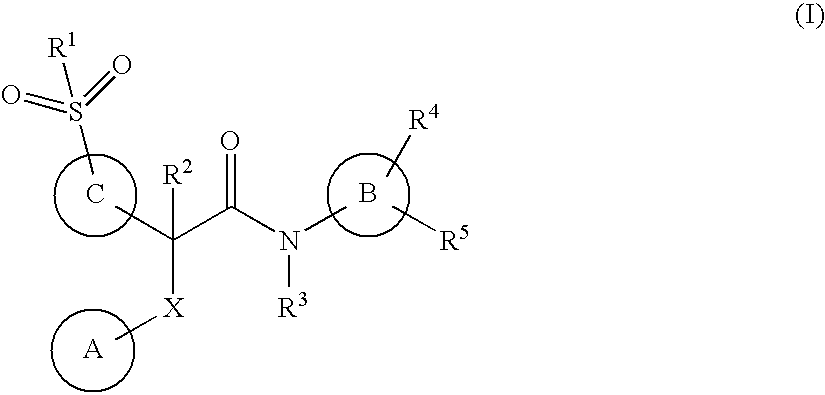
This invention relates to compounds of formula (I)which are activators of glucokinase and thus may be useful for the management, treatment, control, or adjunct treatment of diseases, where increasing glucokinase activity is beneficial.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Dicycloalkylcarbamoyl Ureas As Glucokinase Activators
This invention relates to dicycloalkylcarbamoyl ureas of formula (I), which are activators of glucokinase and thus may be useful for the management, treatment, control, or adjunct treatment of diseases, where increasing glucokinase activity is beneficial.
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA
Dicycloalkyl Urea Glucokinase Activators
Dicycloalkyl urea glucokinase activators compounds are glucokinase inhibitors useful for the treatment of diabetes.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Pharmaceutical composition containing GKAs (glucokinase activators) and B vitamins and application of pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN106474480AReduce complicationsImprove high blood sugarMetabolism disorderUrinary disorderB Vitamin FamilyVitamin
The invention relates to pharmaceutical composition containing GKAs (glucokinase activators) and B vitamins. The pharmaceutical composition is prepared from a therapeutic effective dose of one of GKAs as well as medicinal precursors, active metabolites or GKA salts, one or more of a therapeutic effective dose of the B vitamins and pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, wherein the GKAs mainly comprise TTP399, HMS5552, PF-04937319, LY2608204, PF-04991532 and GKM-001; the content of the B vitamins is 0.01-50 mg and adopt folic acid compounds as the first choice. The invention further relates to an application of the composition in preparation of drugs for treating diabetes mellitus and preventing or delaying complications of diabetic angiopathy.
Owner:深圳泰乐德医疗有限公司 +1
Urea Glucokinase Activators
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
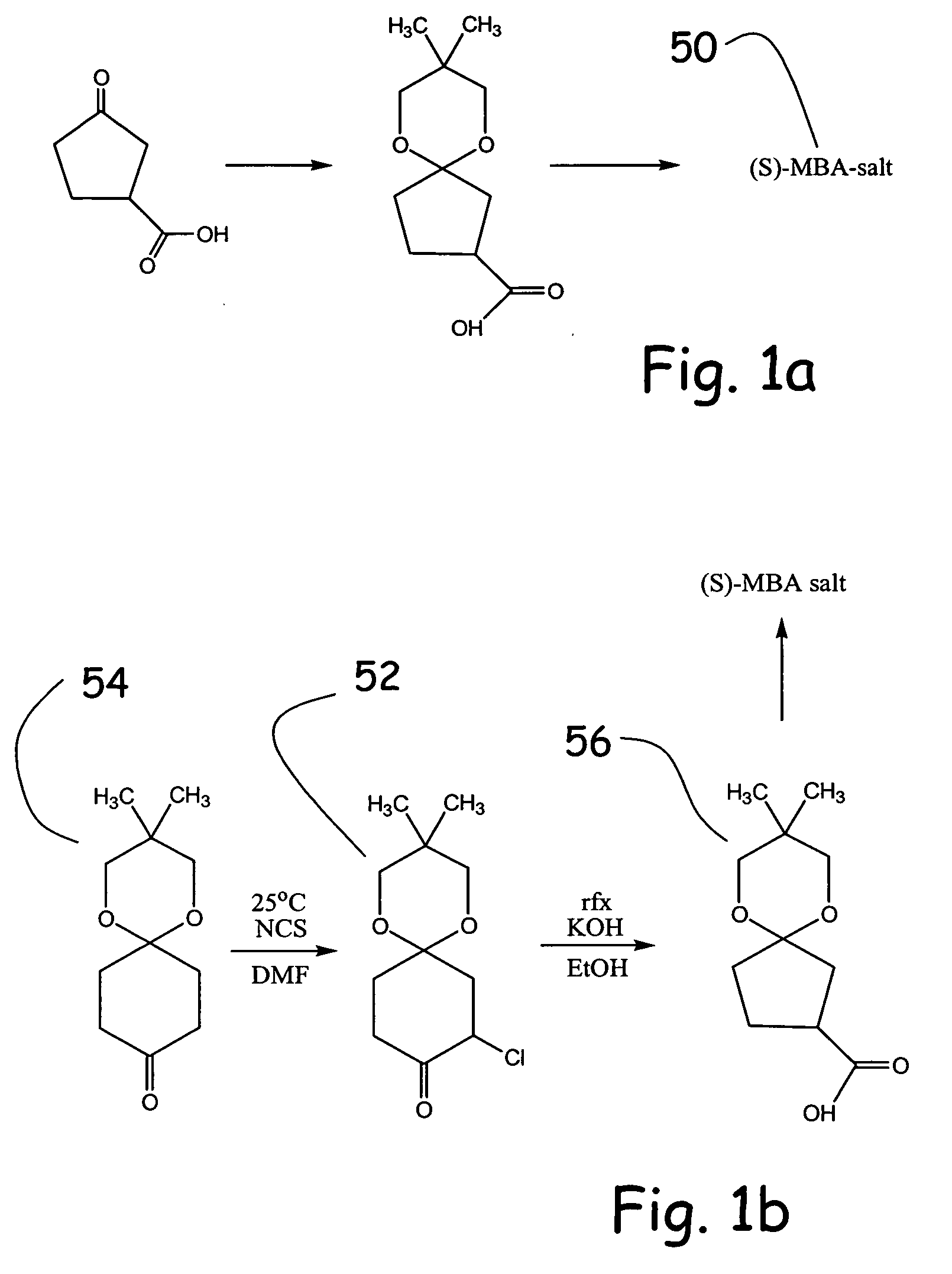
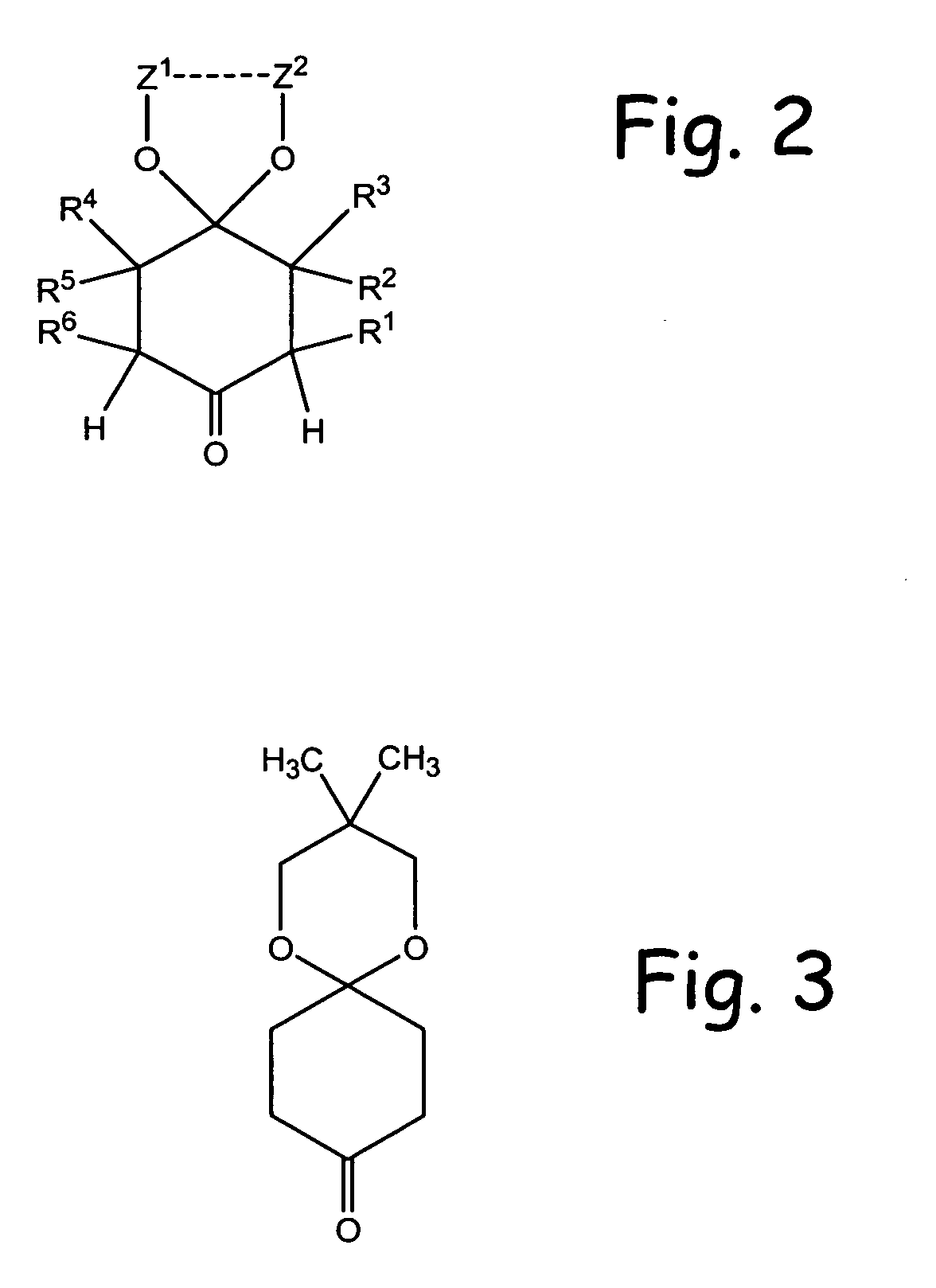
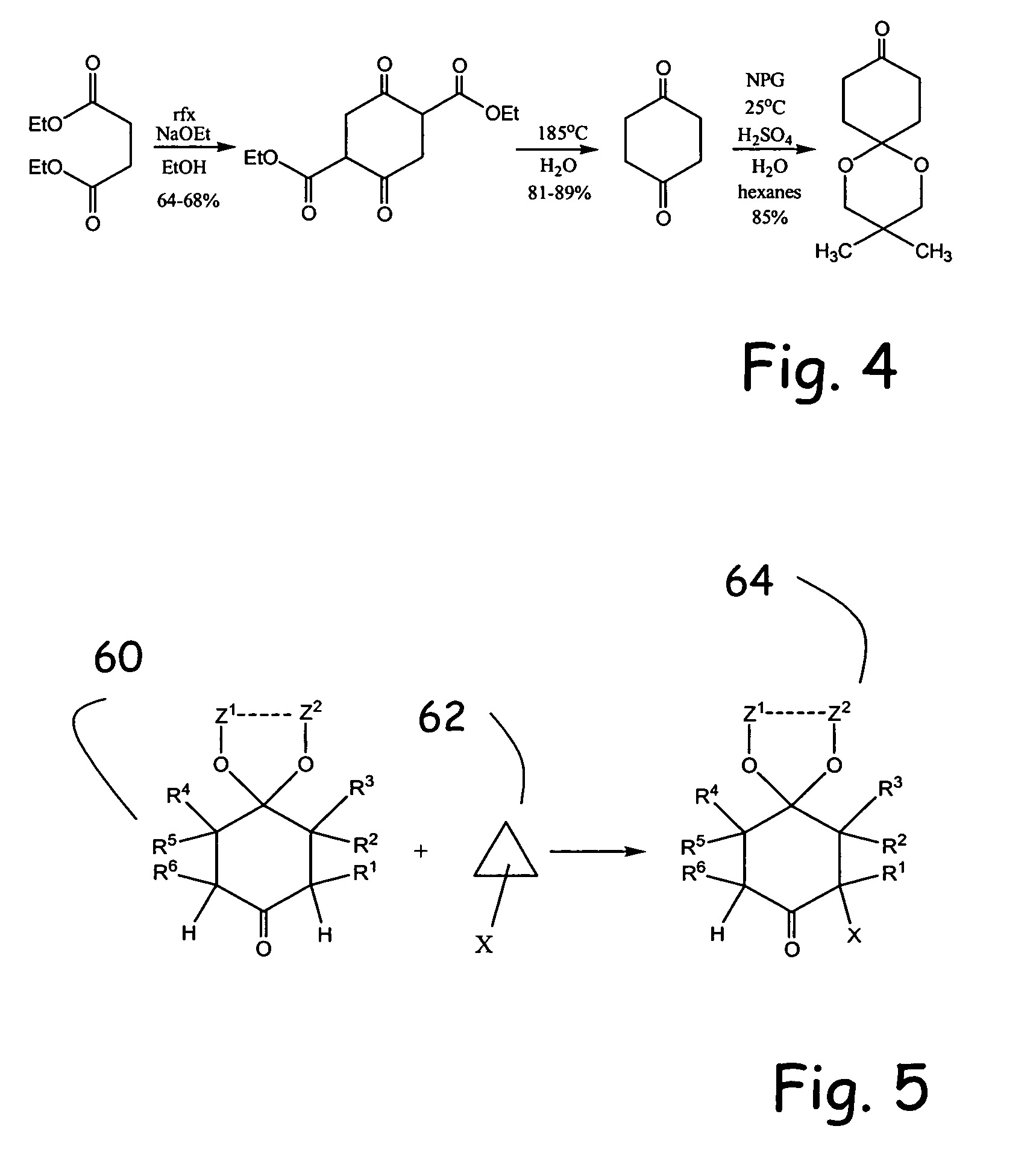
Alpha functionalization of cyclic, ketalized ketones and products therefrom
Methodologies for the alpha-monohalogenation of acid sensitive ketones, especially cyclic, acid-sensitive, ketalized ketones. As one approach, the ketone is reacted with a halogen donor compound, e.g., N-chlorosuccinimide, in anhydrous, highly polar organic reagents such as dimethylformamide (DMF). As another monohalogenation approach, it has been observed that organic salts generated from amines and carboxylic acids catalyze the monohalogenation of ketalized ketone in reagents comprising alcohol solvent (methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, etc.). The monohalogenation is fast even at −5° C. The salt can be rapidly formed in situ from ingredients including amines and / or carboxylic acids without undue degradation of the acid sensitive ketal. Aryl ketones are monooxygenated using iodosylbenzene. This methodology is applied to monohalogenation of an acid sensitive monoketal ketone. The ability to prepare monohalogenated, acid sensitive ketones facilitates syntheses using halogenated, acid sensitive ketones. As just one example, facile synthesis of halogenated, acid sensitive ketones provides a new approach to synthesize the S-ketal-acid S-MBA (S-methylbenzylamine) salt useful as an intermediate in the manufacture of a glucokinase activator. As an overview of this scheme, a monohalogenated, cyclic, ketalized ketone is prepared using monohalogenation methodologies of the present invention. The halogenated compound is then subjected to a Favorskii rearrangement under conditions to provide the racemic acid counterpart of the desired chiral salt. The desired chiral salt is readily recovered in enantiomerically pure form from the racemic mixture.
Owner:HARRINGTON PETER J +2
2-aminopyridine analogs as glucokinase activators
Provided are compounds of formula I that are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of diseases mediated by deficient levels of glucokinase activity, such as diabetes meilitus. Also provided are methods of treating or preventing diseases and disorders characterized by underactivity of glucokinase or which can be treated by activating glucokinase.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Tri(cyclo) substituted amide glucokinase activator compounds
Compounds of Formula (I):or pharmaceutically acceptable salts or N-oxides thereof, are useful in the prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of hyperglycemia and diabetes.
Owner:PROSIDION LIMITED
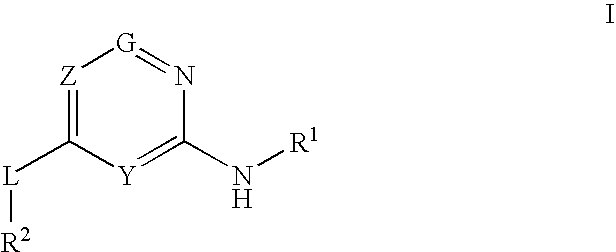
Glucokinase activators
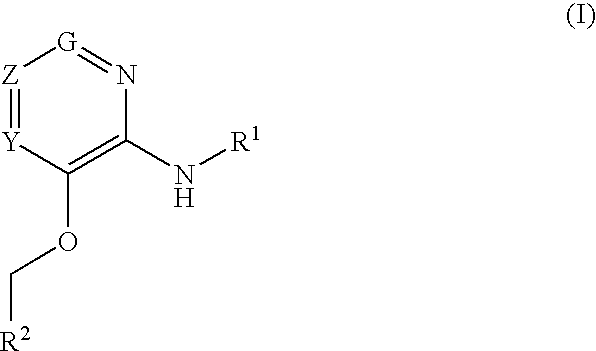
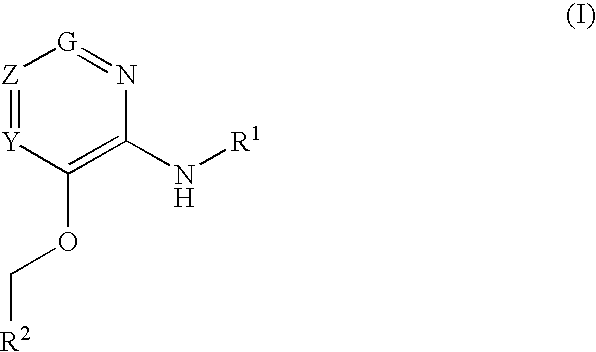
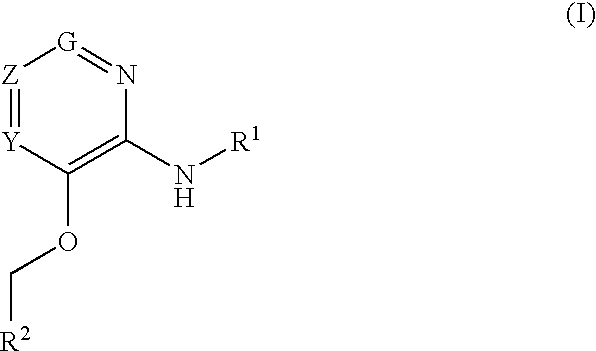
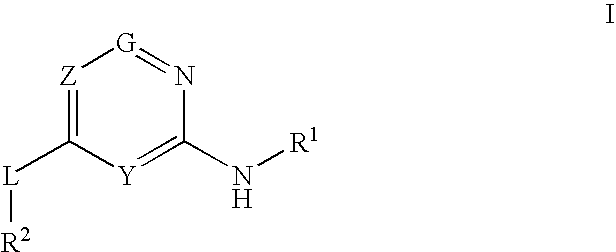
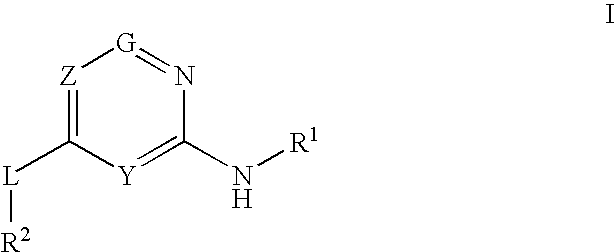
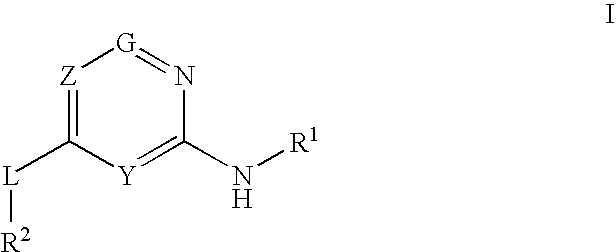
Provided are compounds of formula Iwherein R2, L, Z, Y, G and R1 are as defined herein, that are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of diseases or disorders mediated by deficient levels of glucokinase activity or which can be treated by activating glucokinase including, but not limited to, diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, IFG (impaired fasting glucose) and IFG (impaired fasting glycemia), as well as other diseases and disorders such as those discussed herein.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Glucokinase Activator Compositions for the Treatment of Diabetes
ActiveUS20140066372A1Improve glucose toleranceIncrease secretionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSitagliptinAcetic acid
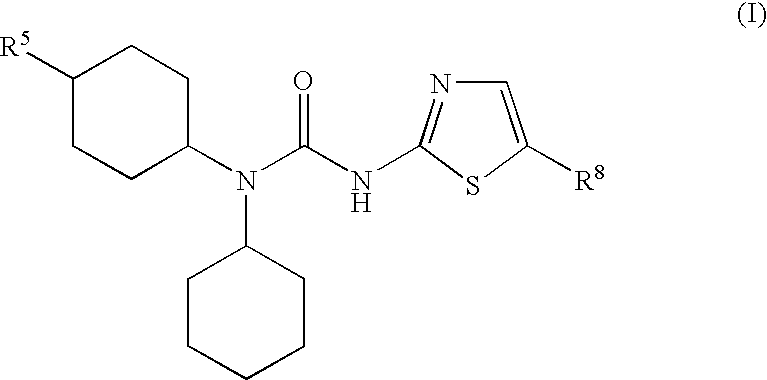
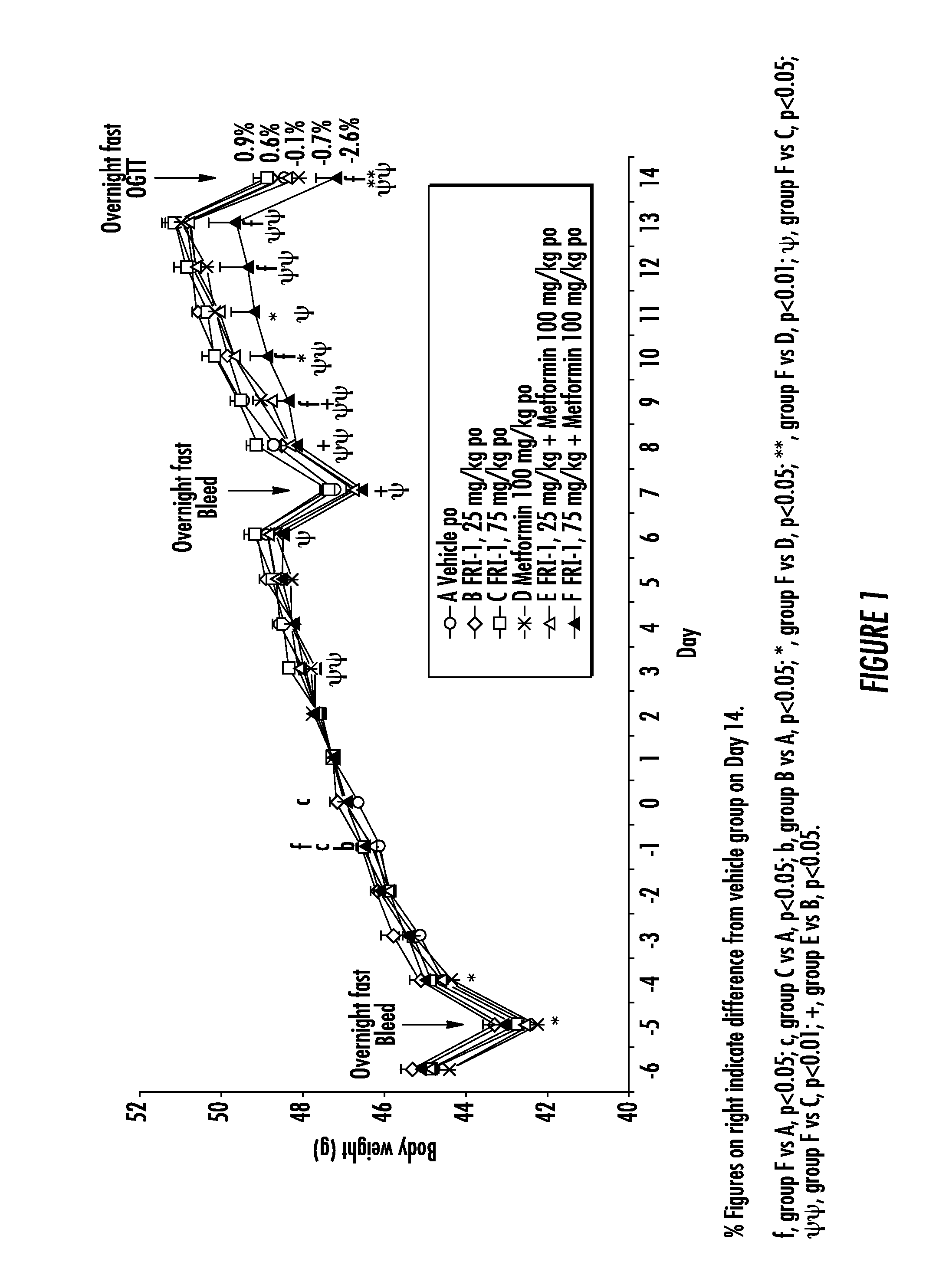
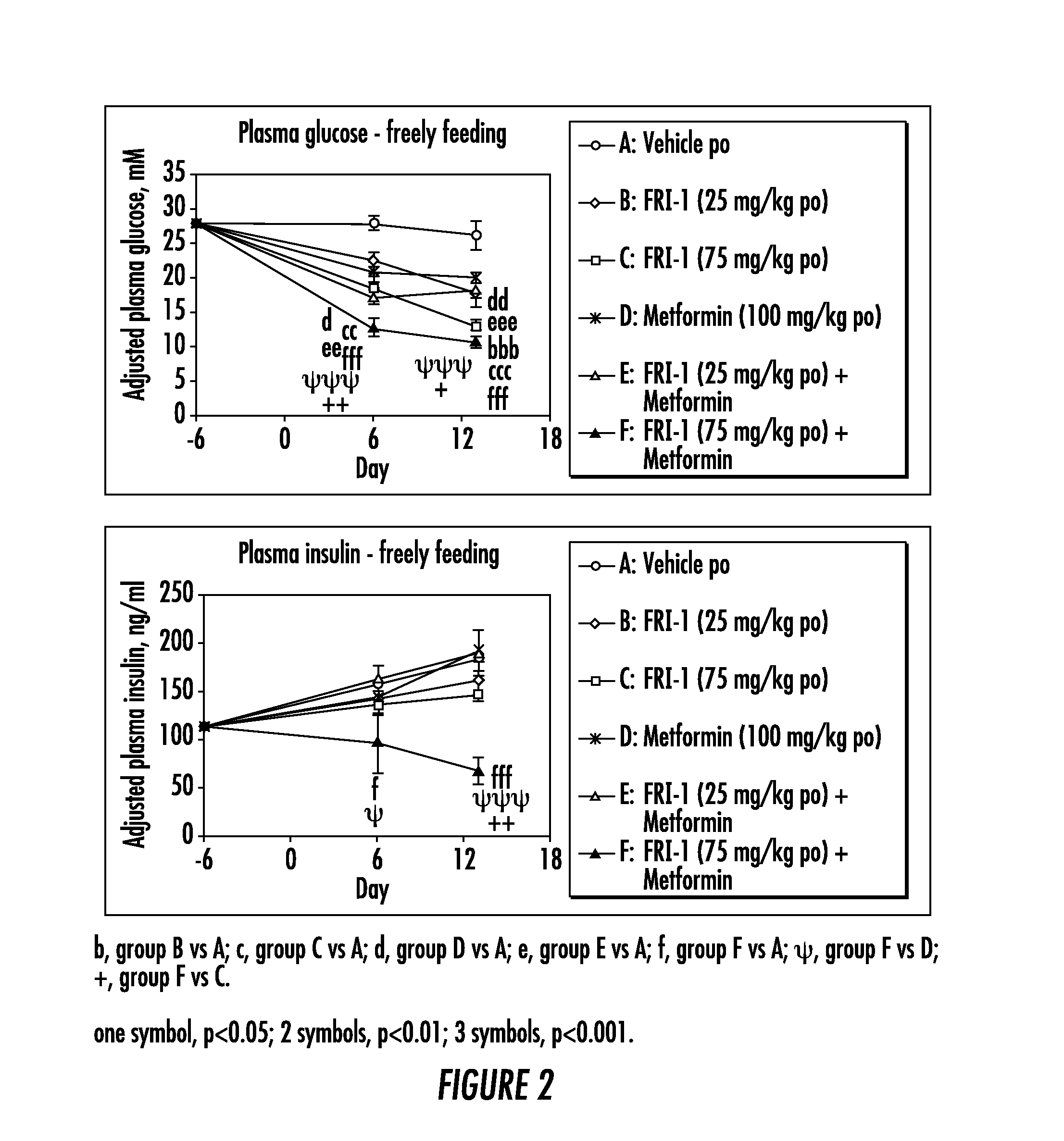
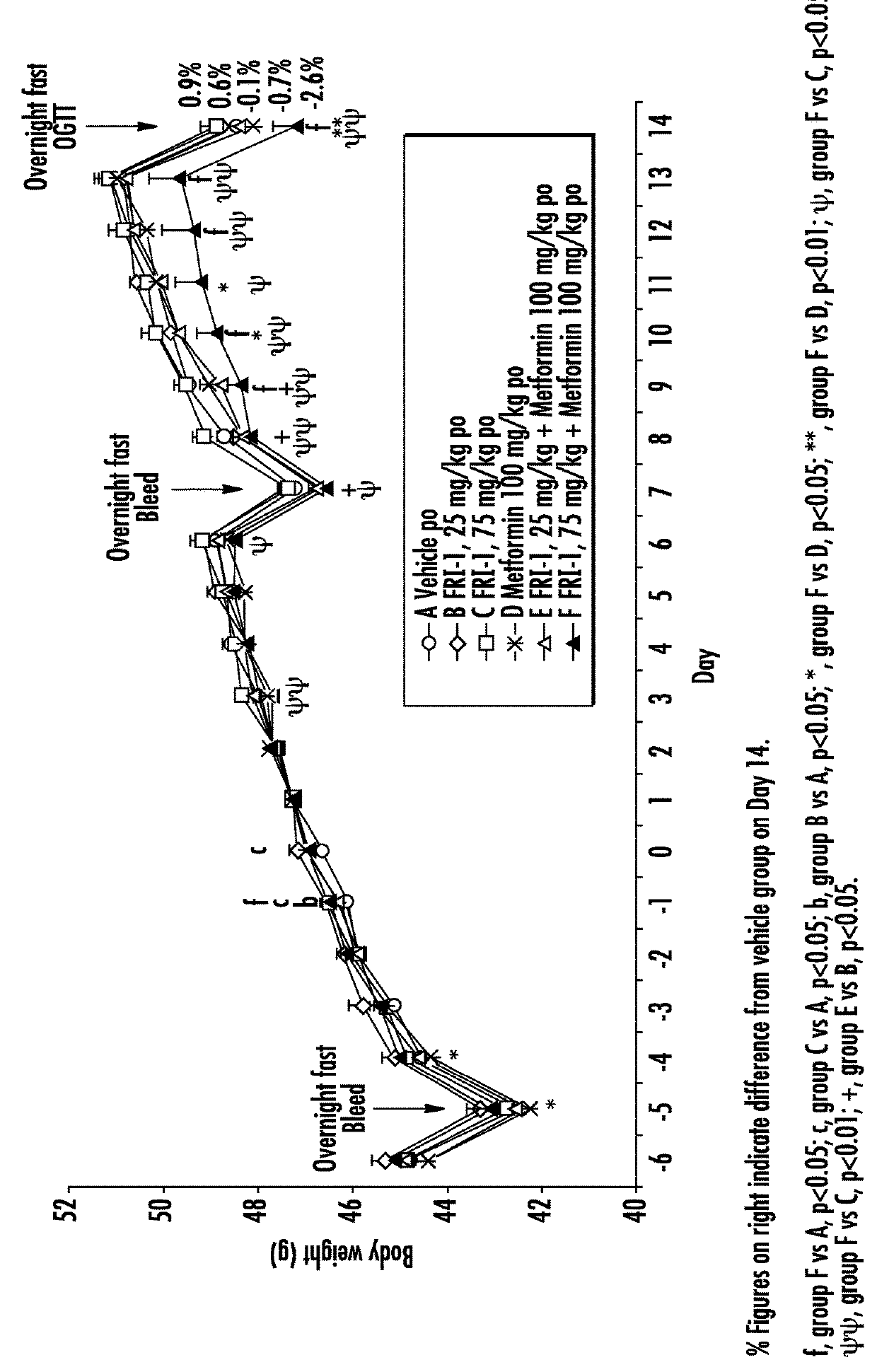
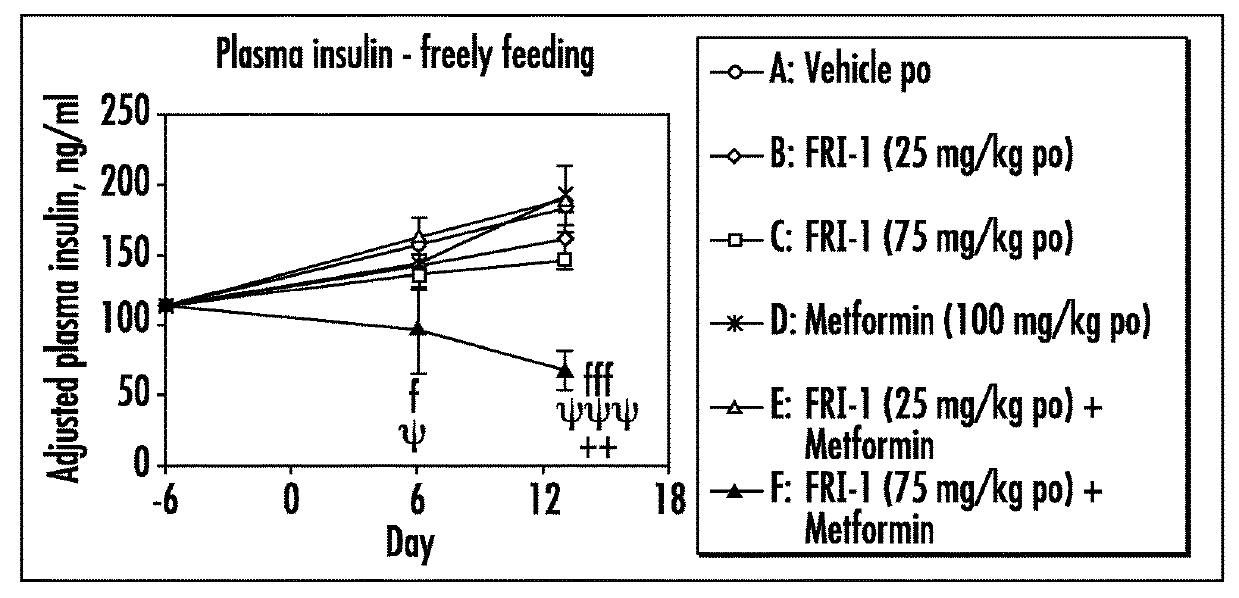
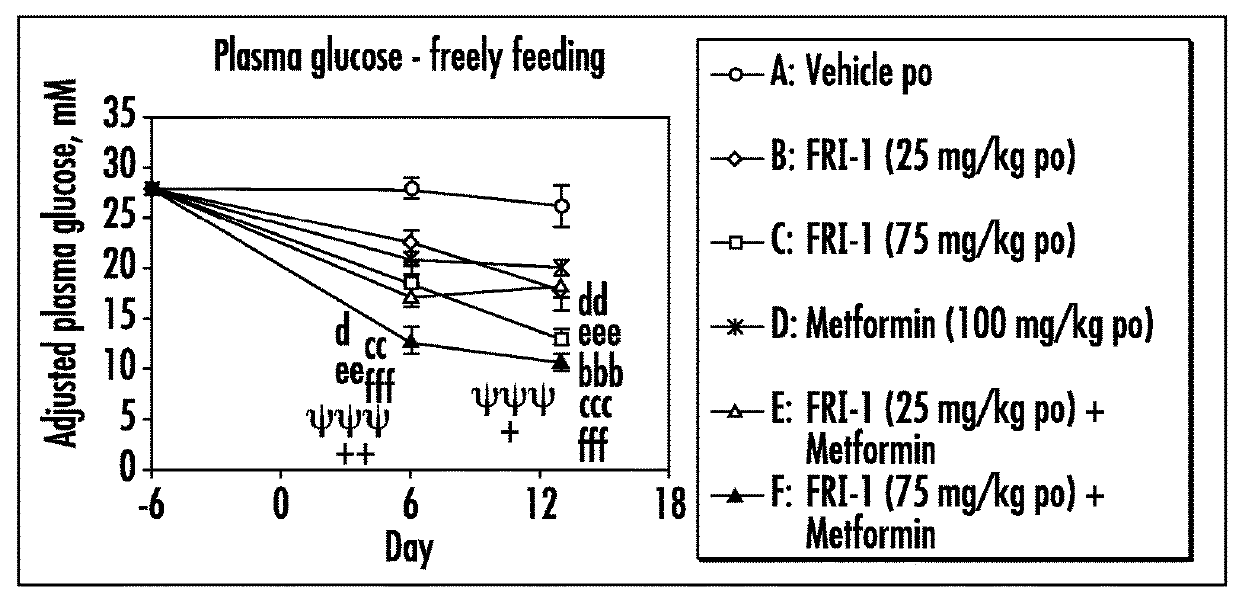
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising {2-[3-cyclohexyl-3-(trans-4-propoxy-cyclohexyl)-ureido]-thiazol-5-ylsulfanyl}-acetic acid (FRI-1) in combination with an anti-diabetic drug selected from the group consisting of metformin, sitagliptin or exenatide. The present invention also relates to the use of the pharmaceutical compositions in restoring insulin sensitivity and treating type II diabetes, including reducing body weight in subjects undergoing type II diabetes treatment.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Use of metformin in combination with a glucokinase activator and compositions comprising metformin and a glucokinase activator
The present invention provides uses of a glucokinase activator in combination with metformin. Uses include treating type 2 diabetes, lowering blood glucose, improving insulin sensitivity, enhancing phosphorylation of glucose, and improving the therapeutic effectiveness of metformin. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions that comprise a GK activator and metformin. The invention also provides a salt formed between metformin and a GK activator.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Aryloxy-Substituted Benzimidazole Derivatives
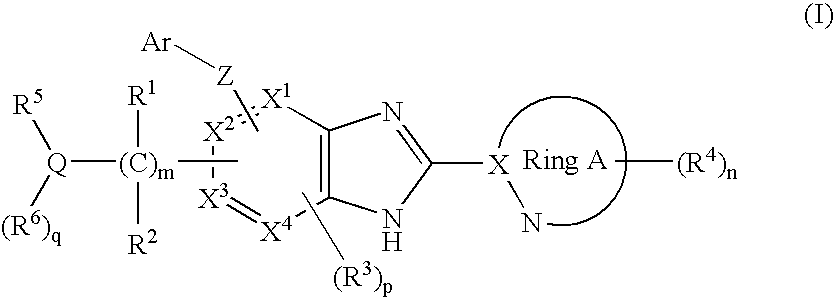
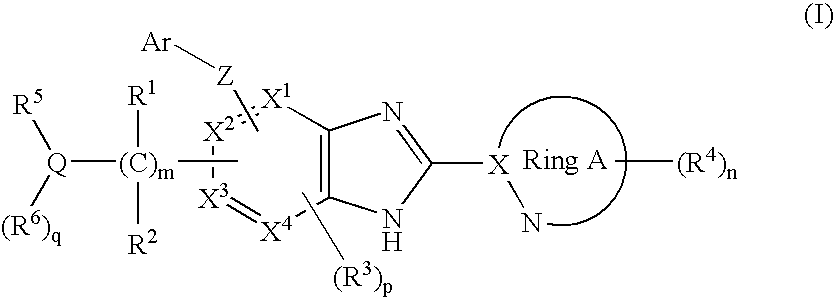
A glucokinase activator is provided; and a treatment and / or a preventive for diabetes, or a treatment and / or a preventive for diabetes such as retinopathy, nephropathy, neurosis, ischemic cardiopathy, arteriosclerosis, and further a treatment and / or a preventive for obesity are provided.The invention relates to a compound of a formula (I):[wherein R1 and R2 represent a hydrogen, etc.; R3 represents a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, etc.; R4 each independently represents a hydrogen atom, a lower alkyl group, etc.; Q represents a carbon atom, a nitrogen atom or a sulfur atom (the sulfur atom may be mono- or di-substituted with an oxo group); R5 and R6 each represent a hydrogen atom, a lower alkyl group, etc.; X1, X2, X3 and X4 each independently represent a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom; Z represents an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom or a nitrogen atom; Ar represents an aryl or heteroaryl group optionally mono to tri-substituted with a group selected from the substituent group β; ring A represents a 5- or 6-membered nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic group; m indicates an integer of from 1 to 6; n indicates an integer of from 0 to 3; p indicates an integer of from 0 to 2 (provided that at least two of X1 to X4 are carbon atoms); q indicates 0 or 1] or its pharmaceutically-acceptable salt, which has an effect of glucokinase activation and is useful as a treatment for diabetes.
Owner:MSD KK
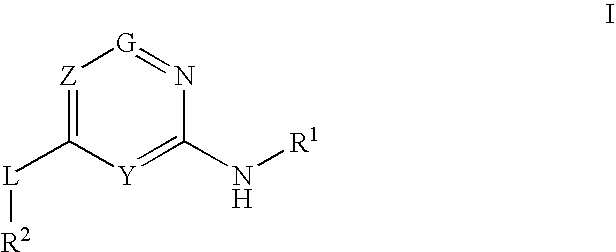
Glucokinase activators
Provided are compounds of Formula I wherein R1, R2, Y, Z and G are as defined herein, that are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of diseases mediated by deficient levels of glucokinase activity, such as diabetes mellitus. Also provided are methods of treating or preventing diseases and disorders characterized by underactivity of glucokinase or which can be treated by activating glucokinase.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Acetamide derivatives as glucokinase activators, their process and medicinal application
ActiveUS8501955B2Maintain good propertiesWell formedBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePerylene derivatives
Acetamide derivatives, their stereoisomers, tautomers, prodrugs, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, polymorphs, solvates and formulations thereof for the prophylaxis, management, treatment, control of progression, or adjunct treatment of diseases and / or medical conditions where the activation of glucokinase would be beneficial, are disclosed.The disclosure also provides process of preparation of these acetamide derivatives.
Owner:IMPETIS BIOSCI LTD
Novel fused ring compound and use thereof
InactiveUS20120035163A1Superior glucokinase activating actionBiocideOrganic chemistryObesityStereochemistry
The present invention provides an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes, obesity and the like, a glucokinase activator, containing a compound represented by the formula (I):wherein each symbol is as defined in the description, or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Stable glucokinase activator compositions
InactiveUS20160015638A1Improve blood sugar controlPowder deliveryBiocideOral medicationGlucokinase activator
The invention relates to stable pharmaceutical compositions comprising a glucokinase (GK) activator suitable for oral administration. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such pharmaceutical compositions.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
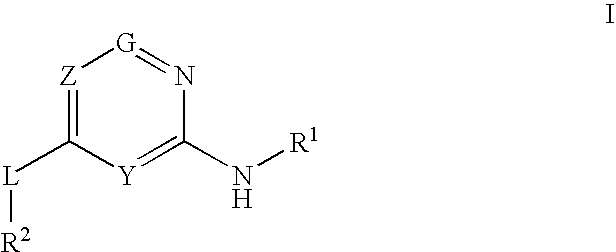
Glucokinase activators
Provided are compounds of formula Iwherein R2, L, Z, Y, G and R1 are as defined herein, that are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of diseases or disorders mediated by deficient levels of glucokinase activity or which can be treated by activating glucokinase including, but not limited to, diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, IFG (impaired fasting glucose) and IFG (impaired fasting glycemia), as well as other diseases and disorders such as those discussed herein.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA INC
Oral preparation of glucokinase activator and preparation method therefor
ActiveUS11266630B2Ensuring efficacy and safety of drugQuick releaseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseCaplet Dosage Form
Owner:HUA MEDICINE (SHANGHAI) LIMITED
2-aminopyridine analogs as glucokinase activators
Provided are compounds of formula I that are useful in the treatment and / or prevention of diseases mediated by deficient levels of glucokinase activity, such as diabetes meilitus. Also provided are methods of treating or preventing diseases and disorders characterized by underactivity of glucokinase or which can be treated by activating glucokinase.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA INC
Ureido-thiazole glucokinase activators
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Glucokinase activator
InactiveUS20100016304A1Less side effectsProlongation of QT interval and hypoglycemiaBiocideOrganic chemistryHalogenAlkoxy group
A compound represented by the following formula (1):(wherein the carbon atom denoted by * is in the R-configuration; R1 and R2 are each independently a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a hydroxyamino group, a nitro group, a cyano group, a sulfamoyl group, a C1-C6 alkyl group, a C1-C6 alkoxy group, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group; and A is a substituted or unsubstituted heteroaryl group), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD +1
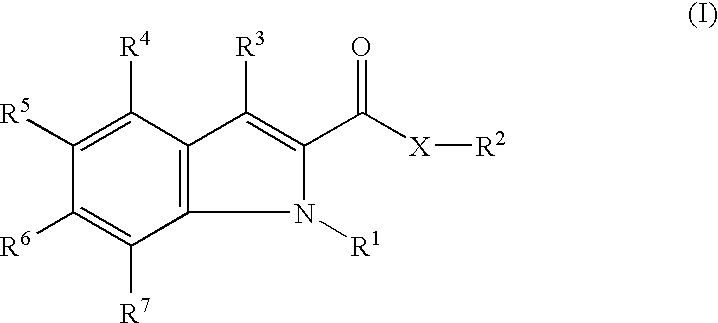
Indole compound
InactiveUS7652133B2Superior glucokinase activating actionMaintain good propertiesBiocideOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusObesity
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a glucokinase activator useful as a pharmaceutical agent such as an agent for the prophylaxis or treatment of diabetes, obesity and the like.The present invention provides a glucokinase activator containing a compound represented by the formula (I):whereinR1 is a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom;R2 is a group represented bywherein each symbol is defined in the specification,or a salt thereof or a prodrug thereof.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Acetamide derivatives as glucokinase activators, their process and medicinal applications
Acetamide derivatives, their stereoisomers, tautomers, prodrugs, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, polymorphs, solvates and formulations thereof for the prophylaxis, management, treatment, control of progression, or adjunct treatment of diseases and / or medical conditions where the activation of glucokinase would be beneficial, are disclosed.The disclosure also provides process of preparation of these acetamide derivatives.
Owner:IMPETIS BIOSCI LTD
Glucokinase activator compositions for the treatment of diabetes
ActiveUS10004782B2Normalizing or lowering blood glucoseLowering of food intakeOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSitagliptinAcetic acid
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising {2-[3-cyclohexyl-3-(trans-4-propoxy-cyclohexyl)-ureido]-thiazol-5-ylsulfanyl}-acetic acid (FRI-1) in combination with an anti-diabetic drug selected from the group consisting of metformin, sitagliptin or exenatide. The present invention also relates to the use of the pharmaceutical compositions in restoring insulin sensitivity and treating type II diabetes, including reducing body weight in subjects undergoing type II diabetes treatment.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com