Closed loop resource allocation
a closed loop and resource allocation technology, applied in the field of wireless communications, can solve the problems of imposing stringent and fixed delay requirements, waste of resources, delay in the decision-making process, etc., and achieve the effects of ensuring resource allocation fairness, high burstness, and flexible us
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
I. Method Overview
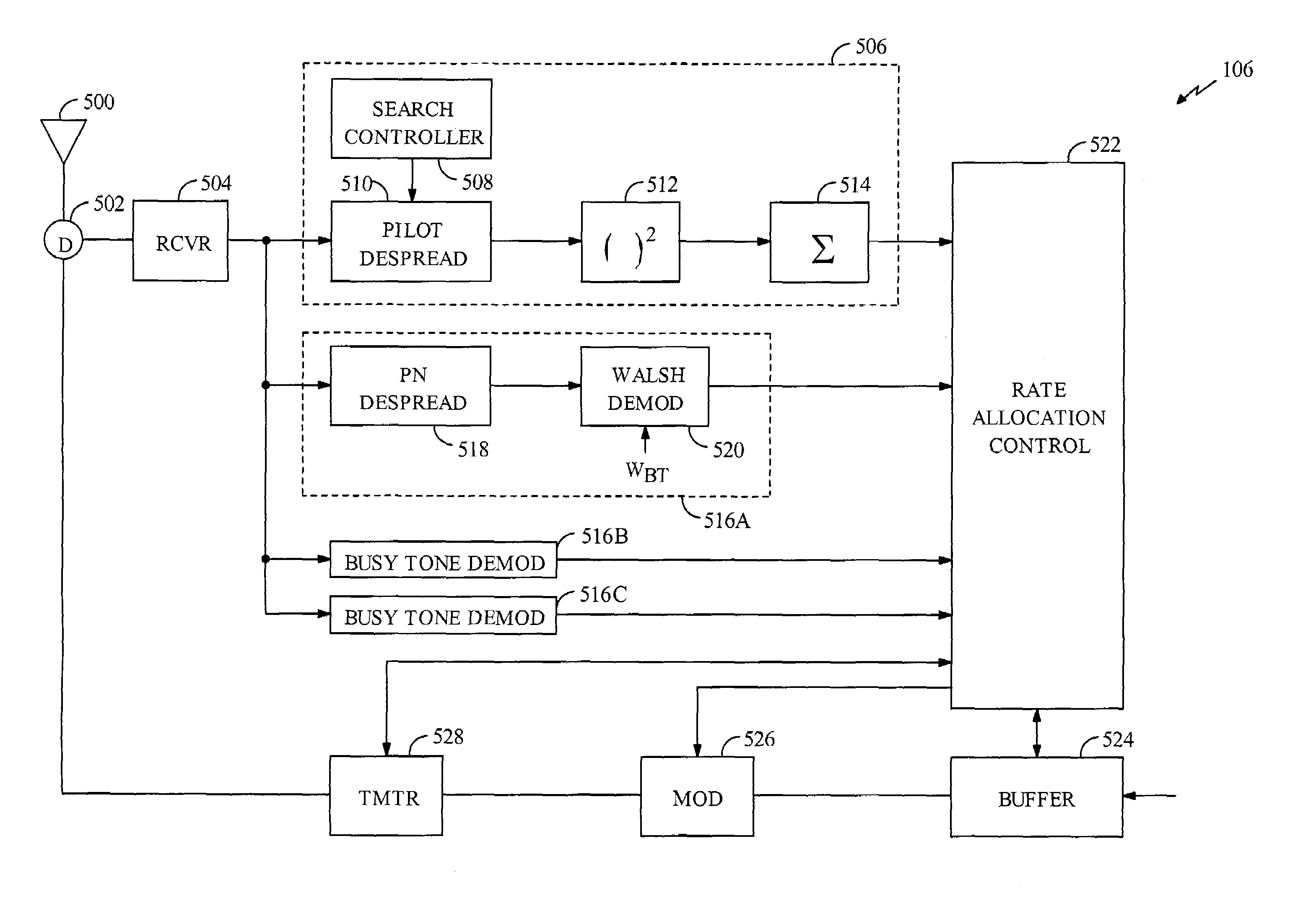
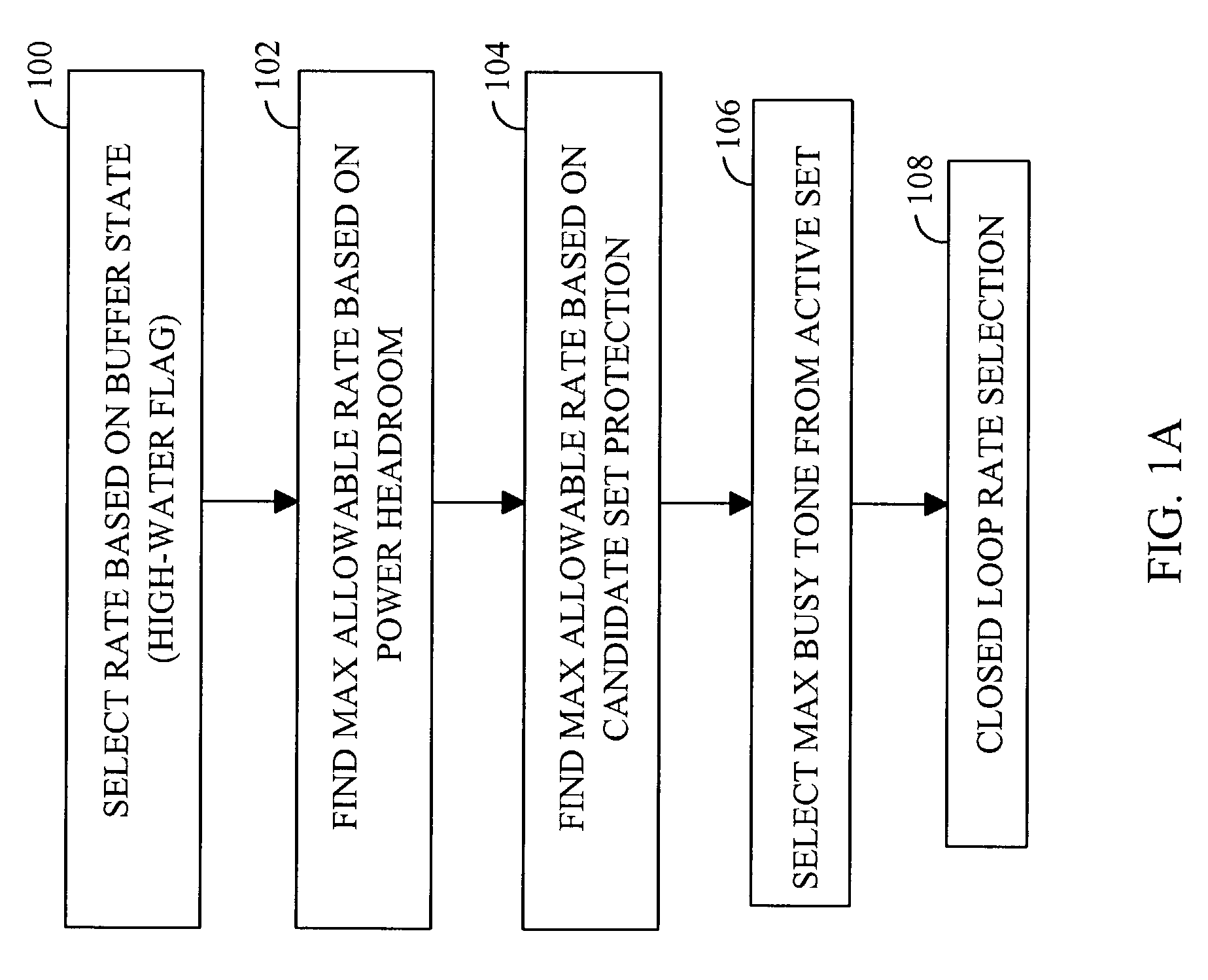
[0033]FIG. 1A is a flowchart describing the preferred method of performing closed loop resource allocation according to the present invention. It will be understood by one skilled in the art that the steps illustrated in FIG. 1A represent no preferred ordering sequence and that the order of the steps may be changed without departing from the scope of the present invention. Moreover, steps of the present invention may be eliminated altogether without departing from the scope of the present invention. In the exemplary embodiment, the present invention is employed to determine the data rate of reverse link transmissions from a subscriber station. In block 100, the subscriber station selects an initial desired rate (Rstep1) based on the buffer state. In the exemplary embodiment, the data rate is determined on a per packet basis.
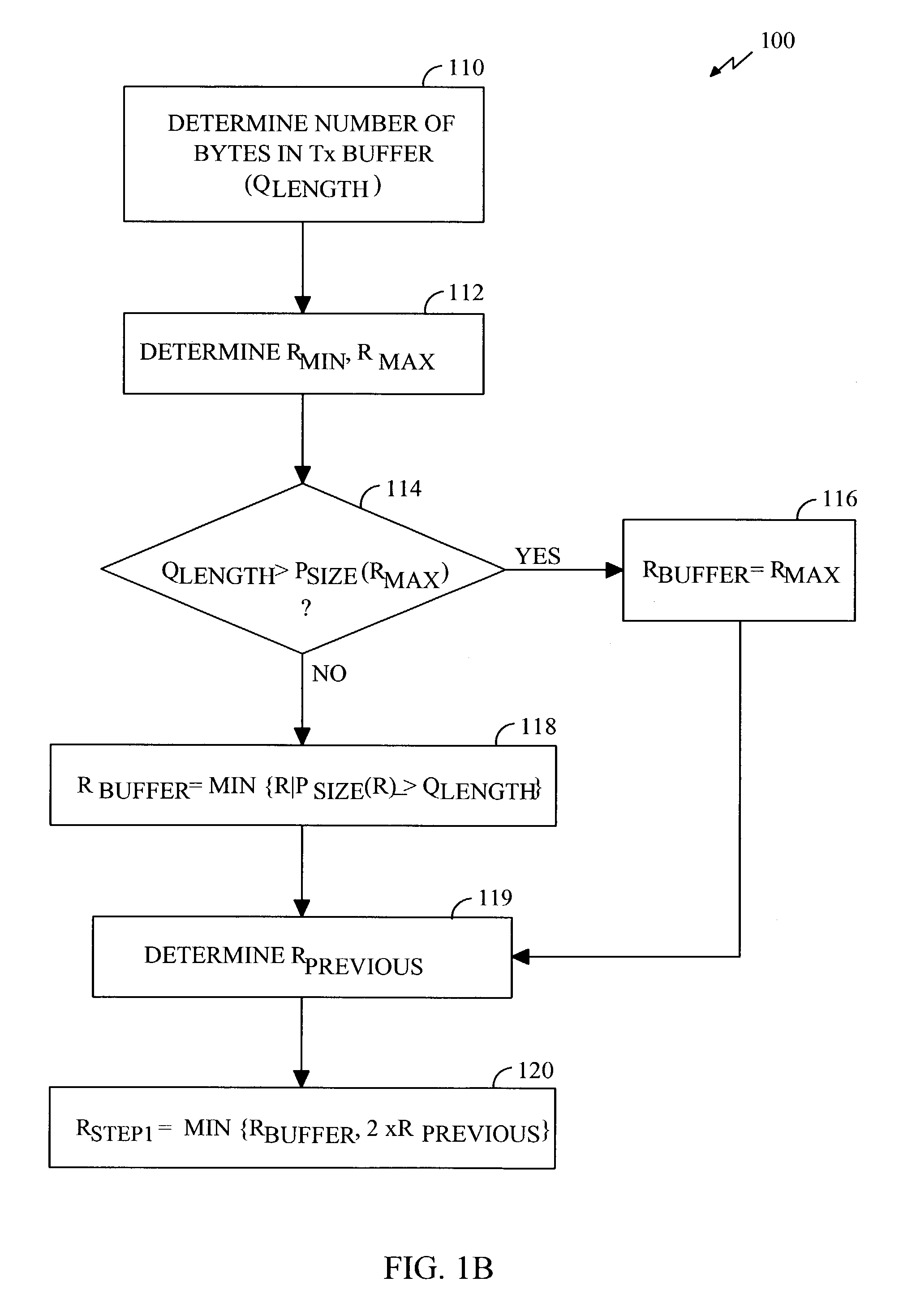
[0034]FIG. 1B is a flowchart describing the rate selection based on the buffer state in greater detail. In block 110, the subscriber station de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com