Methods For Enhancing Paper Strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
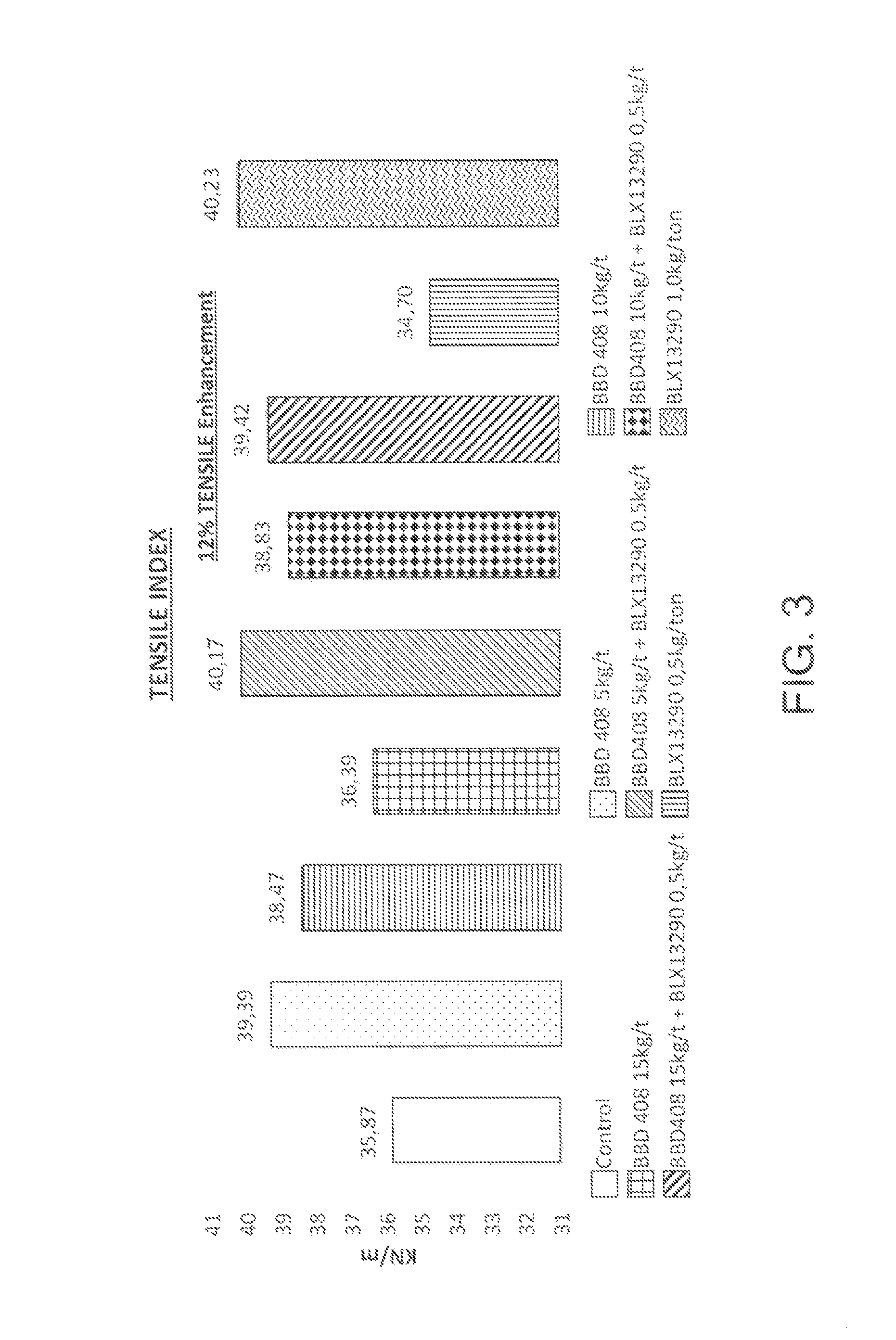
[0049]This example demonstrates the surprising and unexpected results achieved by the methods of the present invention. 110 g / m2 paper was produced on a laboratory scale consistent with the methods of the present invention. Differing amounts of enzyme (BLX 13290) and polymer (Bubond® 408) were used to produce the paper. A ring crush test (RCT) and a tensile strength test were performed on the resulting paper. FIG. 1 is a bar graph and shows results of using enzyme and polymer to increase dry strength based on the RCT. The RCT index is shown in kN / m for the various treatments. FIG. 2 is a bar graph showing the percentage gain in dry strength based on RCT using polymer, enzyme, or a combination thereof. FIG. 3 is a bar graph showing the results of using enzyme and polymer to increase dry strength based on tensile index (kN / m) for the different treatments. FIG. 4 is a bar graph showing the percentage gain in dry strength based on tensile index using polymer, enzyme, or a combination th...
example 2
[0050]This example demonstrates the surprising and unexpected results achieved by the methods of the present invention. A trial was conducted to determine if an existing program could be replaced with a new program in order to increase dry strength increase at lower cost while maintaining or improving other desirable properties. The existing program involved use of cationic polyvinylamine (0.85 kg / metric ton on a dry basis) plus anionic polyvinylamine (0.9 kg / metric ton on a dry basis). The new program involved use of cationic glyoxal polyacrylamide (0.50 kg / metric ton on a dry basis) plus laccase product (0.5 kg / metric ton on a wet basis). BLX 13290 was used as the enzyme (laccase product) and Bubond® 408 was used as the polymer application for strength enhancement. The grade was corrugated medium and testliner, including 117MI, 117NO, 150UH, 165UH, 175UH, and 190UH. The furnish was 100% recycled unbleached fiber paper Paper was produced using a Fourdrinier one ply, two press secti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com