Method of Testing Moisture Retention of Tobacco
a technology of physical moisture retention and tobacco, which is applied in the field of testing and evaluating physical moisture retention of tobacco, can solve the problems of long testing period, large number of repeated manual operations, and complicated methods, and achieves convenient and applicable, high degree of automation, and preferred accuracy and reproducibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
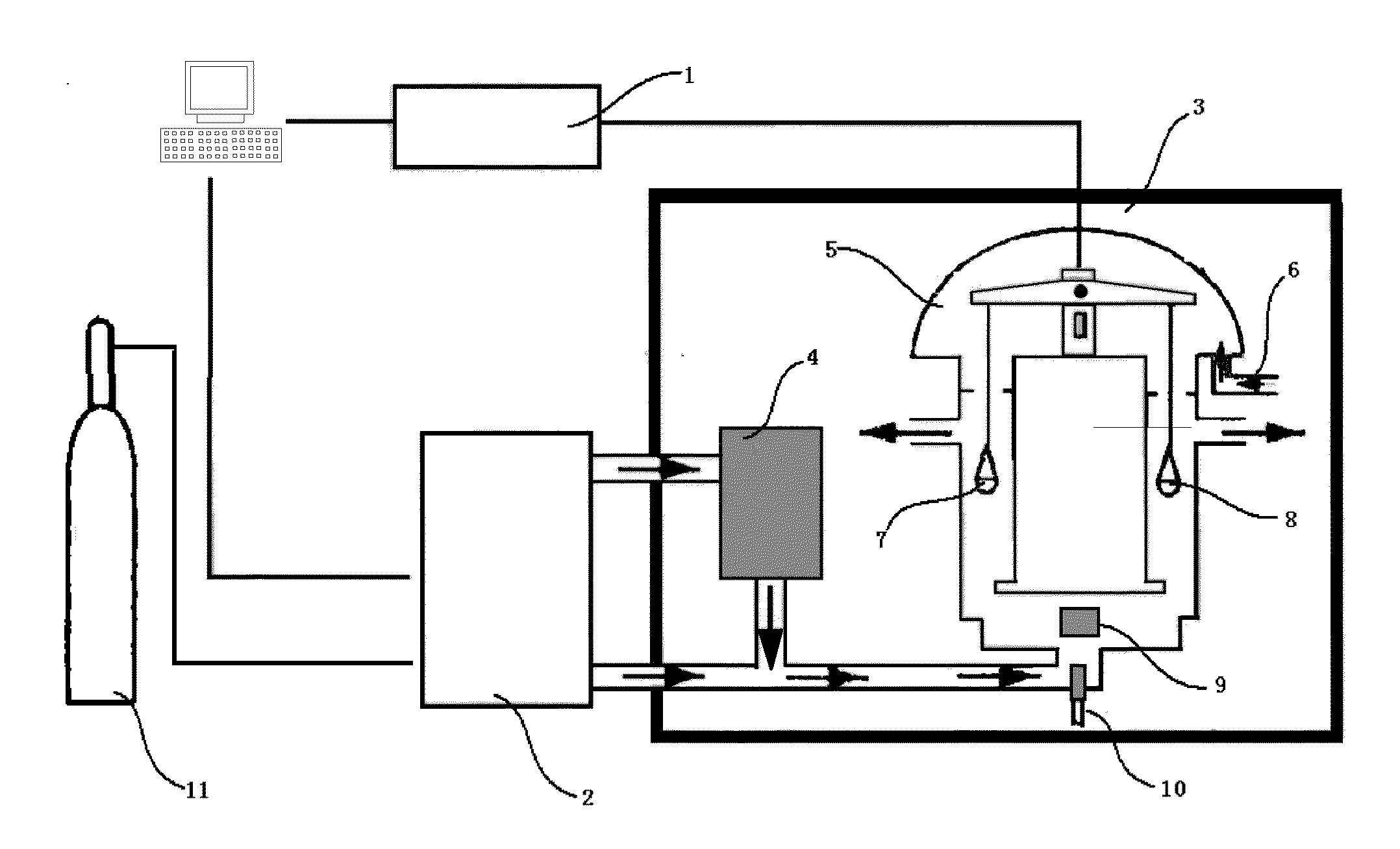
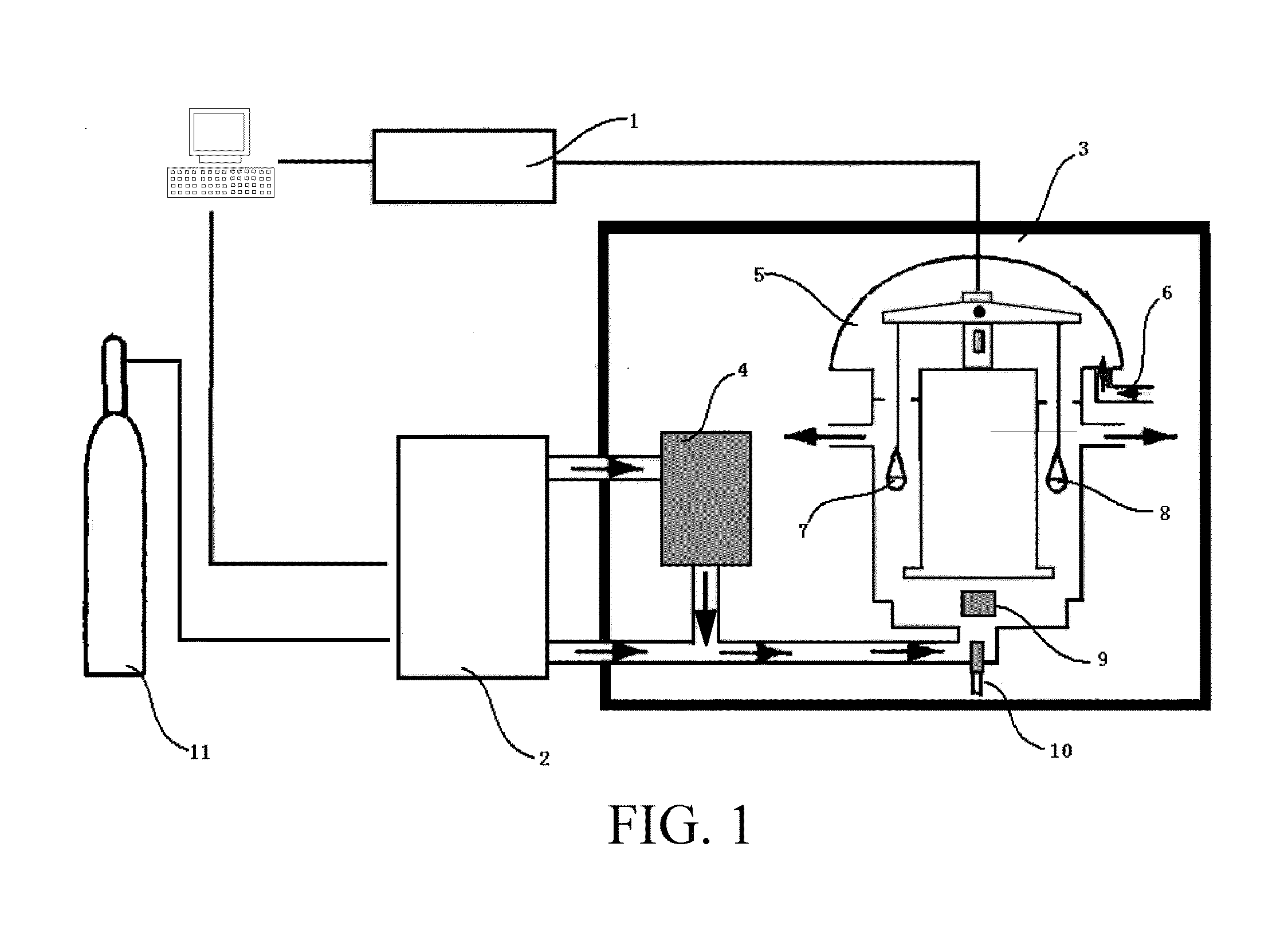
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
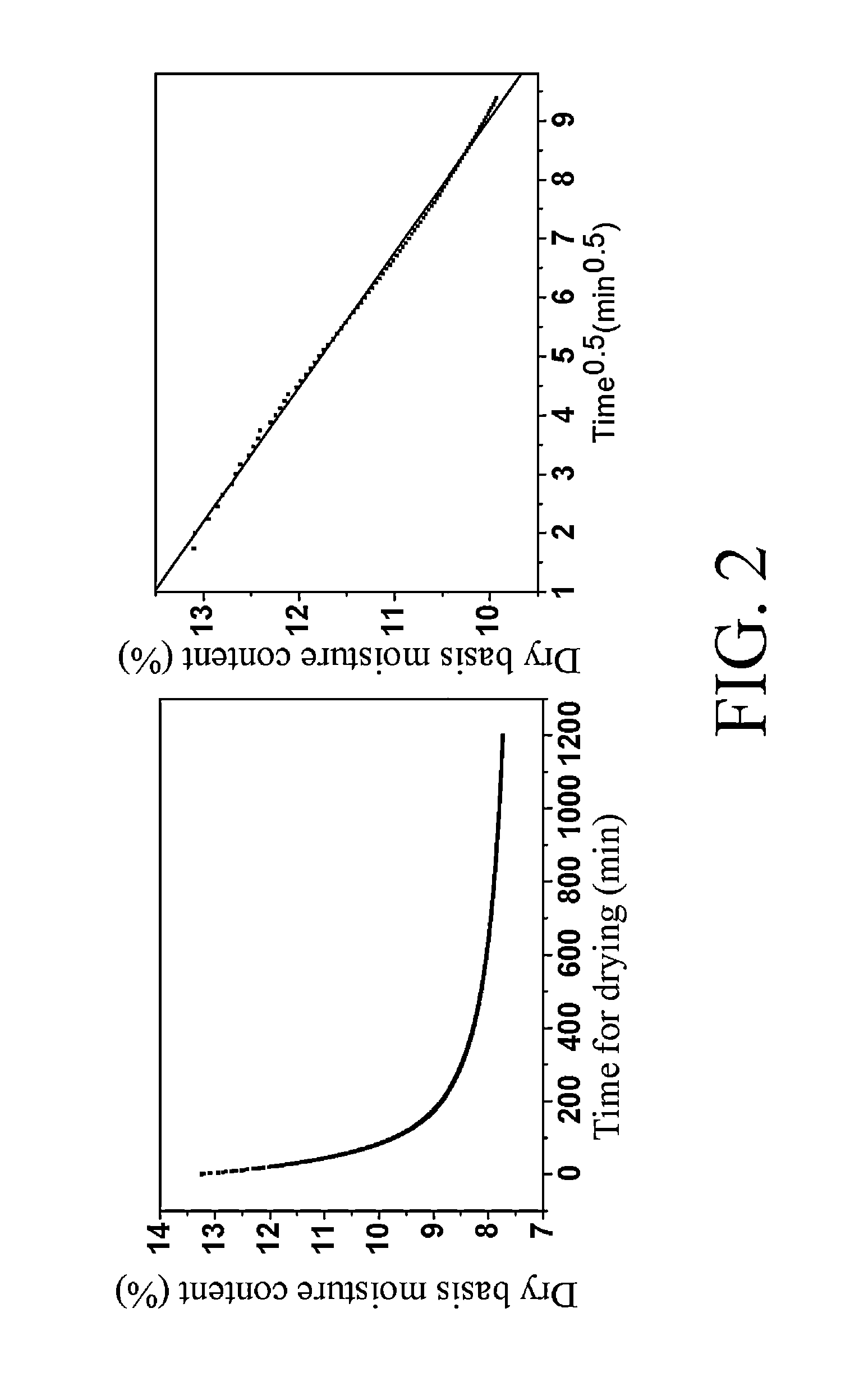
[0033]1.000 g of a cut tobacco sample A to be tested was weighed by using an analytical balance, and then was spread flatly on a sample basket (whose inner diameter was 27 mm) of a microbalance of the DVS system. After reaching equilibrium at a relative humidity of 60%, weight changes against time of the cut tobacco sample A in a dry environment having a relative humidity of 33% were investigated with the equilibrium control mode set as a time control mode (Time=20 h). The computer recorded automatically the weight of the sample every 1 minute, and the apparatus stopped weighing after the cut tobacco sample A reached the equilibrium moisture content. The sample basket was placed in an oven and dried for 2 hours at 100° C. with reference to the oven method, and a dry basis weight of the sample was obtained by using the analytical balance to weigh the sample. Based on the dry basis weight as well as a curve showing the weight changes of the tested sample against the time, values of dr...
embodiment 2
[0034]1.000 g of a cut tobacco sample B to be tested was weighed by using the analytical balance, and then was spread flatly on the sample basket (whose inner diameter was 27 mm) of the microbalance of the DVS system. After reaching equilibrium at the relative humidity of 60%, weight changes against time of the cut tobacco B in a dry environment having the relative humidity of 33% were investigated with the equilibrium control mode set as a speed control mode (dm / dt Mode) dm / dt=0.0002 (% / min). The computer recorded automatically the weight of the sample every 1 minute, and the apparatus stopped weighing after the sample tobacco reached the equilibrium moisture content. The sample basket was placed into the oven and dried for 2 hours at 100° C. with reference to the oven method, and a dry basis weight of the sample was obtained by using the analytical balance to weigh the sample. Based on the dry basis weight as well as a curve showing weight changes of the tested sample against time...
embodiment 3
[0035]1.200 g of a cut tobacco sample C to be tested were weighed by using the analytical balance and then were spread flatly on the sample basket (whose inner diameter was 27 mm) of the microbalance of the DVS system. After reaching equilibrium at a relative humidity of 60%, weight changes against time of the cut tobacco D in a dry environment having the relative humidity of 33% were investigated with the equilibrium control mode set as a speed control mode (dm / dt Mode) dm / dt=0.0002 (% / min). The computer recorded automatically the weight of the sample every 1 minute, and the apparatus stopped weighing after the sample tobacco reached the equilibrium moisture content. The sample basket was placed into the oven and dried for 2 hours at 100° C. with reference to the oven method, and a dry basis weight of the sample was obtained by using the analytical balance to weigh. Based on the dry basis weight and a curve showing weight changes of the tested sample against time, values of dry bas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com