Oxide-dispersion-strengthened alloy
a technology of dispersion and alloy, applied in the field of oxide dispersion strengthened alloy, can solve the problems of not obtaining the effect of improving high temperature oxidation and corrosion resistance, reducing high temperature strength, and negative effect of aluminum addition on ods alloy, etc., to achieve the effect of improving reducing particle diameter and dispersion spacing of oxide, and reducing high temperature oxidation and corrosion resistan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
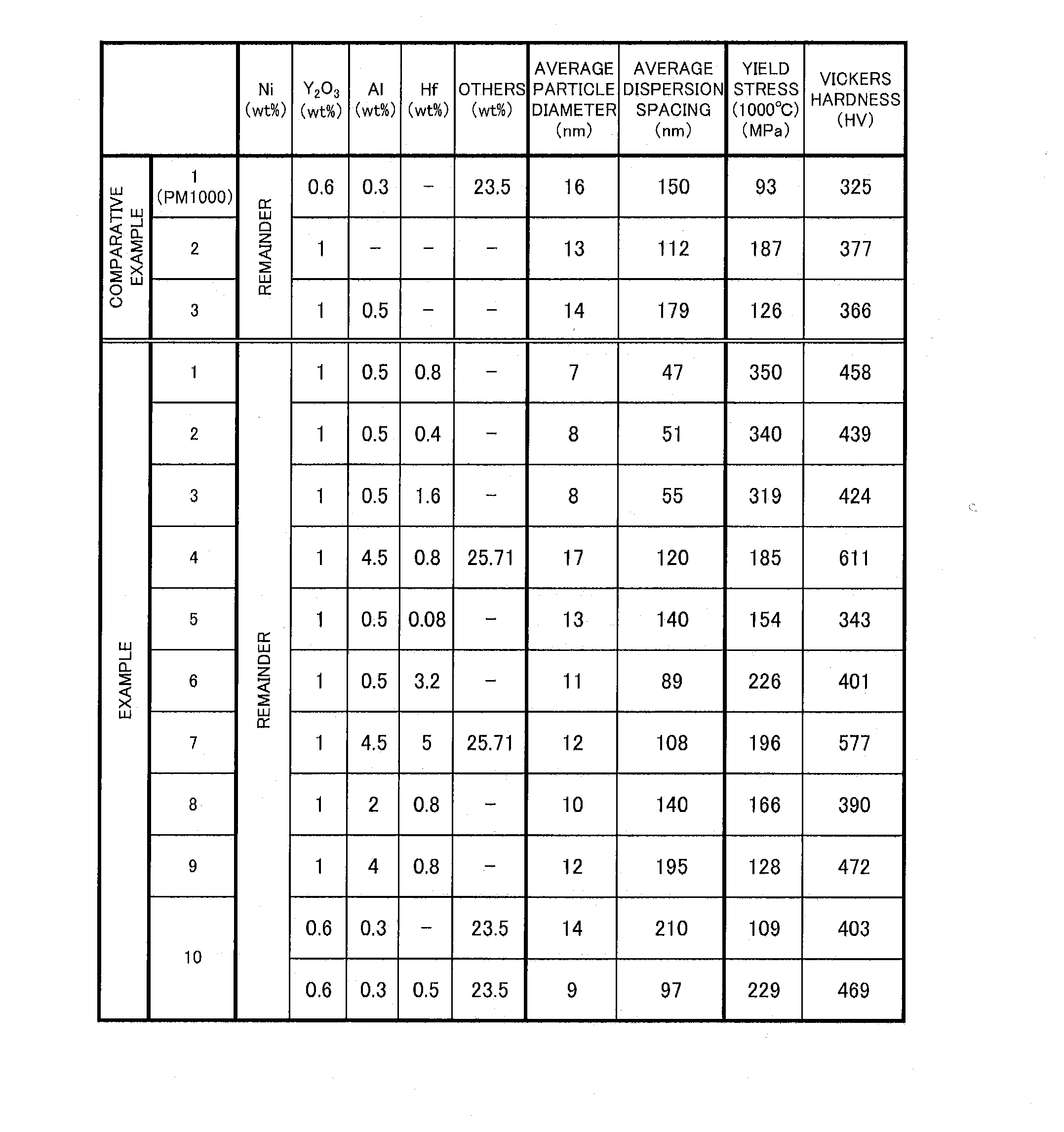
[0069]Next, as Example 1, one obtained by further adding hafnium to the formulation of Comparative Example 3, that is, a nickel-based ODS alloy containing aluminum, hafnium, and yttrium oxide was manufactured. Specifically, 1 wt % of yttrium oxide, 0.5 wt % of aluminum, and 0.8 wt % of hafnium were contained in a nickel-base alloy.
[0070]The amount of hafnium added was determined so that the ratio of the number of molecules of yttrium oxide to the number of molecules of hafnium oxide was 1:1 in order to effectively form a complex oxide of yttrium oxide (Y2O3) and hafnium oxide (HfO2).
[0071]As shown in FIG. 3 and FIG. 7, in the ODS alloy of this Example 1, the oxide particles had an average particle diameter of 7 nm and an average dispersion spacing of 47 nm. In addition, this ODS alloy had a yield stress of 350 MPa at 1000° C. and a Vickers hardness of 458 HV. Therefore, it was confirmed that by the addition of hafnium, the average particle diameter decreased to half, and the average...
example 2
[0074]In Example 2, the amount of hafnium added was reduced with respect to the formulation of Example 1, and a nickel-based ODS alloy containing aluminum, hafnium, and yttrium oxide was manufactured. Specifically, 1 wt % of yttrium oxide, 0.5 wt % of aluminum, and 0.4 wt % of hafnium were contained in a nickel-base alloy. The amount of hafnium added was determined so that the ratio of the number of molecules of yttrium oxide to the number of molecules of hafnium oxide was 1:0.5.
[0075]As shown in FIG. 3 and FIG. 8, in the ODS alloy of this Example 2, the oxide particles had an average particle diameter of 8 nm and an average dispersion spacing of 51 nm. In addition, this ODS alloy had a yield stress of 340 MPa at 1000° C. and a Vickers hardness of 439 HV. Therefore, also in this Example 2, as in Example 1, it was confirmed that by the addition of hafnium, the average particle diameter decreased to almost half, and the average dispersion spacing was reduced to as small as about ¼, co...
example 3
[0077]In Example 3, the amount of hafnium added was increased with respect to the formulation of Example 1, and a nickel-based ODS alloy containing aluminum, hafnium, and yttrium oxide was manufactured. Specifically, 1 wt % of yttrium oxide, 0.5 wt % of aluminum, and 1.6 wt % of hafnium were contained in a nickel-base alloy. The amount of hafnium added was determined so that the ratio of the number of molecules of yttrium oxide to the number of molecules of hafnium oxide was 1:2.
[0078]As shown in FIG. 3 and FIG. 9, in the ODS alloy of this Example 3, the oxide particles had an average particle diameter of 8 nm and an average dispersion spacing of 55 nm. This ODS alloy had a yield stress of 319 MPa at 1000° C. and a Vickers hardness of 424 HV. Therefore, it was confirmed that in the ODS alloy of this Example 3, by the addition of hafnium, the average particle diameter decreased to almost half, and the average dispersion spacing was minimized to as small as about 30%, compared with Co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com