Formulations for parenteral delivery of compounds and uses thereof
a technology of parenteral delivery and compound, which is applied in the field of formulations for parenteral delivery of compounds, can solve the problems of limited pain relief effect of opioids, nausea, vomiting, and urinary retention, and achieve the effects of reducing pancreatic secretion, reducing biliary secretion, and increasing gastroesophageal reflux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification and Characterization of Degradants of Methylnaltrexone Formulations
[0114]Previously, at least three degradation products were demonstrated from HPLC analysis in 20 mg / mL isotonic saline solution (identified as RRT peaks at about 0.72, 0.89, and 1.48 when products were analyzed by HPLC). See, e.g., US Patent Application Publication No. 20040266806A1, published Dec. 30, 2004. We examined 20 mg / mL saline methylnaltrexone solutions for production of degradants, and identification of degradants, as well as identification of inhibitors of formation of different degradant products. We have identified and characterized degradants which accumulate in certain methylnaltrexone solutions. In these degradation experiments, and in the formulations prepared in the examples, R—N-methylnaltrexone was used having less than 0.15 weight percent S—N-methylnaltrexone based on the total weight of methylnaltrexone.
[0115]For HPLC analysis, two (2) different methods were utilized to obtain the...
example 2
Inhibition of Metal and Calcium Mediated Degradation of Methylnaltrexone Formulations
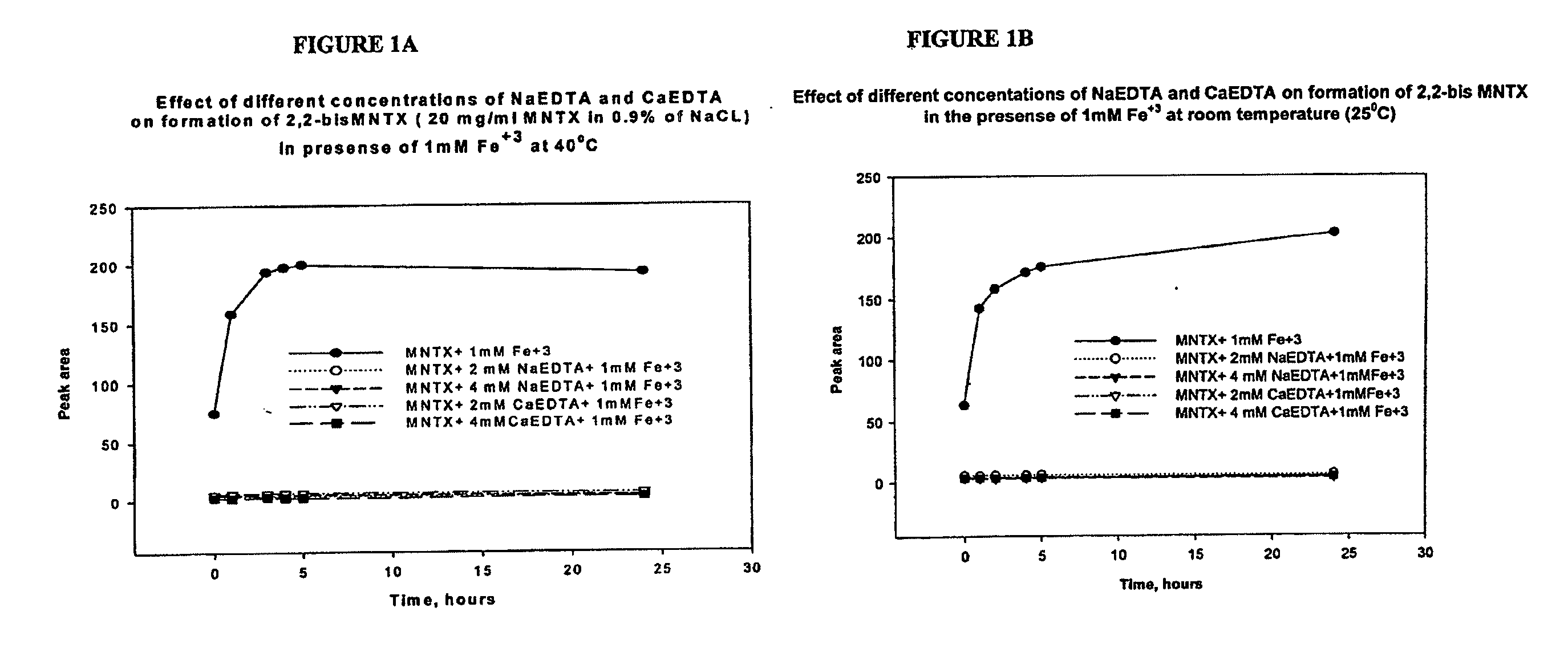
[0124]Inhibition of metal-catalyzed formation of 2,2′ bis methylnaltrexone. We have found Fe3+ facilitates degradation of methylnaltrexone bromide in solution, resulting in formation of a 2,2′ bis methylnaltrexone degradant. We have found by HPLC analysis (Method B) the 2,2′ bis methylnaltrexone degradant results in a peak having an RRT about 1.55. Fe3+ is an ion that can get into the liquid formulation from several sources. For example, it can be leached from stainless steel process equipment, syringe needles, stoppers and amber vials. EDTA, as a metal chelating agent sequesters the available Fe3+ in the solution, thereby preventing catalysis of the undesirable metal-catalyzed reactions. Methylnaltrexone solutions were prepared in 0.9% NaCl, in the presence of iron and various concentrations of sodium EDTA and calcium EDTA. Used throughout the experiments sodium EDTA is EDTA disodium dihydrate, and...
example 3
Inhibition of pH Dependent Degradation of Methylnaltrexone Formulations
[0129]Inhibition of pH influenced formation of methylnaltrexone degradants. We have found in the presence of Ca2+ and EDTA, degradation of methylnaltrexone bromide in solution occurs under some stability conditions, resulting in formation of a third-methylnaltrexone degradant. We have found by HPLC analysis (Method B) the degradant results in a peak having an RRT about 0.79. Identification and production of the 0.79 degradant is described in U.S. provisional patent application 60 / 835,687, filed Aug. 4, 2006, filed concurrently with the present application, the contents of which are incorporated herein in their entirety by reference.
[0130]Formation of the 0.79 methylnaltrexone degradant was lower at room temperature in the CaEDTA formulation described in Example 2 above as compared to refrigerated methylnaltrexone in saline solution. Methylnaltrexone solution as described in Example 2 containing CaEDTA was compare...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com