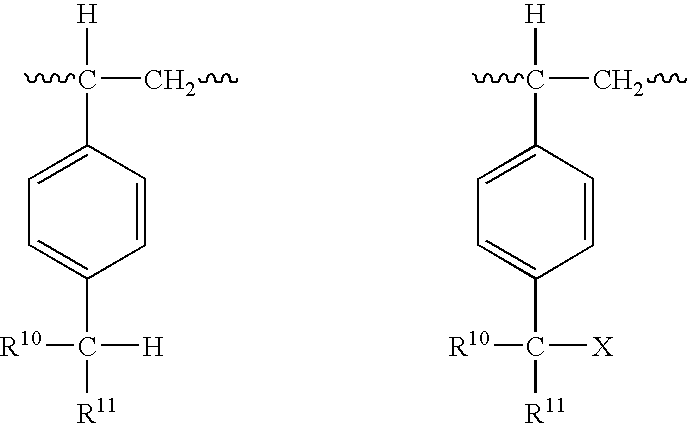
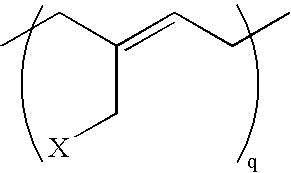
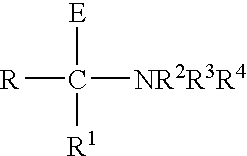Low permeability elastomeric-metal phosphate nanocomposites
a technology of elastomeric metal phosphate and nanocomposite composition, which is applied in the direction of organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, chemical apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of limited success, low reactivity and incompatibility with most, and difficult to disperse ionic nanofillers such as clay into generally inert, etc., to improve barrier and other desirable properties, improve performance, and improve the effect of exfoliation and/or
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
case 1
[0265] 100 phr of BIMSM rubber was compounded with and without primary-primary diamine-treated zirconium phosphates (ZrP) and samples were tested for oxygen permeability. The BIMSM rubber (BIMSM A) had a para-methylstyrene (PMS) content of 10 wt %, and a benzylic bromine content of 0.85 mol % and a Mooney viscosity of about 32 (ML 1+8, 125° C., ASTM 1646. ZrP-HMDA-30-200 was a zirconium phosphate 30% exchanged with hexamethylene diamine with a platelet thickness of 6.3 {acute over (Å)}, length of 150-200 nm and aspect ratio greater than 250, and an aggregate particle thickness of 50 nm and length of 150-200 nm (approximately 40 layers per particle, surface area about 20 m2 / g), and ZrP-HMDA-30-400 was a similar zirconium phosphate 30% exchanged with a platelet thickness of 6.3 {acute over (Å)}, length of 150-400 nm and aspect ratio greater than 500, and an aggregate particle thickness of 20 nm and length of 150-400 nm (approximately 15 layers per particle, surface area about 35 m2 / g)...
case 2
[0268] 100 phr of a BIMSM rubber was compounded with and without a primary-tertiary diamine-treated zirconium phosphate (ZrP) and samples were tested for oxygen permeability. The BIMSM elastomer was BIMSM A as described above. ZrP-APM-100-400 was a zirconium phosphate 100% exchanged with N-3-aminopropyl-morpholine with a platelet aspect ratio of 150-400. N330 carbon black was added at 37 phr. The Zr—P was blended at 4 wt %, with an HSt / ZnO / MBTS curing system at 1 / 1 / 1 phr. The rubber was loaded into a Brabender® mixer at a temperature of 100-120° C. and mixed with the Zr—P and the carbon black for 7 minutes. The mixture was further mixed with the curatives package of equal parts by weight of stearic acid (HSt), zinc oxide (ZnO), and zinc dimethyl dithiocarbamate (ZDMDC), at 90° C. and 40 rpm for 3 minutes. The resulting rubber compounds were milled, compression molded and cured at 170° C. Pads were then prepared and tested as described above.
[0269]The permeability results are present...
example 3
[0270 demonstrates that the addition of the zirconium phosphate nanofiller according to the present invention reduced the permeability by 27% in this example.
[0271]Prophetic Examples 4-11: Cyclohexane (1.7 L) is added to a jacketed glass reactor and heated to 60° C. About 192 to 200 grams of BIMSM elastomer A (described above) are then added to the heated reactor. After all of the elastomer is completely dissolved, 16 grams of ZrP-APM-50-400 (a zirconium phosphate 50% exchanged with N-3-aminopropyl-morpholine with a platelet aspect ratio of about 50 to 400) and 4 or 8 grams of polyisobutylene succinic anhydride (PIBSA) in 50 mL of cyclohexane are added to the reactor and stirred for 40 minutes to form a cement. (The PIBSA is a polyisobutylene succinic anhydride having an Mw of 2,200 and about 2.5 mole % succinic anhydride.) The cement is then poured out and the solvent evaporated. The residual solid is dried under vacuum at 100° C. overnight to form a nanofiller-rubber mixture.
[0272...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aspect ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com