Dose reduced digital medical image simulations
a digital medical image and simulation technology, applied in the field of diagnostic imaging, can solve the problems of poor quality images with reduced diagnostic value, images produced with too little exposure, and radiation from ionizing x-rays can be harmful to living tissues, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing x-ray exposure levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024]The following is a detailed description of the preferred embodiments of the invention, reference being made to the drawings in which the same reference numerals identify the same elements of structure in each of the several figures.
[0025]The present description is directed in particular to elements forming part of, or cooperating more directly with, apparatus in accordance with the invention. It is to be understood that elements not specifically shown or described may take various forms well known to those skilled in the art.
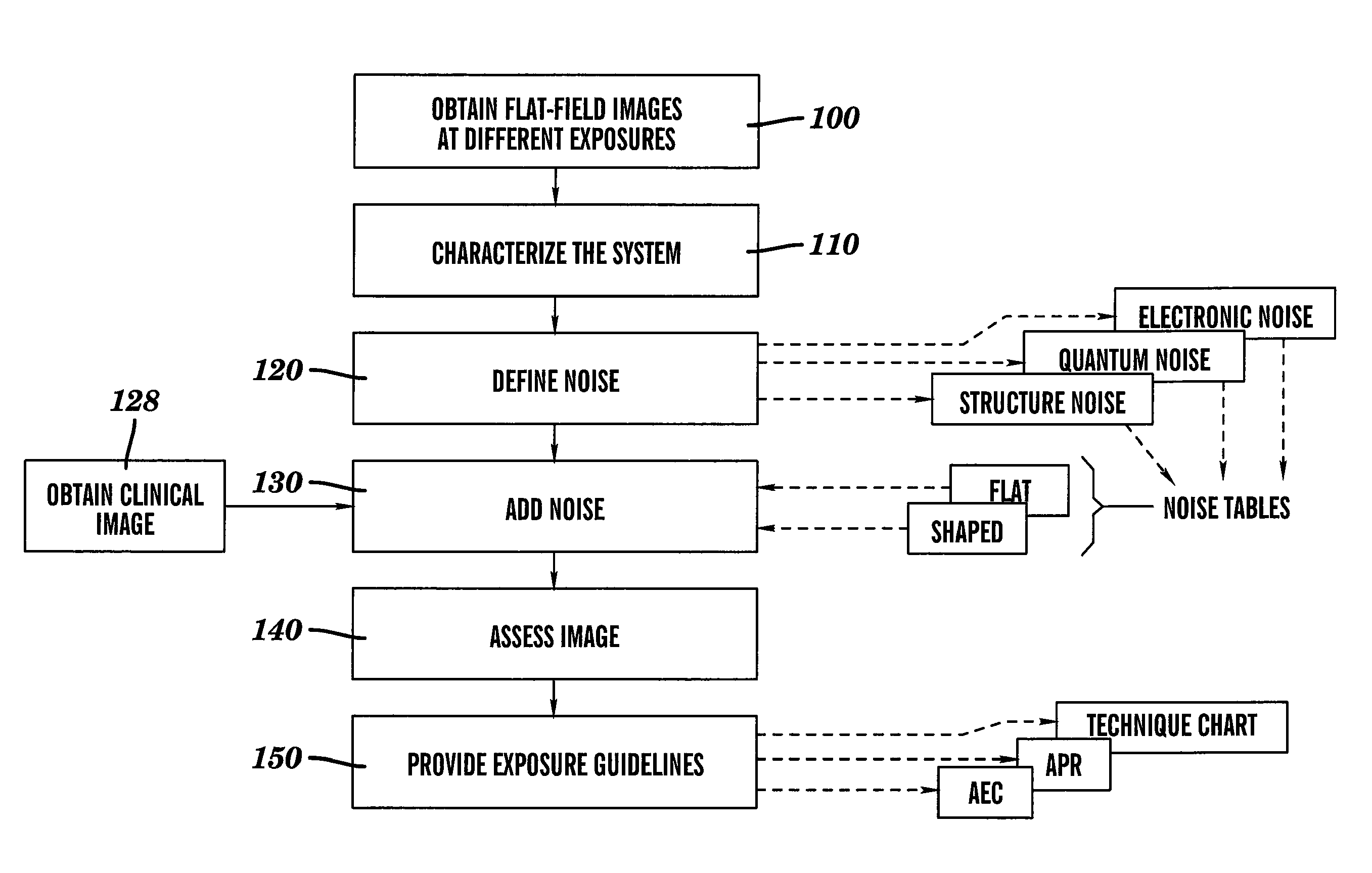
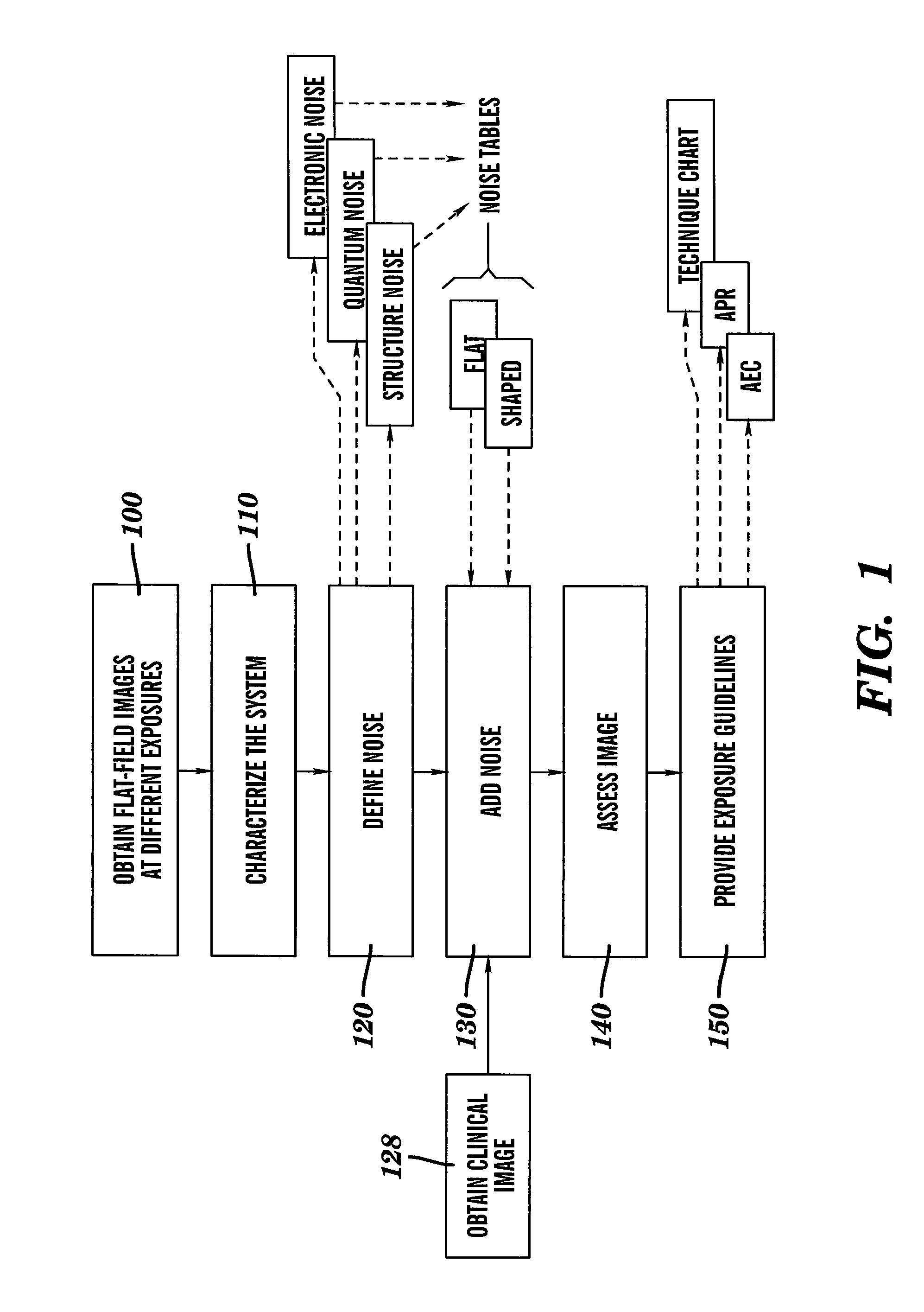
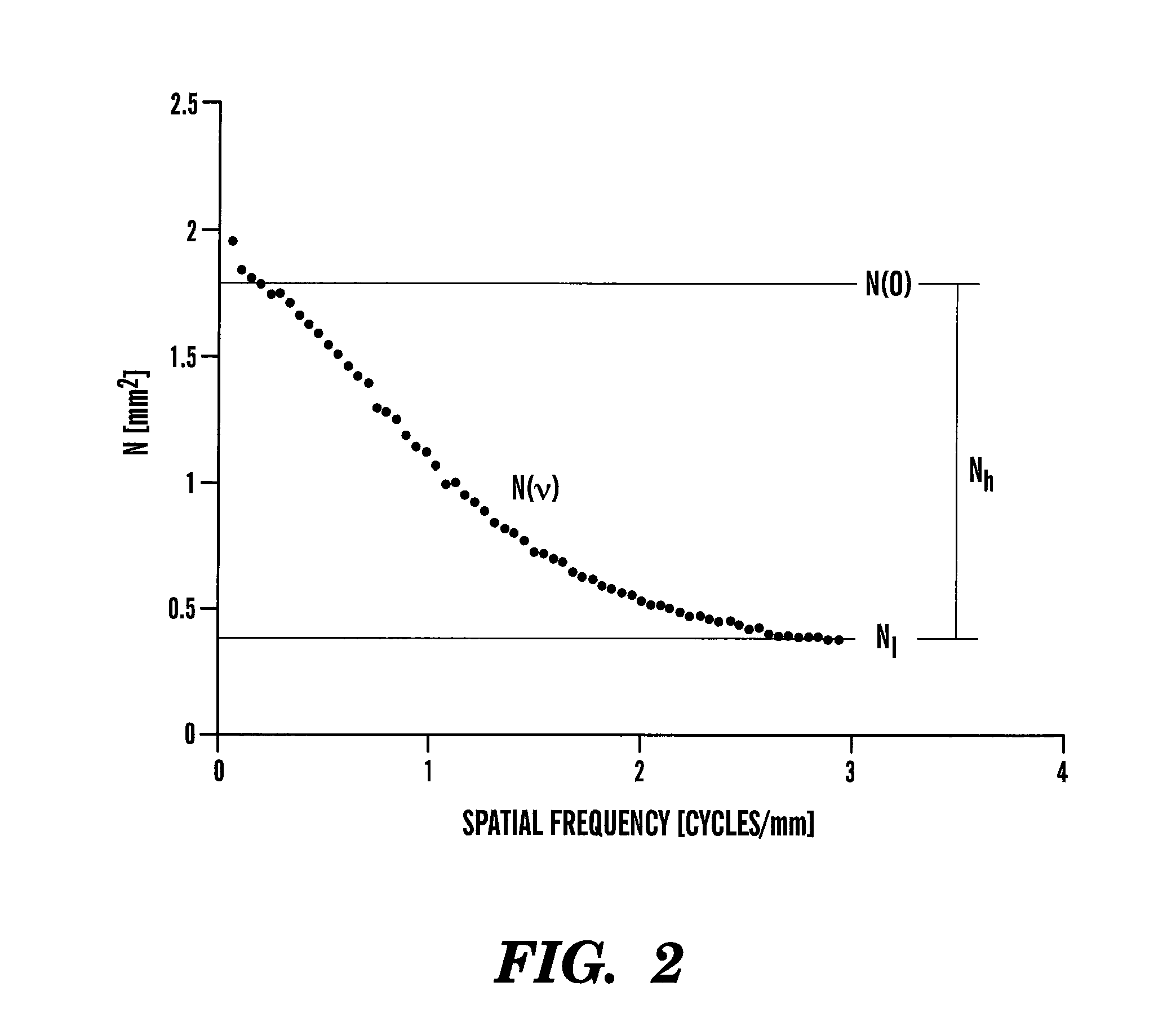
[0026]The present invention provides a method for identifying reduced dose levels for radiographic and related imaging, using noise simulation. For simulating noise effects at lower dose, the method of the present invention can generate a dose that is below the dose of the captured image and is not constrained to the quantum-limited range of the X-ray detector. Thus, once the noise of the radiology imaging system has been characterized over a large exposur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com