Ungulates with genetically modified immune systems
a technology of immune system and ungulate, which is applied in the field of ungulate animals with genetically modified immune systems, can solve the problems of insufficient human antibody availability for therapeutic and prophylactic therapies, inability to induce protective response by vaccination, and large abandonment of wide-scale serum therapy, etc., and achieve the effect of eliminating the expression of xenoantigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
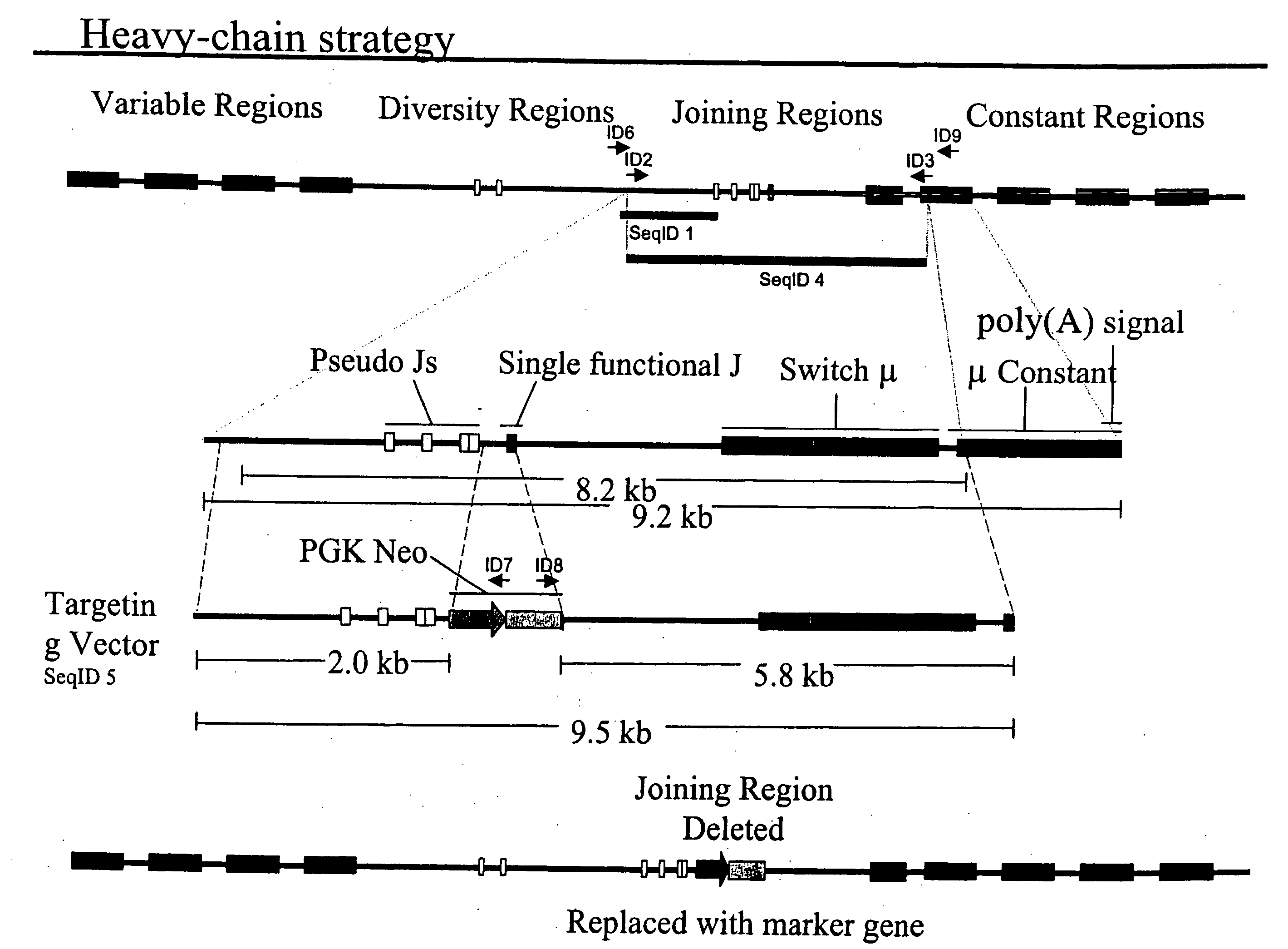
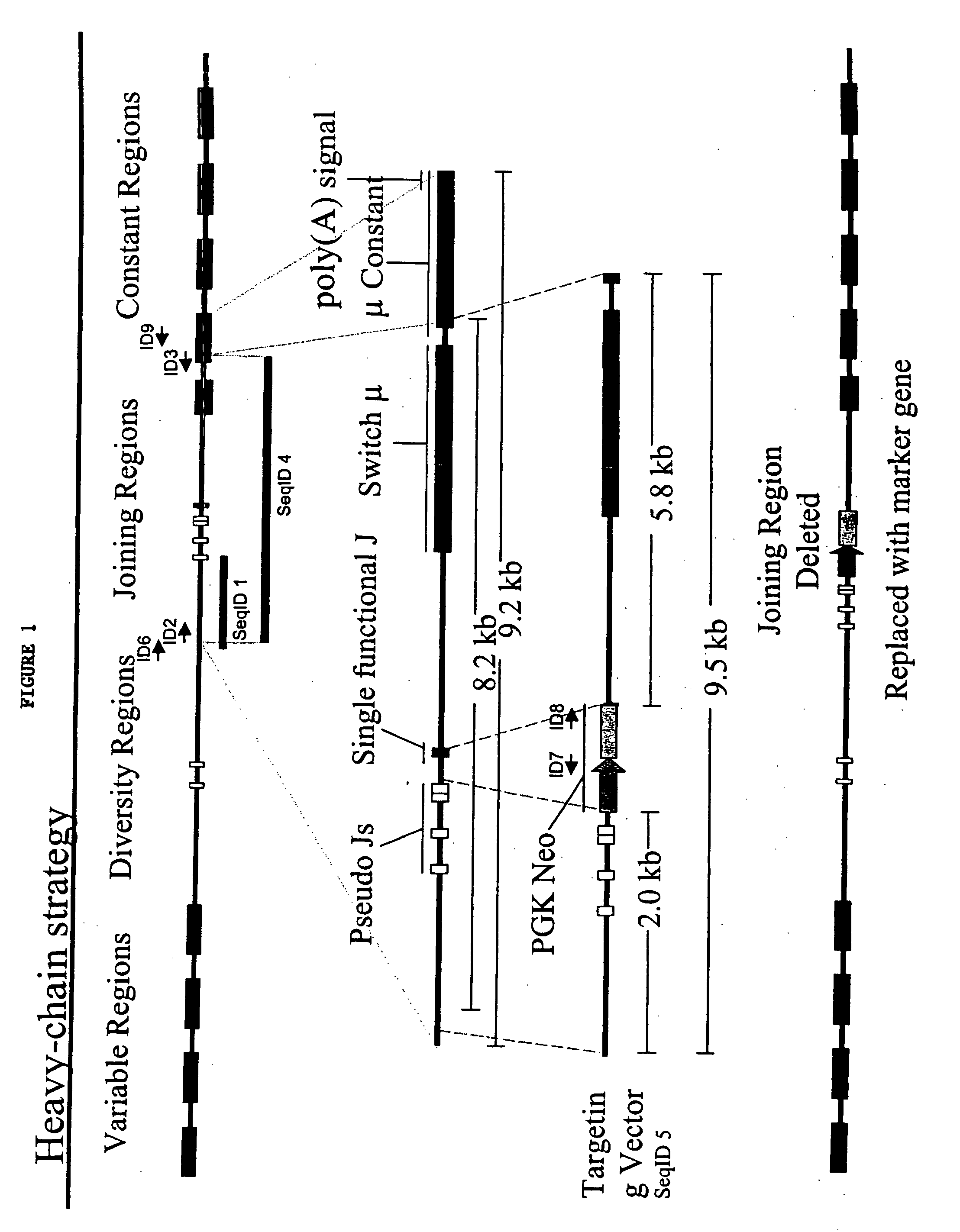
Porcine Heavy Chain Targeting and Generation of Porcine Animals that Lack Expression of Heavy Chain
[0285] A portion of the porcine Ig heavy-chain locus was isolated from a 3× redundant porcine BAC library. In general, BAC libraries can be generated by fragmenting pig total genomic DNA, which can then be used to derive a BAC library representing at least three times the genome of the whole animal. BACs that contain porcine heavy chain immunoglobulin can then be selected through hybridization of probes selective for porcine heavy chain immunoglobulin as described herein.
[0286] Sequence from a clone (Seq ID 1) was used to generate a primer complementary to a portion of the J-region (the primer is represented by Seq ID No. 2). Separately, a primer was designed that was complementary to a portion of Ig heavy-chain mu constant region (the primer is represented by Seq ID No. 3). These primers were used to amplify a fragment of porcine Ig heavy-chain (represented by Seq ID No. 4) that led...
example 2
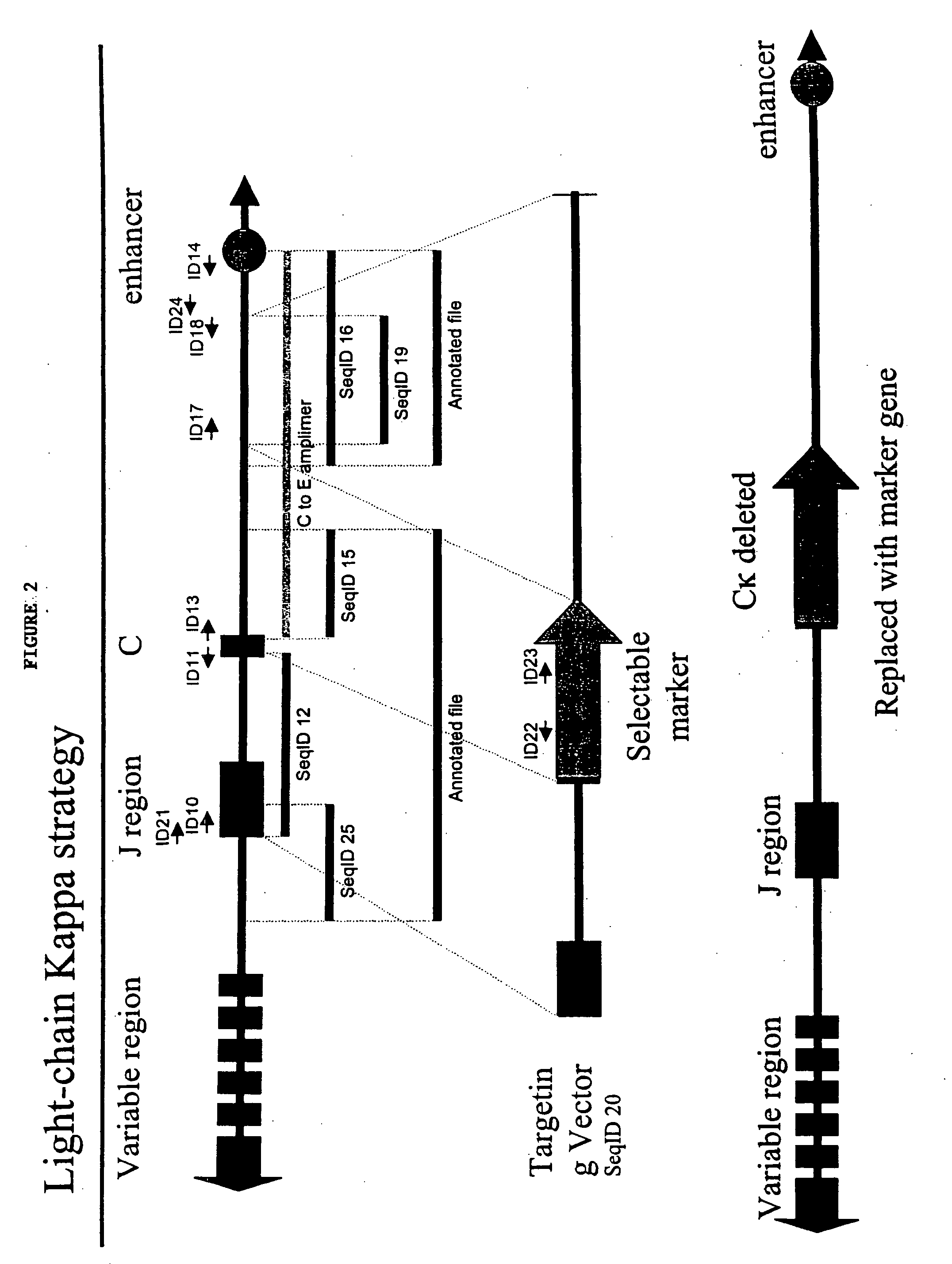
Porcine Kappa Light Chain Targeting and Generation of Porcine Lacking Expression of Kappa Light Chain
[0293] A portion of the porcine Ig kappa-chain locus was isolated from a 3× redundant porcine BAC library. In general, BAC libraries can be generated by fragmenting pig total genomic DNA, which can then be used to derive a BAC library representing at least three times the genome of the whole animal. BACs that contain porcine kappa chain immunoglobulin can then be selected through hybridization of probes selective for porcine kappa chain immunoglobulin as described herein.
[0294] A fragment of porcine Ig light-chain kappa was amplified using a primer complementary to a portion of the J-region (the primer is represented by Seq ID No. 10) and a primer complementary to a region of kappa C-region (represented by Seq ID No.11). The resulting amplimer was cloned into a plasmid vector and maintained in Stable2 cells at 30° C. (Seq ID No. 12). See FIG. 2 for a schematic illustration.
[0295] ...
example 3
Characterization of the Porcine Lambda Gene Locus
[0302] To disrupt or disable porcine lambda, a targeting strategy has been devised that allows for the removal or disruption of the region of the lambda locus that includes a concatamer of J to C expression cassettes. BAC clones that contain portions of the porcine genome can be generated. A portion of the porcine Ig lambda-chain locus was isolated from a 3× redundant porcine BAC library. In general, BAC libraries can be generated by fragmenting pig total genomic DNA, which can then be used to derive a BAC library representing at least three times the genome of the whole animal. BACs that contain porcine lambda chain immunoglobulin can then be selected through hybridization of probes selective for porcine lambda chain immunoglobulin as described herein.
[0303] BAC clones containing a lambda J-C flanking region (see FIG. 3), can be independently fragmented and subcloned into a plasmid vector. Individual subdlones have been screened by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com