Auto exposure measurement system for an x-ray digital image capturer
a digital image capturer and exposure measurement technology, applied in the field of digital xray systems, can solve the problems of film cost, system efficiency reduction, film-based x-ray systems, etc., and achieve the effects of maximizing the light path, reducing the size of the x-ray imaging system, and maximizing the collection of emitted ligh
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
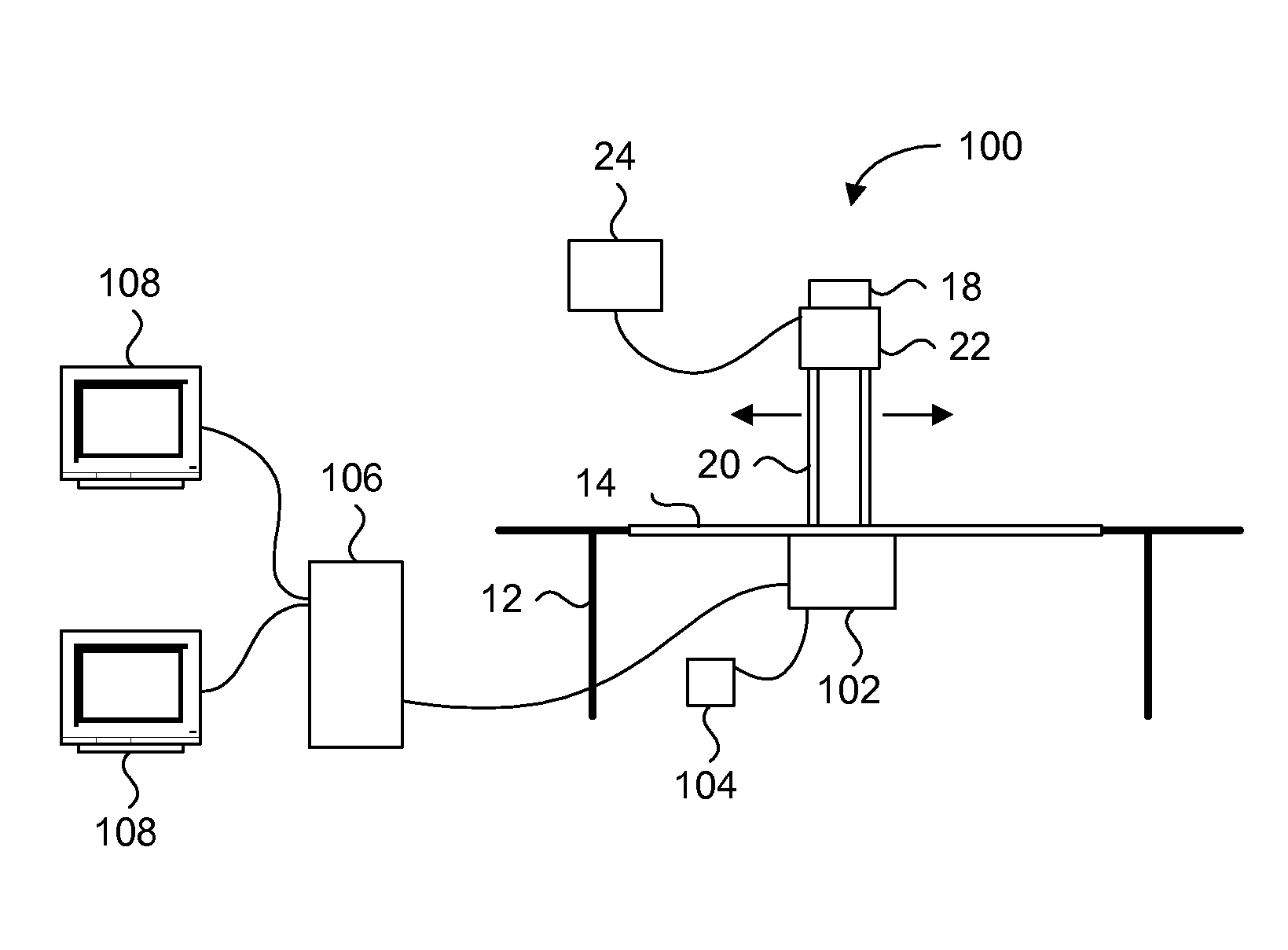
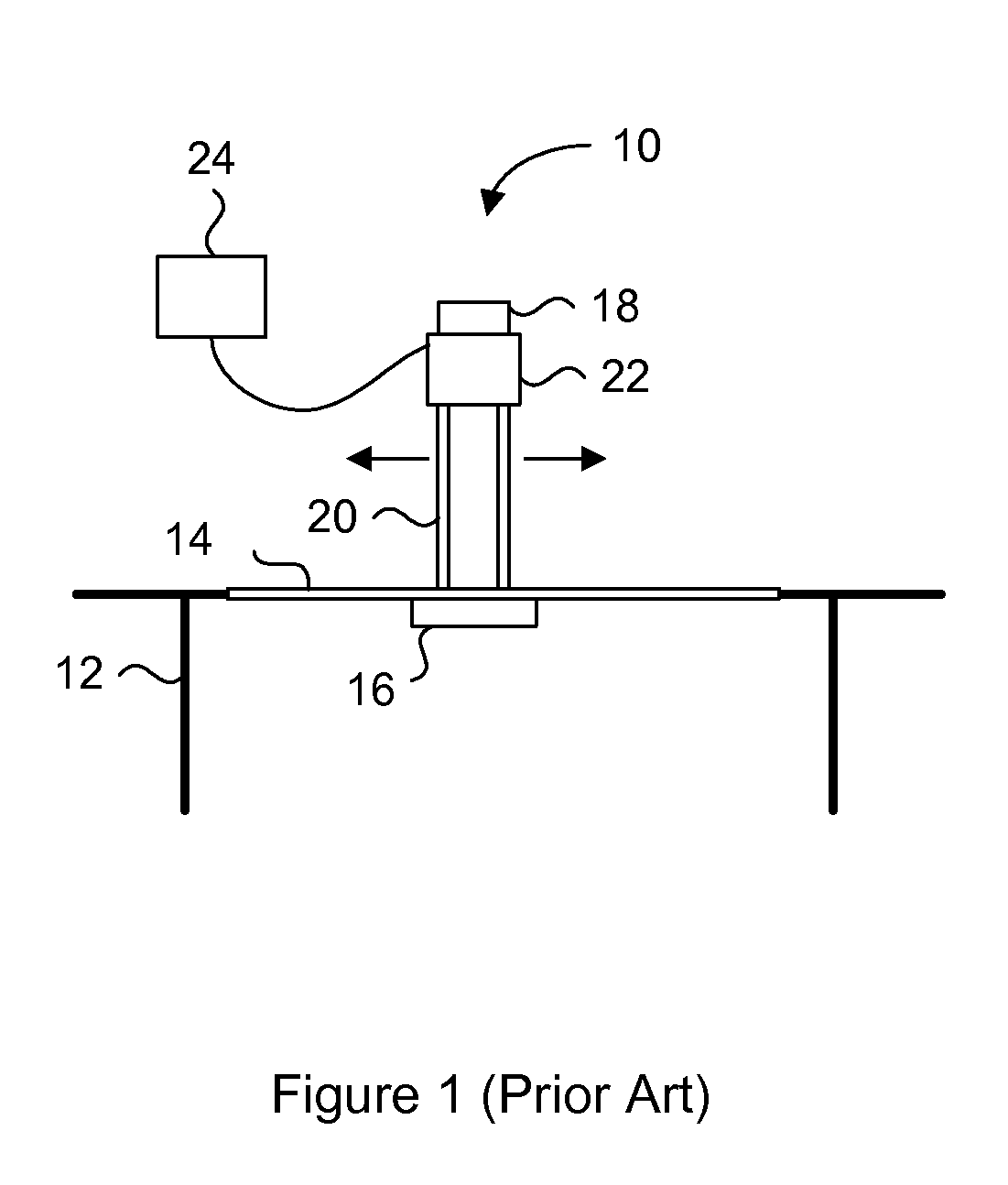
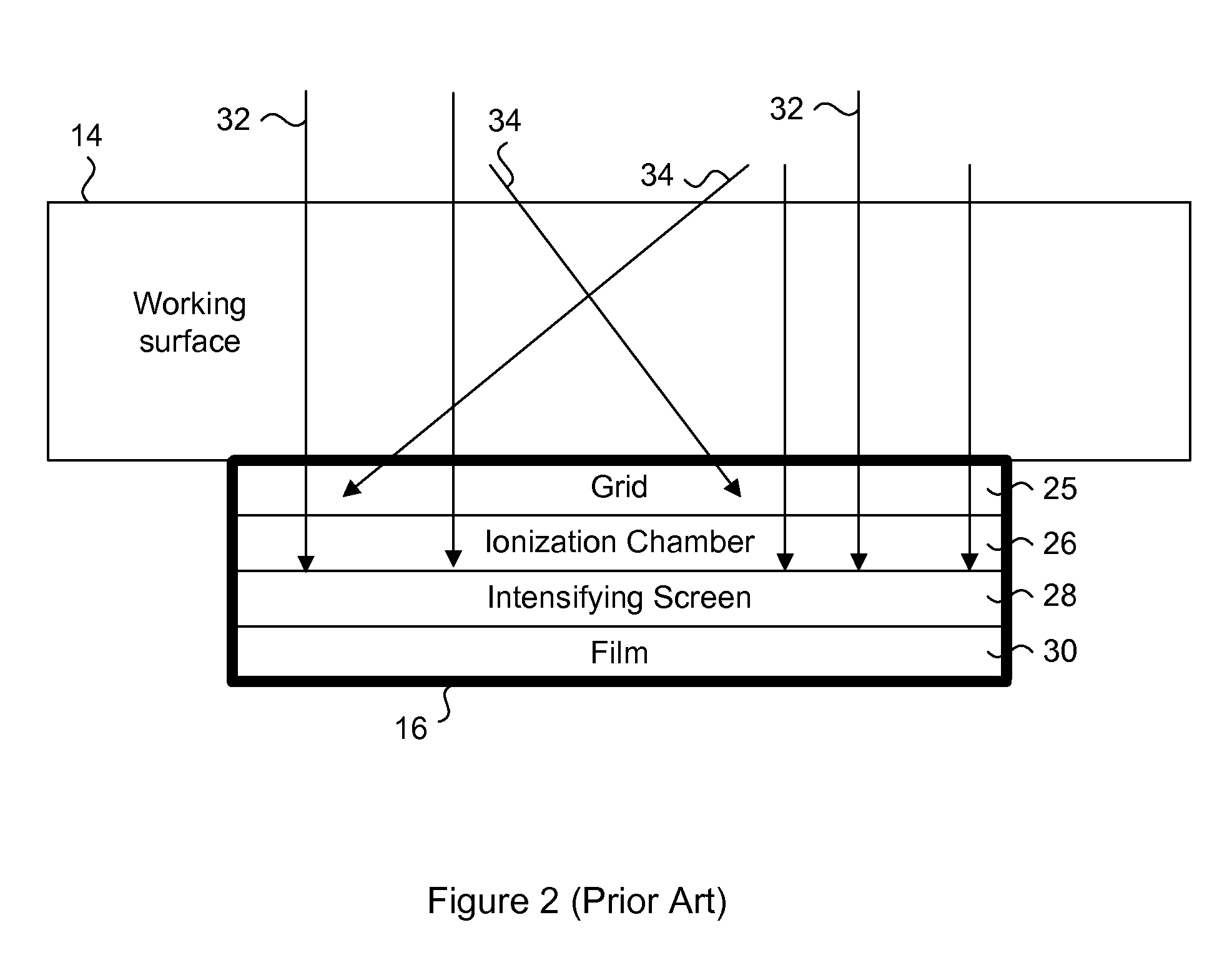
[0029] Generally, the present invention provides a digital X-ray system for capturing high quality images by maximizing the collection of emitted light from an intensifying screen in response to X-ray impact. The digital X-ray system includes a housing having an intensifying screen for receiving emitted X-rays and a combination of two planar reflectors for optimizing the light path between the intensifying screen and the lens assembly. A CCD chip receives the light from the lens assembly, to provide a digital image for immediate on-board processing or post-processing by a computer. The housing is compact, and can be used as a direct replacement for traditional film cartridges without major modifications to the system. The lens assembly includes freeform matched lenses to remove any optical distortions, and the housing includes a light sensor for providing exposure measurement and feedback. The system is designed to be quasi-monochromatic to maintain consistent image quality over the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com