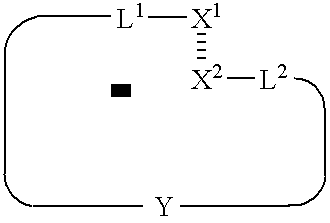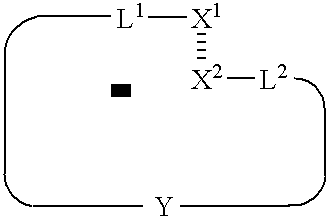Methods of enzymatic discrimination enhancement and surface bound double-stranded DNA
a technology of enzymatic discrimination and surface bound doublestrands, which is applied in the field of methods of enzymatic discrimination enhancement and surface bound doublestranded dna, can solve the problems of large number of complex operations, large number of manual manipulations, and complex preparation, and achieve the effect of improving the quality of hybridization signals, facilitating determination or verification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0254] The following examples are provided to illustrate the efficacy of the inventions herein.
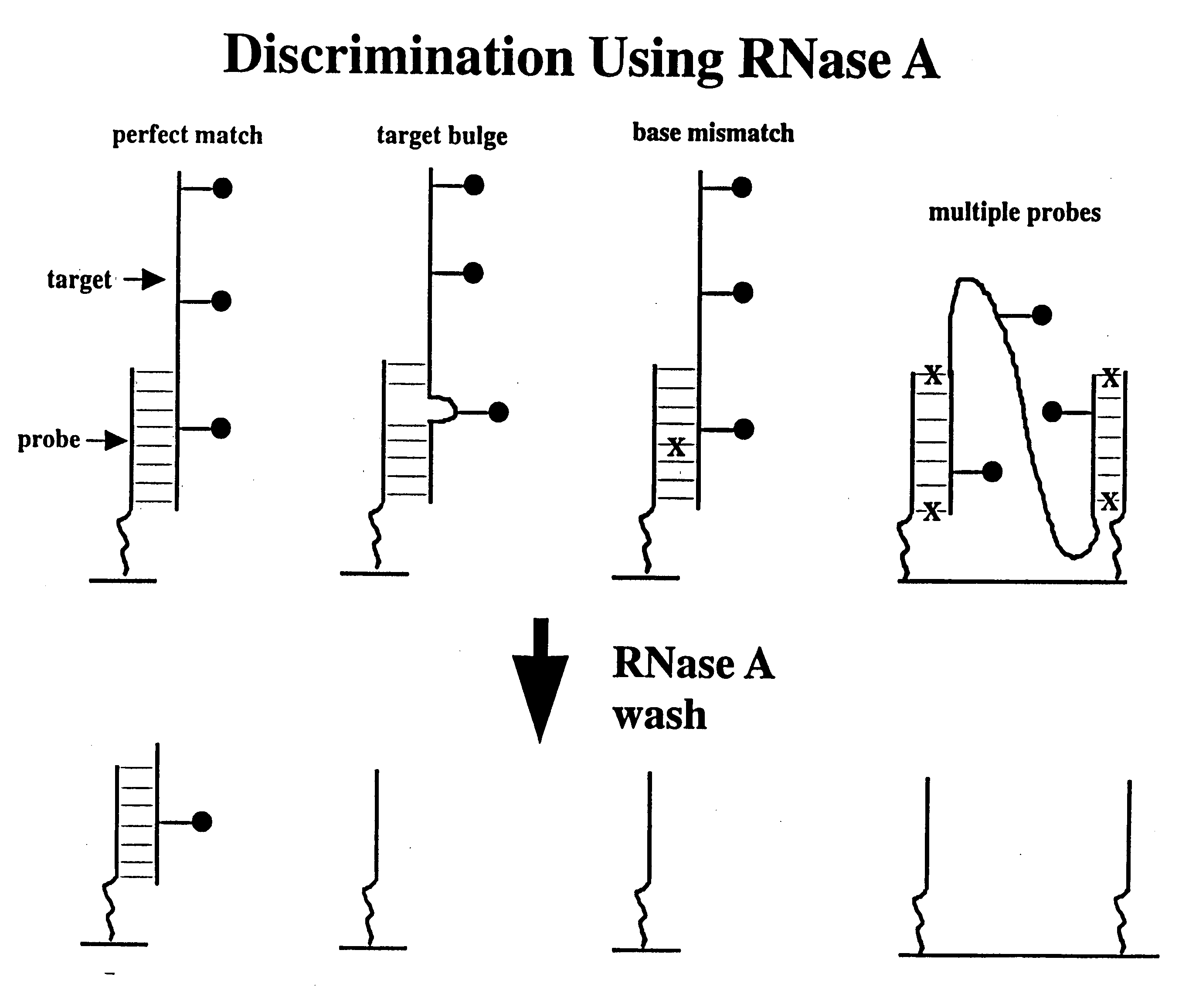
[0255] A. Enhanced Discrimination Using RNase A
[0256] This example illustrates the ability of RNase A to recognize and cut single-stranded RNA, including RNA in DNA:RNA hybrids that is not in a perfect double-stranded structure. RNA bulges, loops, and even single base mismatches can, for example, be recognized and cleaved by RNase A. RNase A treatment is used herein to improve the quality of RNA hybridization signals on high density oligonucleotide arrays.
Example I
[0257] The high density array of oligonucleotide probes on a glass substrate (referred to as a “chip”) is prepared using the standard VLSIPS protocols set forth above. Moreover, the pattern of oligonucleotide probes is based on the standard tiling strategy described shown in FIG. 5. Briefly, the chip used in this example consists of an overlapping set of DNA 15-mers covalently linked to a glass surface. A set of four probes f...
example iv
[0284] In this example, a chip was made using the tiling strategy (A, C, G, T -containing probes for each base in the sequence) described above that covers a 50 base region of the protease gene of HIV-1 (SF2 strain). The probes are 11-mers, linked to the glass support by three PEG linkers. The substitution position (the position being interrogated by an A, C, G, or T base in the probe) is varied between the 5′ end of the probe, and five bases in from the 5′ end (referred to as positions end, -1, -2, -3, -4 and -5). The chip is synthesized using standard VLSIPS protocols. Prior to hybridization and ligation, the chip is phosphorylated using T4 polynucleotide kinase for 5 hours at 37° C. The target is a 75-mer oligonucleotide (denoted Hpro1), labelled at the 5′ end with fluorescein, that spans the complementary 50 base region on the chip.
[0285] The chip was initially hybridized with a 10 nM solution of Hpro1 in 6XSSP-T at 22° C. for 30 minutes. After hybridization, the chip was read,...
example i
[0290] This example illustrates the general synthesis of an array of unimolecular, double-stranded oligonucleotides on a solid support.
[0291] Unimolecular double stranded DNA molecules were synthesized on a solid support using standard light-directed methods (VLSIPS™ protocols). Two hexaethylene glycol (PEG) linkers were used to covalently attach the synthesized oligonucleotides to the derivatized glass surface. Synthesis of the first (inner) strand proceeded one nucleotide at a time using repeated cycles of photo-deprotection and chemical coupling of protected nucleotides. The nucleotides each had a protecting group on the base portion of the monomer as well as a photolabile MeNPoc protecting group on the 5′ hydroxyl. Upon completion of the inner strand, another MeNPoc-protected PEG linker was covalently attached to the 5′ end of the surface-bound oligonucleotide. After addition of the internal PEG linker, the PEG is photodeprotected, and the synthesis of the second strand proceed...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com