Tundish stopper rod for continuous molten metal casting
a stopper rod and continuous molten metal technology, applied in the field of stopper rods, can solve the problems of inclusions, typically present, and detrimentally affecting the flow control characteristics of the stopper rod
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0041] Computer simulations were conducted based on a mathematical fluid turbulence model coupled with a Lagrange model for trajectory of particles. The selected model for momentum transfer was the turbulent regime known as κ-ε. A constant casting rate of 4.0 tons / minute was simulated for each of the stopper rods being examined.
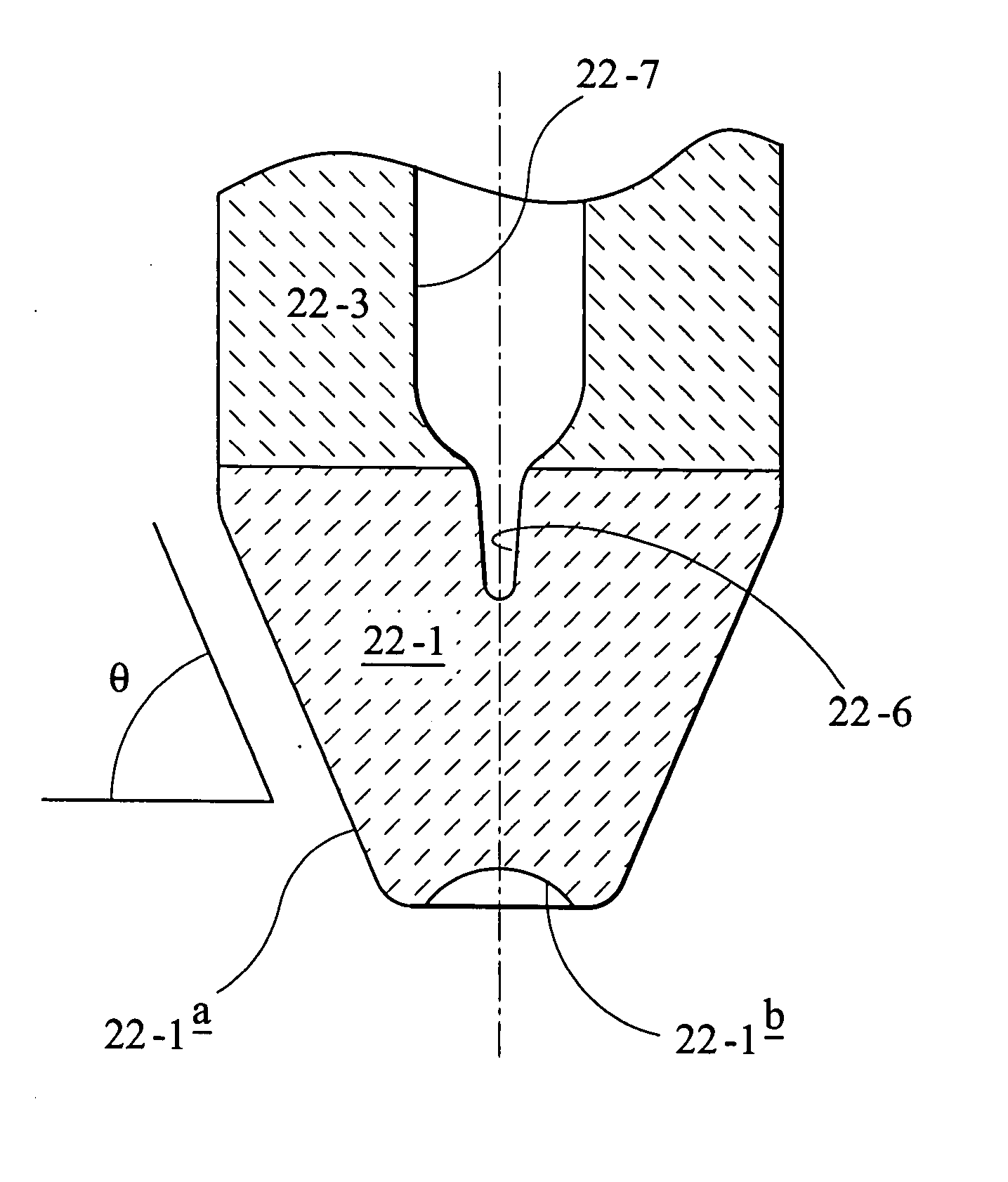
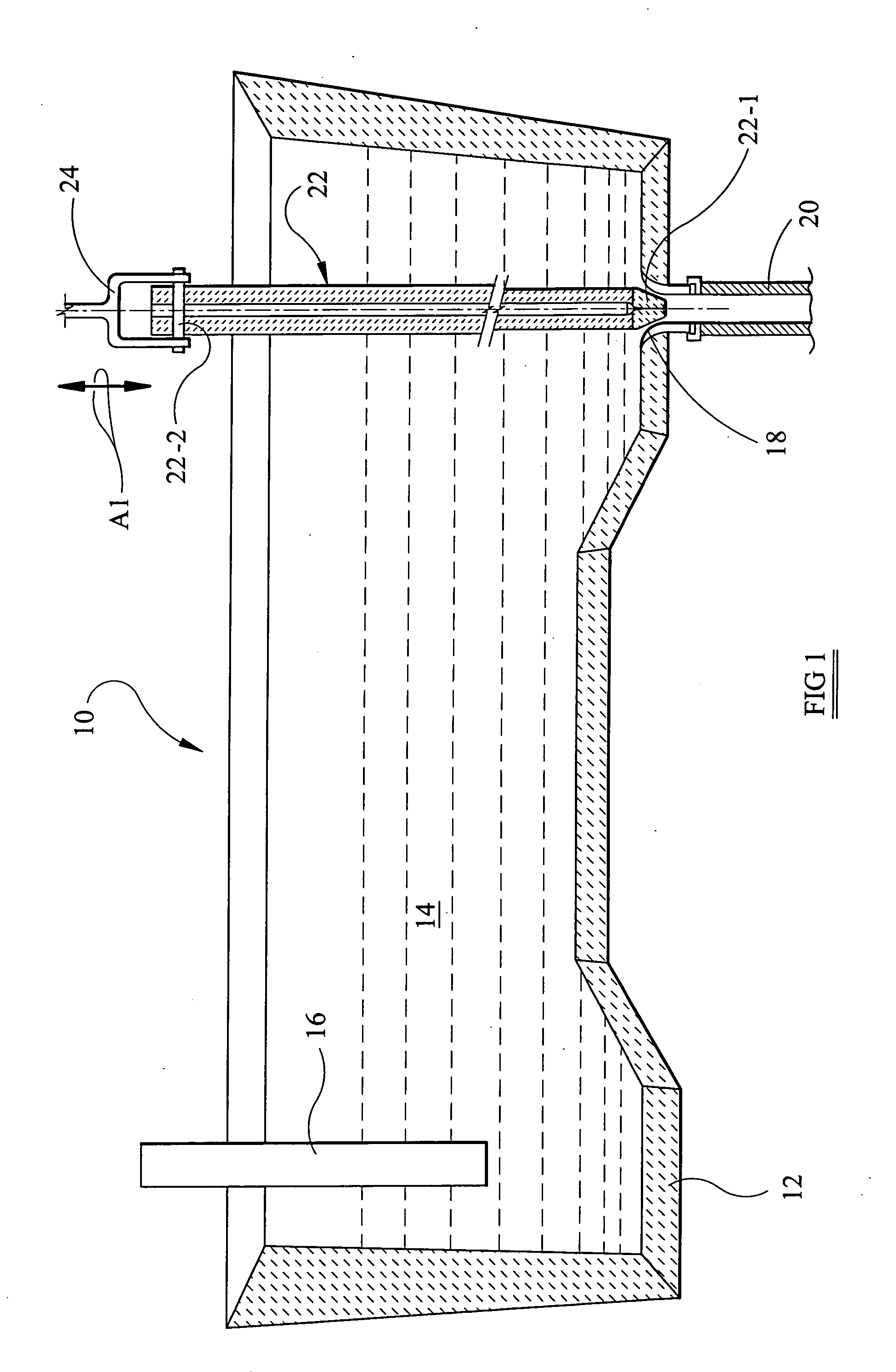
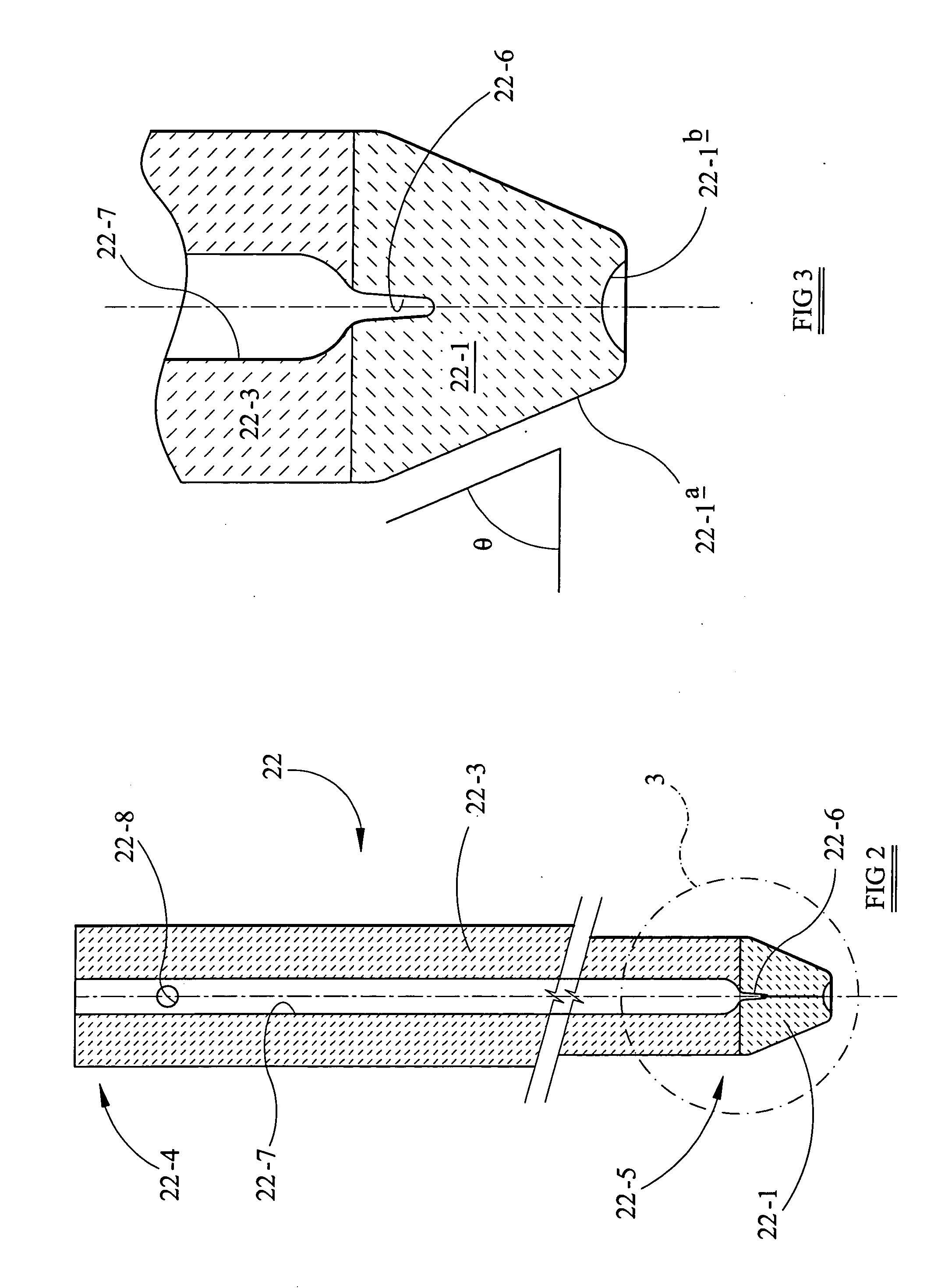
[0042] Comparative Stopper Rod No. 1 (CSR1) was formed with a stopper rod tip configured to have an upper cylindrical surface portion, an intermediate frustoconical surface portion, and a terminal smoothly convex nose. The Comparative Stopper Rod No. 2 (CSR2) was formed with a stopper rod tip having a hemi-ellipsoidal surface configuration. The stopper rod according to the present invention was configured as shown in FIGS. 1-3 above. A bar graph plot of percentage of trapped inclusions to form a clog for each of the stopper rods is shown in FIG. 4. It is evident that the stopper rod according to the present invention results in substantially less percentage ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com