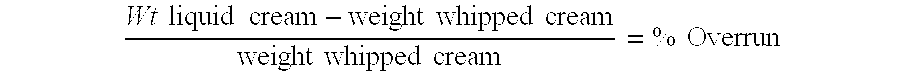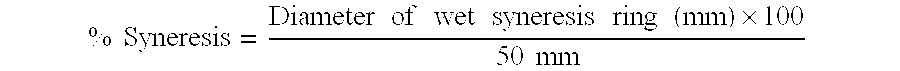Process of reducing fouling during heat processing of foods and beverages
a technology of heat processing and food, applied in the field of reducing heat transfer surface fouling, can solve the problems of significant increases in capital and operating costs annually, particularly in the fouling and subsequent cleaning of processing equipment, and the heat exchanger surface of the processing equipment is particularly affected, and achieves the effect of reducing the fouling of the heat exchanger
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0033] Whipping cream is a food product known to present difficulty in heat processing. The protein, high fat content, and viscosity tend to promote burn on, also known as fouling, in the heat processing equipment. Product burn on constricts flow, increasing back-pressure on the equipment. In addition, product is not heated sufficiently, due to the burned on layer, and the heat sensors summon more heat as the product within the equipment does not reach desired temperatures.
[0034] During processing of whipped cream, as a result of fouling, two product streams enter the holding tube section just after the plate heat exchanger. One stream is cooler than the desired heat treatment temperature as it runs over the burned on product on the interior of the heat exchanger. The other stream is very hot as it is exposed to the maximum heat the plate heat exchanger is reaching as it tries to accommodate the call for heat. The hold tube has two sensors, picking up temperatures as the cream ente...
examples 1-8
[0040] The invention is demonstrated by the Examples in Tables 1 and 2. The whipping cream formulations are shown in Table 1. Formulation Examples 3, 4, 7, and 8 contain hydroxypropyl cellulose.
Formulations
[0041] The whipping cream in Table 1 was formulated and processed with light homogenization and ultra high temperature (UHT) treatment. UHT treatment is used to produce commercially sterile products for the optimum shelf life. Batches were formulated with skim milk and double cream to obtain the desired fat levels of 31% and 24% in the final cream. Ingredients were added to study the impact of no hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), HPC without an emulsifier present and HPC with emulsifier. Emulsifiers are often added to UHT treated whipping cream to aid in foam creation. All formulations contained carrageenan, a common ingredient in heat treated cream to aid in the prevention of the coalescence of fat during storage and prior to whipping. Table 1 contains formulation information; bat...
examples 9-26
[0059] The invention is further demonstrated in Table 3 in heat sterilized cream samples. Examples 11-14, 22, and 24 contain HPC. Examples 15-18, 20, and 25 contain MHPC, and Example 19 contains a blend of polymers.
Formulations and Processing
[0060] The UHT creams in Table 3 were subjected to a preheat temperature of 75° C. and final heat to 138° C. with a holding time of 8 seconds. Single stage cooling was used to achieve temperatures of <60° C. Prior to the final heat stage, 2-stage homogenization was provided to all products at a value of 750 / 250 psi using a homogenizer.
[0061] After mixing the cream composition, the cream mixture was then heated to 50-55° C. in a water bath and then pumped into a Microthermics Thermal processor at a flow rate of 1.14-1.2 Liters / min. The Microthermics unit was equipped with two sets of plate heat exchangers and a 2-stage pressure homogenization unit. The first set of PHE was used to preheat the cream to a temperature of 75° C. prior to introduct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com