Method and apparatus for mounting and removing an electronic component
a technology for electronic components and mounting methods, applied in sustainable manufacturing/processing, program control, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as short circuit of solders, reduced reliability of connection, and accumulation of thermal stresses in substrates, so as to simplify preprocessing and reduce stress and costs , the effect of enhancing reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
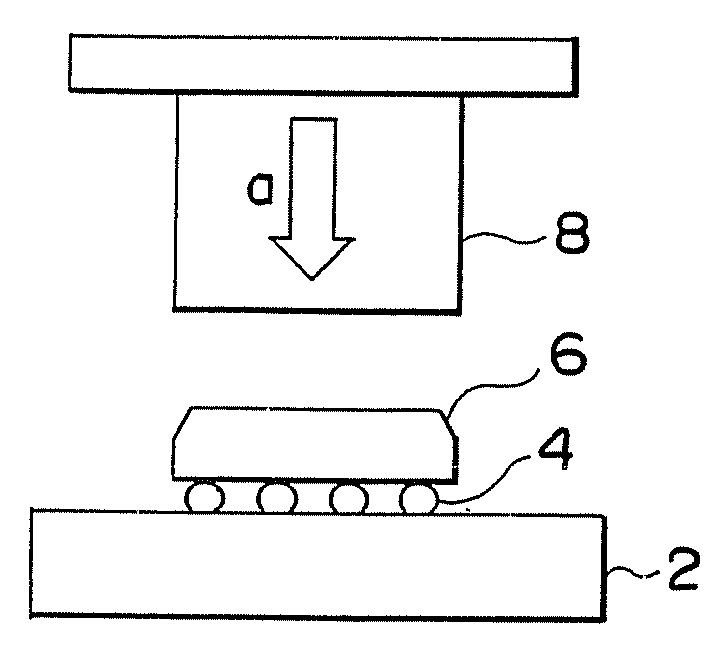
[0053] A first embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to FIG. 3 to FIG. 5. FIG. 3 to FIG. 5 shows a bonding apparatus as an embodiment of a method and an apparatus for mounting and removing electronic components of the present invention; FIG. 3 is a side view showing a head unit and a control table; FIG. 4 is a front view of the head unit; and FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a control unit.
[0054] A bonding apparatus 20 is comprised of a control table 22 movable in the X and Y directions (e.g., horizontal direction); the control table 22 is comprised of, for example, a heating platform portion 24 and a package loading platform 26; and the heating platform portion 24 is comprised of a heater 28 as a first heating unit with in a chassis made up of corrosion resistant metal such as stainless steel. The package loading platform 26 is comprised of a flat loading surface made up of quartz glass. The package loading platform 26 is equipped with...
second embodiment
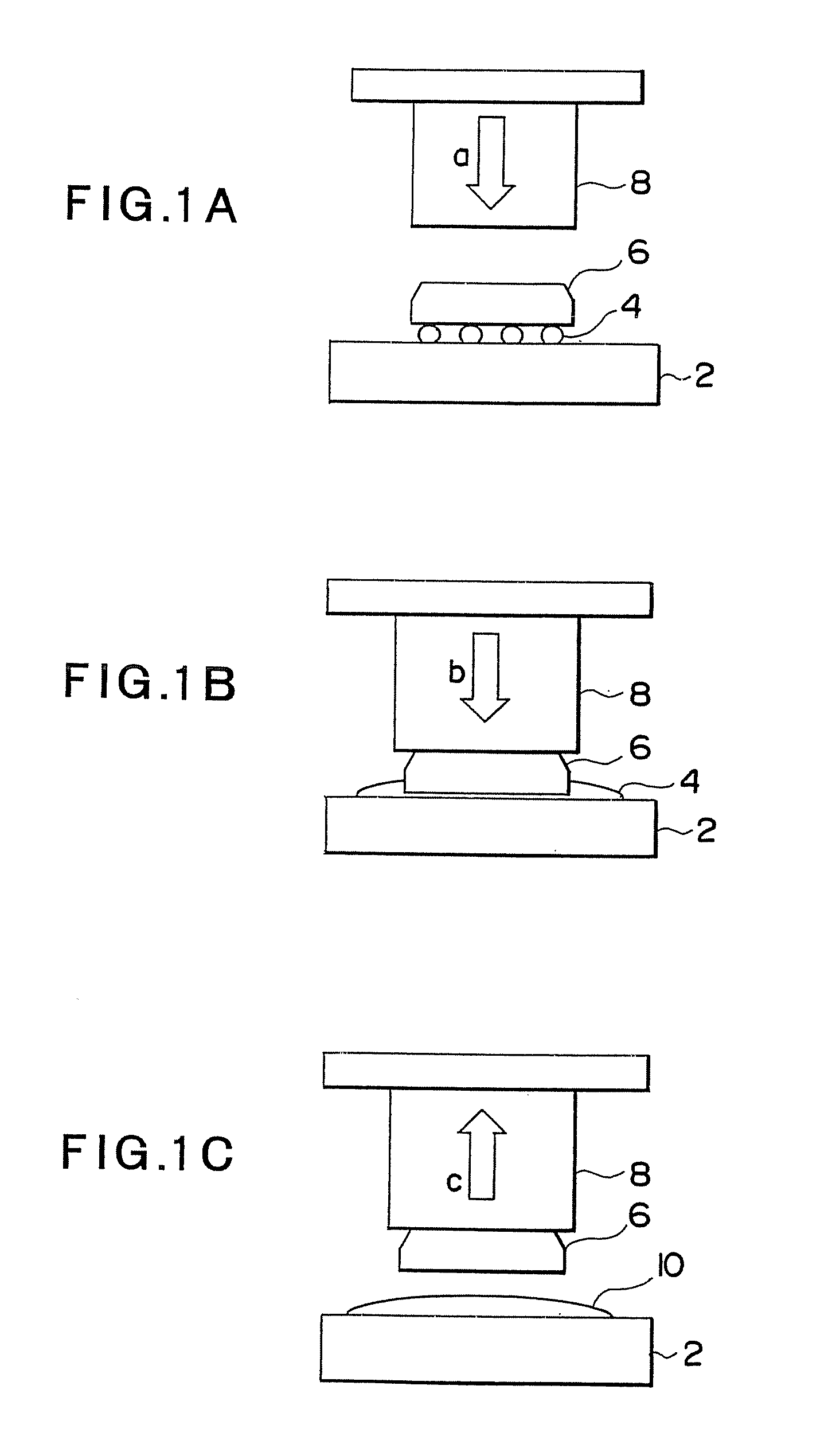
[0065] Then, as a method for mounting electronic components which is a second embodiment of the present invention, the reflow processing is described with reference to FIG. 6 to FIGS. 9A and 9B. FIG. 6 is a process chart showing an operation sequence of the reflow processing, and FIGS. 7A and 7B to FIGS. 9A and 9B are diagrams showing an operation sequence.
[0066] The reflow processing is constituted by preprocessing, a preparation operation, a height control / reference position detection operation, a bonding-portion heating and height-control operation, and a termination operation. In preprocessing, flux is applied to the bear chip 32 (process P1) and the entire package 34 is preheated (process P2). In this case, the flux is applied to the entire area of the solder bump connection portion of the bear chip 32 and the package 34 is preheated by heating the control table 22. In this preheating, in order to reduce thermal distortion due to difference in temperature, the preheating tempe...
third embodiment
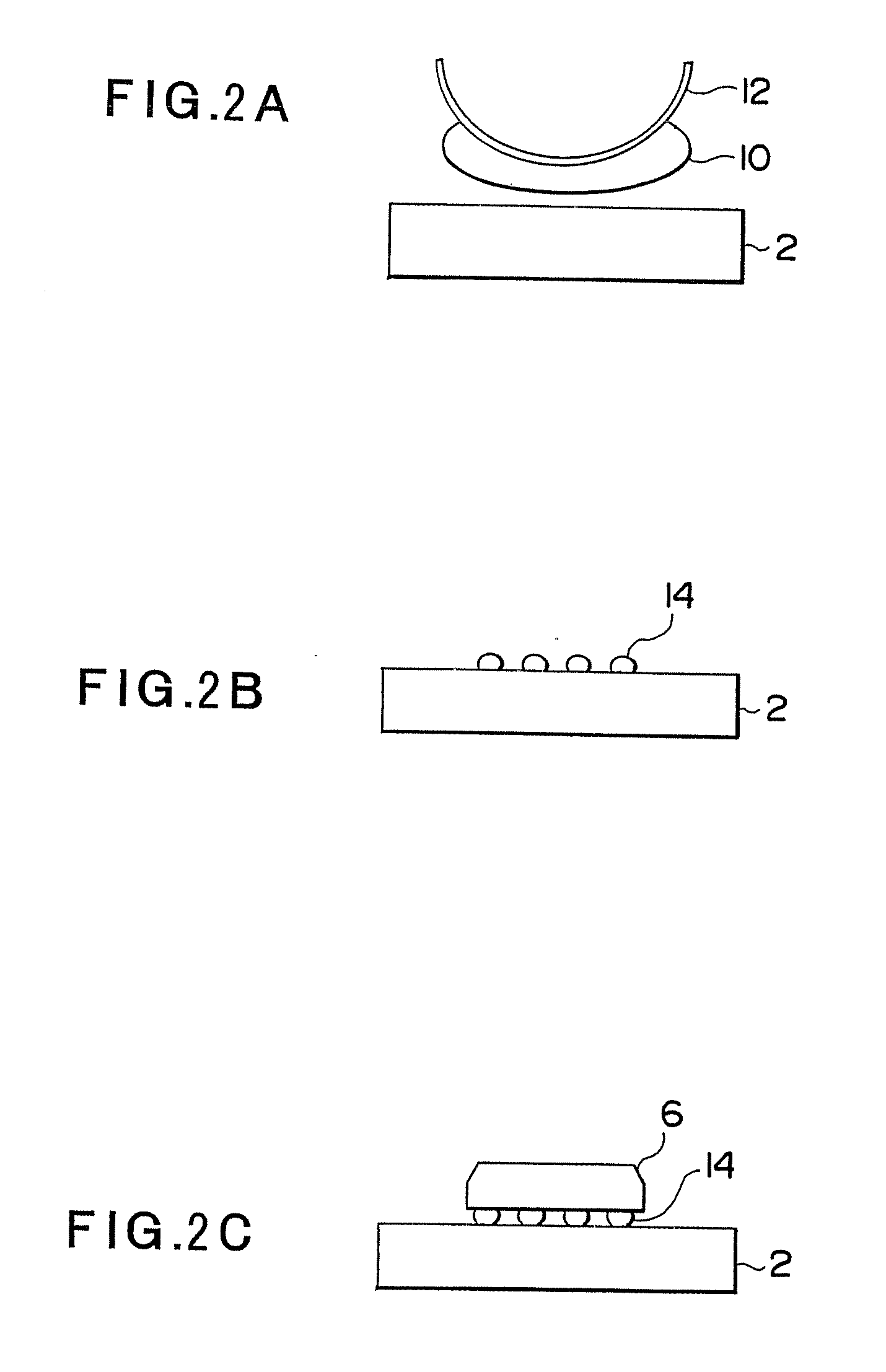
[0082] Then, a third embodiment of the present invention, i.e., a method for removing electronic components is described with reference to FIG. 13 to FIGS. 16A and 16B. FIG. 13 is a process chart showing an operation sequence of remove processing and FIGS. 14A and 14B to FIGS. 16A and 16B are diagrams showing an operation of the head unit 40.
[0083] The remove processing is constituted by preprocessing, a preparation operation, a height control / reference position detection operation, a bear-chip remove operation, and a termination operation. In preprocessing, filling with flux (process P21) and preheating of the entire package 34 (process P22) are performed. The entire connection portion of the solder bumps 114 of the bear chip 32 is filled with the flux utilizing a capillary phenomenon (process P21) and, at this point, preheating the package 34 facilitates the filling with the flux. The package is preheated by heating the control table 22 and, in this preheating, in order to reduce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com