Multi-spectral techniques for defocus detection
a multi-spectral technique and defocus detection technology, applied in the field of integrated circuit processing, can solve the problems of local or global focus problems, full-field focus problems, and suffer from microcircuit yield loss, so as to improve the sensitivity to extended defocus defects and reduce cost. , the effect of increasing the sensitivity to defocus defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
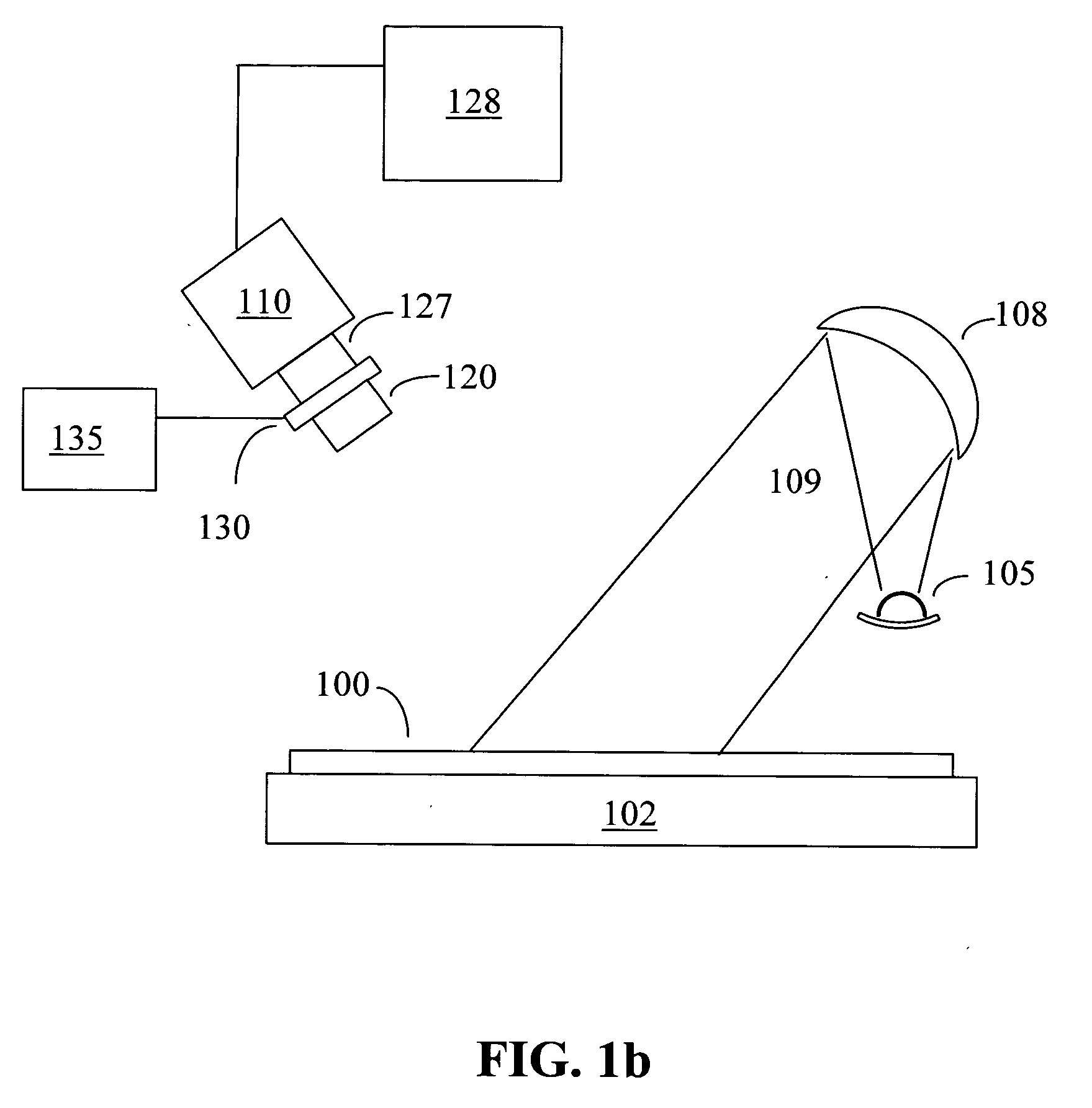
[0033] In the invention, defocus is detected by accumulating information about the detected scattered and diffracted light in an image of a region of interest of a wafer, collected for several different discrete wavelengths or for a wavelength spectrum. The information collected is both spatial (i.e., image), and wavelength spectral. This technique when employed with high spectral finesse, is often referred to as “hyperspectral imaging”.
[0034] A conventional monochromatic image is a function of the two spatial dimensions, I(x,y), where I is the intensity of the scattered and diffracted light from each point (x,y). In hyperspectral imaging, additional information is collected by varying wavelength λ, to yield an intensity image I(x,y,λ). In practice, the spectral information is typically not collected continuously, but rather at a number of discrete wavelengths. The spectral information can be derived in several ways:
a) Sequential Illumination with or Collection of Narrow-Band Ligh...
second embodiment
[0049] A basic principle of Fourier optics is that effects which are localized in physical space are diffuse in the Fourier domain, and that effects which are diffuse in physical space are localized in the Fourier domain. This phenomenon leads to the observation that transferring into Fourier space can enhance the detection and location of a diffuse effect such as diffuse defocus. the present invention provides an optical Fourier transform, i.e., a Fourier Transform of the spatial image, to achieve the transference.
[0050] When an object is illuminated with a plane wave, i.e., coherent monochromatic light, the light that impinges on it will diffract and scatter in such a way that, at infinity (far-field), a pattern of light is seen which is the spatial Fourier transform of the object being illuminated. No refractive or reflective optics is necessary for this effect to occur. On the surface of the object, information is purely spatial. At infinity, it is purely frequency information, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com