Semiconductor optical modulator, an optical amplifier and an integrated semiconductor light-emitting device
a semiconductor light-emitting device and optical modulator technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor amplifiers, semiconductor lasers, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of severe degradation of the s/n ratio of optical modulation, affecting the performance of optical modulation, and affecting the efficiency of optical modulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
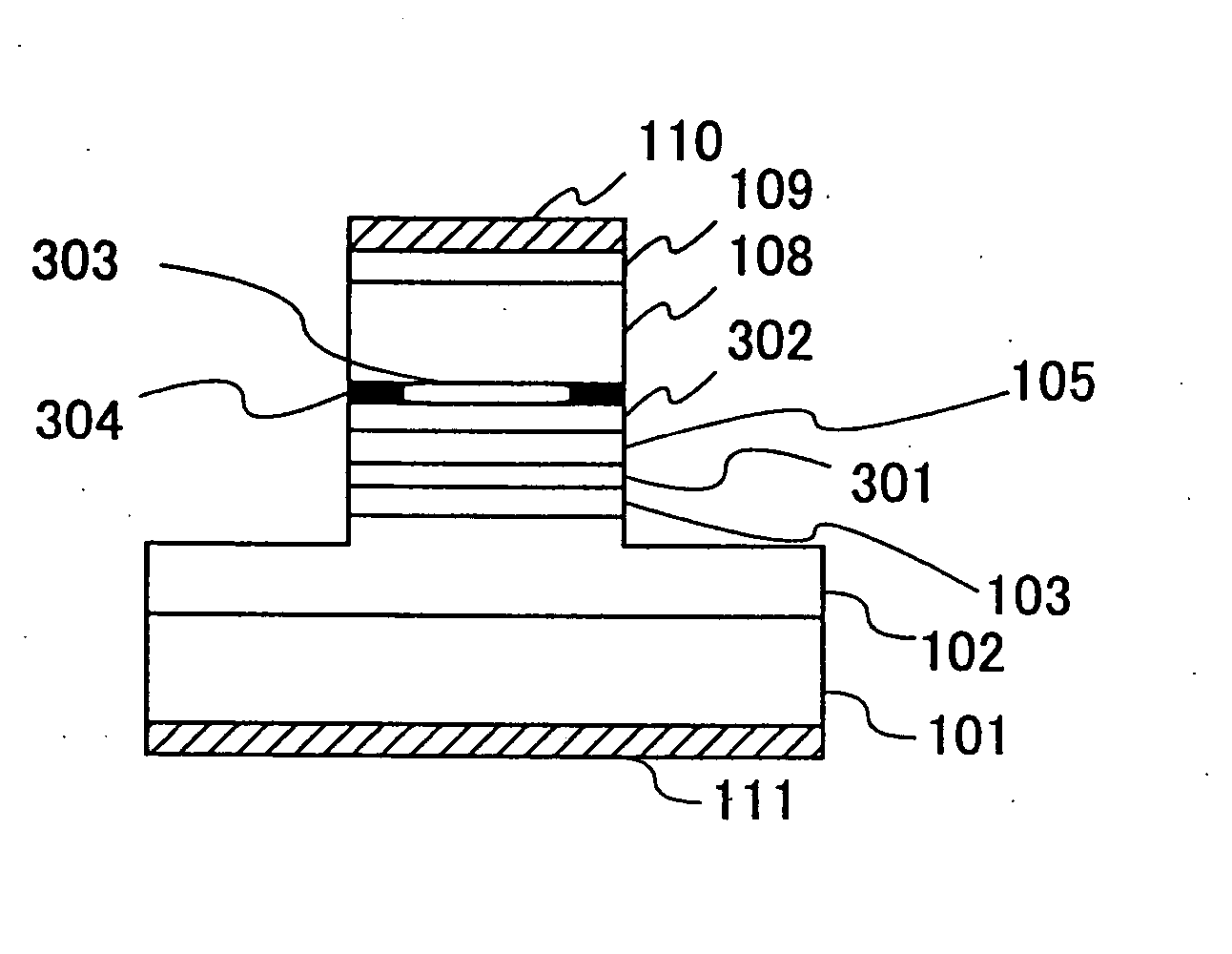
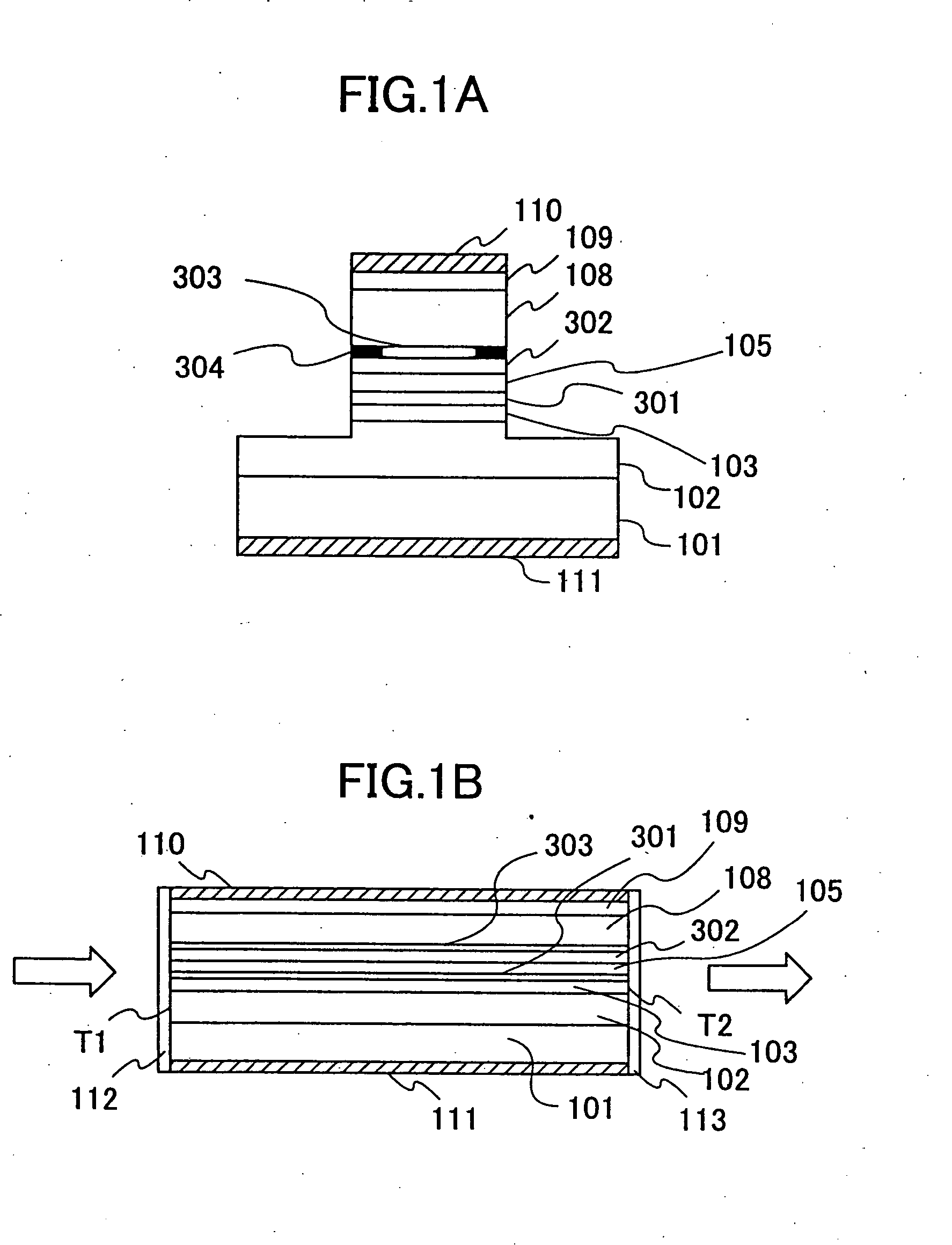
[0056]FIGS. 1A and 1B show the construction of a semiconductor optical modulator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, wherein FIG. 1A shows the semiconductor optical modulator in a front end view while FIG. 1B shows the semiconductor optical modulator in a longitudinal cross-sectional view.
[0057] Referring to FIGS. 1A and 1B, the semiconductor optical modulator is constructed on an n-type GaAs substrate 101 and includes a lower cladding layer 102 of n-type AlGaAs having a composition of Al0.4Ga0.6As and grown epitaxially on the substrate 101, a lower optical waveguide layer 103 of GaAs grown epitaxially on the cladding layer 102 and a multiple quantum well structure 301 grown epitaxially on the lower optical waveguide layer 103.
[0058] On the multiple quantum well structure 301, an upper optical waveguide layer 105 of GaAs is grown epitaxially, and a first upper cladding layer 302 of p-type AlGaAs having a composition represented as Al0.4Ga0.6As, a p-type AlAs select...
embodiment 2
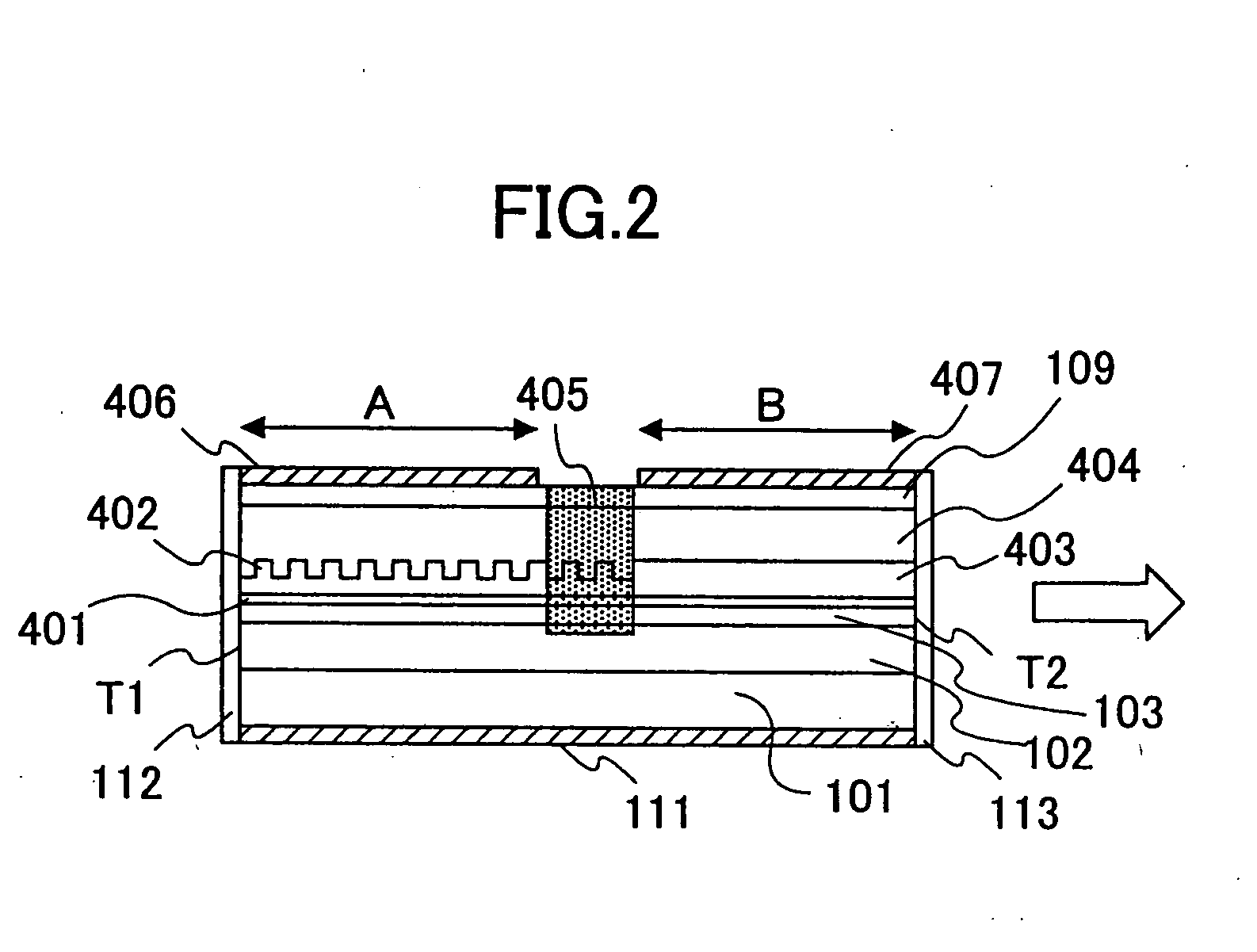
[0086]FIG. 2 shows the construction of an integrated semiconductor light-emitting device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0087] Referring to FIG. 2, the integrated semiconductor light-emitting device is a laser diode device having an integral optical modulator, and includes a laser diode part A that produces a laser beam and an EA-type semiconductor optical modulator B that modulates the intensity of the optical beam produced by the laser diode part A, such that the laser diode part A and the semiconductor optical modulator B are integrated on the n-type GaAs substrate 101 commonly and monolithically.
[0088] Here, it should be noted that the laser diode part A includes the n-type AlGaAs layer 102 having the composition of Al0.4Ga0.6As as a cladding layer, the GaAs layer 103 as a lower optical waveguide layer, and a multiple quantum well structure 401 is formed on the lower optical waveguide layer 103. Further, a diffraction grating layer 402 and a p-type cladding...
embodiment 3
[0106]FIGS. 3A and 3B show another construction of the integrated semiconductor light-emitting device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, wherein FIG. 3A shows the device in a plan view while FIG. 3B shows the device in a longitudinal cross-sectional view.
[0107] Referring to FIGS. 3A and 3B, the integrated semiconductor light-emitting device is constructed on a Si substrate 1001 and includes a vertical-cavity surface-emission laser diode 1002 formed on the Si substrate 1001, wherein there are provided four such laser diodes 1002 on the substrate 1001 in the form of an array. Further, the Si substrate 1001 carries thereon an optical waveguide 1004 having a 45° mirror 1003 at an end thereof, and an EA-type semiconductor optical modulator 1005 is provided further on the Si substrate 1001 in optical coupling with the other end of the optical waveguide 1004. The EA-type semiconductor optical modulator 1005 includes four channels, and optical fibers 1006 are coupled to re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com